Consulting in anticipatory governance focuses on proactive strategies and predictive analytics to address emerging challenges before they escalate, contrasting with traditional governance's reactive and compliance-based approach. Emphasizing foresight and adaptability, anticipatory governance integrates diverse stakeholder input and technology-driven insights for better decision-making. Explore how consulting can drive this transformation to enhance organizational resilience and innovation.
Why it is important
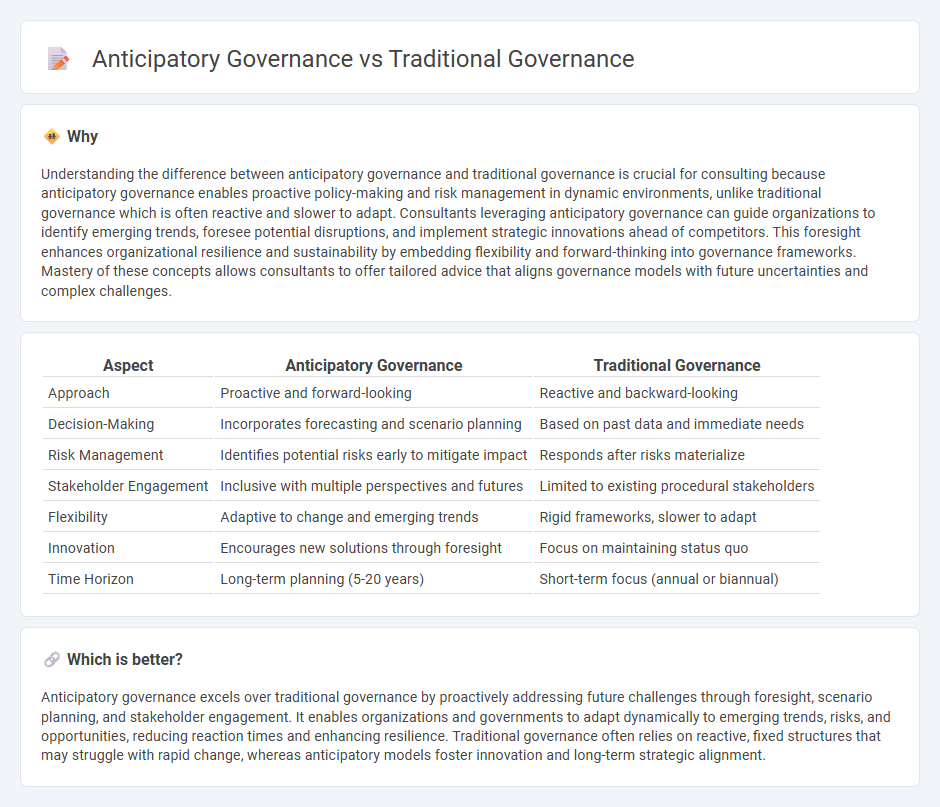
Understanding the difference between anticipatory governance and traditional governance is crucial for consulting because anticipatory governance enables proactive policy-making and risk management in dynamic environments, unlike traditional governance which is often reactive and slower to adapt. Consultants leveraging anticipatory governance can guide organizations to identify emerging trends, foresee potential disruptions, and implement strategic innovations ahead of competitors. This foresight enhances organizational resilience and sustainability by embedding flexibility and forward-thinking into governance frameworks. Mastery of these concepts allows consultants to offer tailored advice that aligns governance models with future uncertainties and complex challenges.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Anticipatory Governance | Traditional Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Proactive and forward-looking | Reactive and backward-looking |
| Decision-Making | Incorporates forecasting and scenario planning | Based on past data and immediate needs |
| Risk Management | Identifies potential risks early to mitigate impact | Responds after risks materialize |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Inclusive with multiple perspectives and futures | Limited to existing procedural stakeholders |
| Flexibility | Adaptive to change and emerging trends | Rigid frameworks, slower to adapt |
| Innovation | Encourages new solutions through foresight | Focus on maintaining status quo |
| Time Horizon | Long-term planning (5-20 years) | Short-term focus (annual or biannual) |
Which is better?
Anticipatory governance excels over traditional governance by proactively addressing future challenges through foresight, scenario planning, and stakeholder engagement. It enables organizations and governments to adapt dynamically to emerging trends, risks, and opportunities, reducing reaction times and enhancing resilience. Traditional governance often relies on reactive, fixed structures that may struggle with rapid change, whereas anticipatory models foster innovation and long-term strategic alignment.
Connection
Anticipatory governance complements traditional governance by integrating foresight and proactive strategies into established decision-making frameworks. It enhances policy resilience through scenario planning, early risk detection, and adaptive regulation within conventional governance structures. This connection enables organizations to navigate uncertainties effectively while maintaining adherence to regulatory standards and institutional accountability.
Key Terms
Decision-making processes
Traditional governance relies on hierarchical decision-making processes with established rules and reactive responses to issues as they arise, emphasizing stability and compliance. Anticipatory governance employs forward-looking and adaptive decision-making frameworks that integrate scenario planning, stakeholder engagement, and real-time data to proactively address emerging challenges and opportunities. Explore how anticipatory governance transforms decision-making to enhance resilience and innovation in complex environments.
Risk management
Traditional governance centers on reactive risk management, relying on historical data and established protocols to address known threats after they materialize. Anticipatory governance emphasizes proactive identification and mitigation of emerging risks through foresight, scenario planning, and continuous monitoring of evolving trends. Explore comprehensive strategies and frameworks that distinguish anticipatory governance in advancing risk management effectiveness.
Foresight
Traditional governance relies on reactive decision-making based on historical data and past experiences, often limiting the ability to address emerging challenges. Anticipatory governance emphasizes foresight by integrating forward-looking scenarios, risk assessments, and strategic planning to proactively shape policies and responses. Explore how foresight techniques transform governance to learn more about building resilient and adaptive institutions.
Source and External Links
Traditional Governance - Anishinaabe Governance - B'Maakonigan - Traditional governance among the Anishinaabe was clan-based, consensus-driven, and inclusive, contrasting with the imposed western majority-rule system; there is current interest in reviving these traditional models in modern First Nation contexts for more participatory decision-making.
Traditional Governance, Citizen Engagement and Local Public Goods - Traditional governance systems, grounded in indigenous participatory democracy and community obligations, help improve local public goods provision by preventing elite capture and ensuring communal engagement and justice parallel to formal systems.
Traditional Governance Systems - Participedia - Indigenous traditional governance systems are rooted in local knowledge and collaborative practices, often adapted for modern resource management and self-determination, sometimes gaining formal recognition within colonial state frameworks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com