RISC-V is an open standard instruction set architecture (ISA) designed for modern computing with scalable performance and energy efficiency, while the Zilog Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor introduced in the 1970s, known for its widespread use in early personal computers and embedded systems. The RISC-V architecture supports extensibility and customization, making it ideal for today's diverse applications, contrasting with the Z80's legacy simplicity and limited instruction set. Explore the key differences and evolving applications of RISC-V and Zilog Z80 to understand their impact on technology.
Why it is important
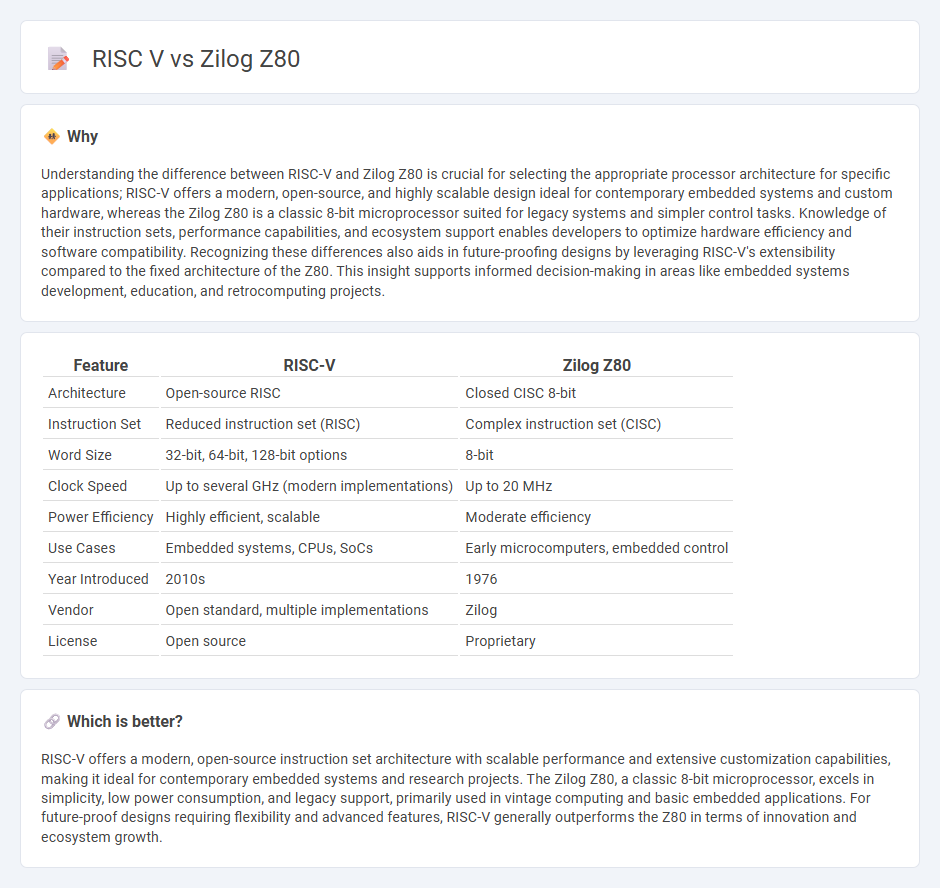
Understanding the difference between RISC-V and Zilog Z80 is crucial for selecting the appropriate processor architecture for specific applications; RISC-V offers a modern, open-source, and highly scalable design ideal for contemporary embedded systems and custom hardware, whereas the Zilog Z80 is a classic 8-bit microprocessor suited for legacy systems and simpler control tasks. Knowledge of their instruction sets, performance capabilities, and ecosystem support enables developers to optimize hardware efficiency and software compatibility. Recognizing these differences also aids in future-proofing designs by leveraging RISC-V's extensibility compared to the fixed architecture of the Z80. This insight supports informed decision-making in areas like embedded systems development, education, and retrocomputing projects.
Comparison Table
| Feature | RISC-V | Zilog Z80 |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Open-source RISC | Closed CISC 8-bit |
| Instruction Set | Reduced instruction set (RISC) | Complex instruction set (CISC) |
| Word Size | 32-bit, 64-bit, 128-bit options | 8-bit |
| Clock Speed | Up to several GHz (modern implementations) | Up to 20 MHz |
| Power Efficiency | Highly efficient, scalable | Moderate efficiency |
| Use Cases | Embedded systems, CPUs, SoCs | Early microcomputers, embedded control |
| Year Introduced | 2010s | 1976 |
| Vendor | Open standard, multiple implementations | Zilog |
| License | Open source | Proprietary |
Which is better?
RISC-V offers a modern, open-source instruction set architecture with scalable performance and extensive customization capabilities, making it ideal for contemporary embedded systems and research projects. The Zilog Z80, a classic 8-bit microprocessor, excels in simplicity, low power consumption, and legacy support, primarily used in vintage computing and basic embedded applications. For future-proof designs requiring flexibility and advanced features, RISC-V generally outperforms the Z80 in terms of innovation and ecosystem growth.
Connection
RISC-V and Zilog Z80 share a foundational impact on computer architecture, with the Z80 being a seminal 8-bit microprocessor widely used in early computing, and RISC-V representing a modern, open-source instruction set architecture designed for efficiency and scalability. Both architectures emphasize simplicity and modular design, enabling diverse applications from embedded systems to advanced processors. The Z80's legacy influences contemporary CPU design principles that underpin RISC-V's development in customizable and extensible processor technology.
Key Terms
CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computing)
The Zilog Z80 microprocessor, a classic CISC architecture, features a rich instruction set designed for efficient code density and backward compatibility with the Intel 8080, facilitating complex operations within fewer instructions. In contrast, RISC-V employs a simplified, modular instruction set focused on reducing instruction complexity to optimize performance and ease hardware implementation, representing the RISC philosophy. Explore the detailed architectural comparisons to understand how CISC and RISC influence modern processor design choices.
Open-source ISA (Instruction Set Architecture)
Z80, a classic 8-bit microprocessor introduced in 1976, features a proprietary ISA widely used in embedded systems, while RISC-V, a modern open-source ISA, offers scalable 32/64/128-bit architectures designed for flexibility and extensibility in various applications. The open-source nature of RISC-V reduces licensing costs and encourages community-driven innovation, contrasting with Z80's closed design and established ecosystem. Explore the technical and practical implications of adopting RISC-V over Z80 in your next hardware project.
Legacy compatibility
The Zilog Z80 microprocessor boasts extensive legacy compatibility, supporting a vast range of vintage software and hardware from the late 1970s and 1980s, making it pivotal for retro computing enthusiasts and embedded systems. RISC-V, as an open standard instruction set architecture (ISA), offers modular flexibility but lacks the direct backward compatibility with legacy instruction sets that the Z80 inherently provides. Explore detailed comparisons and implications for legacy system integration to fully understand the impact of compatibility choices.
Source and External Links
Zilog Z80 - The Zilog Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor released in 1976, compatible with the Intel 8080 but offering better integration and performance, widely used in early personal computers, game consoles, and calculators.
Z80 Family CPU User Manual - The Z80 CPU family are fourth-generation enhanced microprocessors with 6-20 MHz speed options, featuring dual register sets, 16-bit index registers, and designed for efficient memory use and system integration.
Zilog Z80 Deep Dive - How does it work? - A technical explanation of the Z80's simple instruction set architecture, focusing on loading/storing data, basic arithmetic/logical operations, and programming with assembly language.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com