Corporate venturing leverages external partnerships and investments to stimulate innovation by integrating startup technologies with established business models, accelerating growth beyond internal capabilities. Internal innovation focuses on harnessing existing resources, employee expertise, and organizational culture to drive incremental improvements and breakthrough developments within the company. Explore the strategic benefits and implementation tactics of both approaches to maximize corporate innovation.
Why it is important
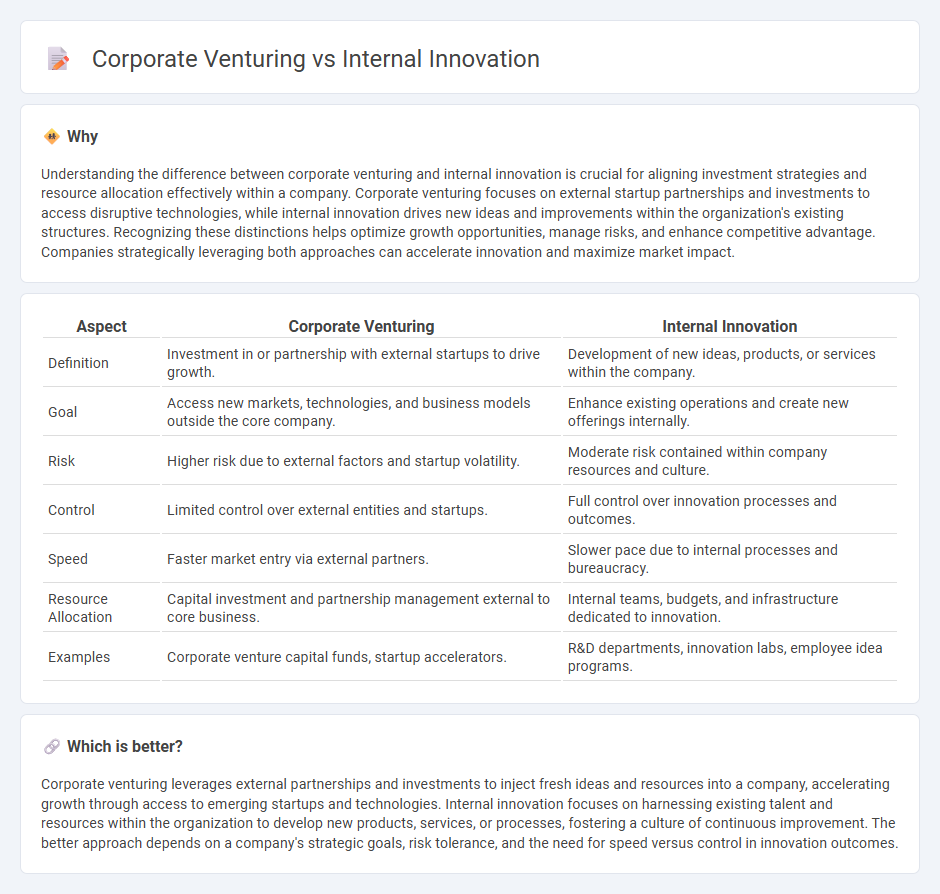
Understanding the difference between corporate venturing and internal innovation is crucial for aligning investment strategies and resource allocation effectively within a company. Corporate venturing focuses on external startup partnerships and investments to access disruptive technologies, while internal innovation drives new ideas and improvements within the organization's existing structures. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize growth opportunities, manage risks, and enhance competitive advantage. Companies strategically leveraging both approaches can accelerate innovation and maximize market impact.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Corporate Venturing | Internal Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in or partnership with external startups to drive growth. | Development of new ideas, products, or services within the company. |
| Goal | Access new markets, technologies, and business models outside the core company. | Enhance existing operations and create new offerings internally. |
| Risk | Higher risk due to external factors and startup volatility. | Moderate risk contained within company resources and culture. |
| Control | Limited control over external entities and startups. | Full control over innovation processes and outcomes. |
| Speed | Faster market entry via external partners. | Slower pace due to internal processes and bureaucracy. |
| Resource Allocation | Capital investment and partnership management external to core business. | Internal teams, budgets, and infrastructure dedicated to innovation. |
| Examples | Corporate venture capital funds, startup accelerators. | R&D departments, innovation labs, employee idea programs. |
Which is better?
Corporate venturing leverages external partnerships and investments to inject fresh ideas and resources into a company, accelerating growth through access to emerging startups and technologies. Internal innovation focuses on harnessing existing talent and resources within the organization to develop new products, services, or processes, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. The better approach depends on a company's strategic goals, risk tolerance, and the need for speed versus control in innovation outcomes.
Connection
Corporate venturing accelerates internal innovation by injecting external entrepreneurial insights and funding into company projects, fostering a dynamic environment for new product development and business models. Internal innovation benefits from corporate venturing through access to startups' cutting-edge technologies and agile methodologies, enhancing a company's capacity to adapt and evolve in competitive markets. This symbiotic relationship drives strategic growth by combining corporate resources with startup creativity, establishing a continuous pipeline of innovation.
Key Terms
Intrapreneurship
Internal innovation leverages intrapreneurship by empowering employees to develop new ideas and solutions within the company's existing structure, fostering a culture of creativity and agility. Corporate venturing involves investing in or partnering with startups to access external innovations and market opportunities beyond the company's core competencies. Explore how combining intrapreneurship and corporate venturing can drive sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Spin-off
Internal innovation drives new product development within existing corporate structures by leveraging in-house resources and expertise, whereas corporate venturing often involves creating spin-offs to explore disruptive technologies independently. Spin-offs enable firms to separate high-risk projects from core operations, enhancing agility and attracting dedicated investment for breakthrough innovation. Discover how spin-offs can transform corporate growth strategies and foster sustainable competitive advantage.
Open Innovation
Internal innovation leverages a company's existing resources and expertise to develop new products or processes within the organization, enhancing core competencies. Corporate venturing involves investing in or partnering with startups to access external innovation and emerging technologies, broadening market reach. Explore how integrating internal innovation with corporate venturing strategies accelerates open innovation and drives competitive advantage.
Source and External Links
Injecting Innovation Into Your Company Culture at the Speed ... - ISM - Internal innovation can be fostered by creating an internal innovation incubator that empowers employees to propose, develop, and own innovative ideas, enhancing company culture, employee morale, and competitive advantage.
6 Internal Sources of Innovation - ITONICS - Internal innovation originates from various corporate elements such as leadership (including C-level executives driving vision), centralized and decentralized R&D units, and innovation labs, with top management playing a critical role in setting the strategy and culture for innovation.
4 Ways to Drive Growth-Unlocking Internal Innovation in Your ... - Internal innovation involves organizational changes and improvements that empower teams with the tools to succeed, potentially offering more sustainable growth than external innovation focused only on products or services.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com