Zero-day work contracts, known as "zero-hours contracts," offer flexible labor arrangements without guaranteed working hours, contrasting with part-time employment which provides fixed hours and predictable income. These contracts impact economic stability, labor market flexibility, and workers' rights across various industries. Explore the comparative effects of zero-day contracts and part-time work on economic growth and employment quality.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between zero-day work contracts and part-time employment is crucial for accurately assessing labor market flexibility and workers' rights. Zero-day contracts often lack guaranteed hours, impacting income stability and social benefits, while part-time employment typically offers fixed schedules and legal protections. This distinction influences economic policy, wage standards, and unemployment statistics. Recognizing these differences enables better regulation and support for vulnerable workers in the evolving economy.
Comparison Table
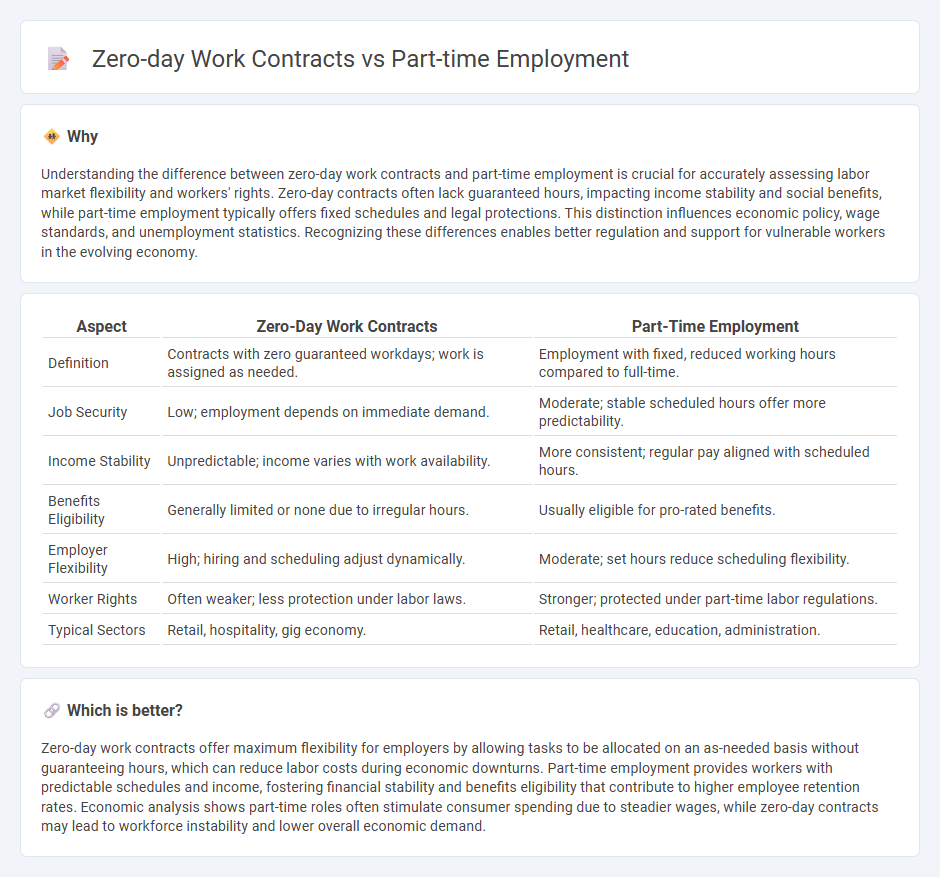
| Aspect | Zero-Day Work Contracts | Part-Time Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contracts with zero guaranteed workdays; work is assigned as needed. | Employment with fixed, reduced working hours compared to full-time. |
| Job Security | Low; employment depends on immediate demand. | Moderate; stable scheduled hours offer more predictability. |
| Income Stability | Unpredictable; income varies with work availability. | More consistent; regular pay aligned with scheduled hours. |
| Benefits Eligibility | Generally limited or none due to irregular hours. | Usually eligible for pro-rated benefits. |
| Employer Flexibility | High; hiring and scheduling adjust dynamically. | Moderate; set hours reduce scheduling flexibility. |
| Worker Rights | Often weaker; less protection under labor laws. | Stronger; protected under part-time labor regulations. |
| Typical Sectors | Retail, hospitality, gig economy. | Retail, healthcare, education, administration. |
Which is better?
Zero-day work contracts offer maximum flexibility for employers by allowing tasks to be allocated on an as-needed basis without guaranteeing hours, which can reduce labor costs during economic downturns. Part-time employment provides workers with predictable schedules and income, fostering financial stability and benefits eligibility that contribute to higher employee retention rates. Economic analysis shows part-time roles often stimulate consumer spending due to steadier wages, while zero-day contracts may lead to workforce instability and lower overall economic demand.
Connection
Zero-day work contracts and part-time employment both contribute to labor market flexibility by allowing employers to adjust workforce size and hours with minimal notice. These arrangements often lead to reduced job security and limited employee benefits, affecting income stability and long-term financial planning. The prevalence of such contracts reflects broader economic trends toward gig and precarious work models in modern economies.
Key Terms
Job Security
Part-time employment offers greater job security with regulated working hours, employee benefits, and legal protections that safeguard workers' rights. Zero-day work contracts lack these guarantees, often resulting in unpredictable income and minimal recourse against unfair dismissal. Explore the detailed differences to understand which option better secures your employment future.
Income Stability
Part-time employment typically offers greater income stability due to regular hours and predictable paychecks, while zero-day work contracts lack guaranteed hours, leading to fluctuating income levels. Workers on zero-day contracts face uncertainty, as their earnings depend solely on available shifts, making financial planning more challenging. Explore deeper insights into how income stability varies between these employment types to make informed career decisions.
Worker Rights
Part-time employment offers workers pro-rated benefits, legal protections, and job security under labor laws, while zero-day work contracts often bypass these rights, leading to job insecurity and limited access to social benefits. Workers under zero-day contracts typically face unpredictable work schedules and lack safeguards such as paid leave, minimum wage guarantees, and unemployment insurance. Explore comprehensive comparisons of worker rights between part-time employment and zero-day contracts to understand the impact on labor protections.
Source and External Links
Part Time Jobs in Sioux Falls, SD (NOW HIRING) - ZipRecruiter - Offers a comprehensive list of current part-time job openings in Sioux Falls, SD, with flexible schedules and opportunities in various industries, including customer service, retail, and hospitality.
Part-Time vs Full-Time: How Many Hours & How to Classify? - Defines part-time employment as typically 1-34 hours per week in the U.S., distinguishing it from full-time (35+ hours), and notes that benefits may be limited compared to full-time roles.
Part Time jobs in Sioux Falls, SD - Indeed - Provides access to hundreds of flexible part-time job listings in Sioux Falls, SD, across sectors like retail, food service, delivery, and healthcare, including roles with benefits for qualifying employees.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com