Vector databases specialize in storing and querying high-dimensional data, ideal for AI and machine learning applications that require efficient similarity searches. Object databases, on the other hand, focus on managing complex data structures by storing data as objects, providing seamless integration with object-oriented programming languages. Explore more to understand which database suits your project's unique data management needs.
Why it is important
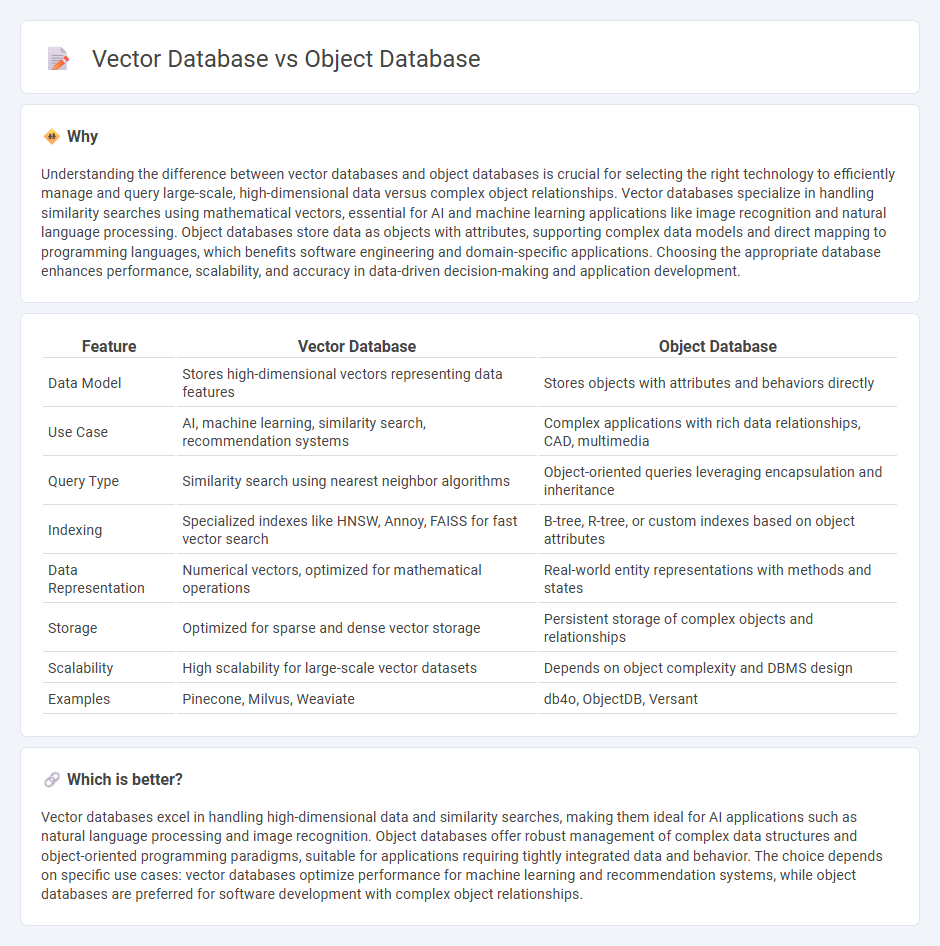
Understanding the difference between vector databases and object databases is crucial for selecting the right technology to efficiently manage and query large-scale, high-dimensional data versus complex object relationships. Vector databases specialize in handling similarity searches using mathematical vectors, essential for AI and machine learning applications like image recognition and natural language processing. Object databases store data as objects with attributes, supporting complex data models and direct mapping to programming languages, which benefits software engineering and domain-specific applications. Choosing the appropriate database enhances performance, scalability, and accuracy in data-driven decision-making and application development.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Vector Database | Object Database |
|---|---|---|
| Data Model | Stores high-dimensional vectors representing data features | Stores objects with attributes and behaviors directly |
| Use Case | AI, machine learning, similarity search, recommendation systems | Complex applications with rich data relationships, CAD, multimedia |
| Query Type | Similarity search using nearest neighbor algorithms | Object-oriented queries leveraging encapsulation and inheritance |
| Indexing | Specialized indexes like HNSW, Annoy, FAISS for fast vector search | B-tree, R-tree, or custom indexes based on object attributes |
| Data Representation | Numerical vectors, optimized for mathematical operations | Real-world entity representations with methods and states |
| Storage | Optimized for sparse and dense vector storage | Persistent storage of complex objects and relationships |
| Scalability | High scalability for large-scale vector datasets | Depends on object complexity and DBMS design |
| Examples | Pinecone, Milvus, Weaviate | db4o, ObjectDB, Versant |
Which is better?
Vector databases excel in handling high-dimensional data and similarity searches, making them ideal for AI applications such as natural language processing and image recognition. Object databases offer robust management of complex data structures and object-oriented programming paradigms, suitable for applications requiring tightly integrated data and behavior. The choice depends on specific use cases: vector databases optimize performance for machine learning and recommendation systems, while object databases are preferred for software development with complex object relationships.
Connection
Vector databases store high-dimensional vector representations of data, enabling efficient similarity searches and machine learning applications. Object databases manage complex data as objects, encapsulating both data and behavior, which often include vector attributes for advanced analytics. Integrating vector data within object databases enhances semantic search capabilities and supports sophisticated AI-driven technology solutions.
Key Terms
Data Model
Object databases store data as objects, closely mirroring object-oriented programming structures, enabling complex data relationships and encapsulation within the data model. Vector databases, designed for high-dimensional vector representations, facilitate efficient similarity searches and numerical computations, essential for AI and machine learning applications. Explore the distinct data models and use cases of object and vector databases to optimize your data strategy.
Query Mechanism
Object databases organize data as objects, allowing queries based on object attributes, relationships, and methods, which makes retrieval efficient for complex data structures. Vector databases specialize in similarity searches, using high-dimensional vectors and algorithms like nearest neighbor search to retrieve results based on vector closeness. Explore the nuances of query mechanisms in both database types to optimize your data retrieval strategy.
Scalability
Object databases manage complex data structures with hierarchical relationships, offering moderate scalability for applications requiring rich data models. Vector databases excel in handling large-scale, high-dimensional data, scaling efficiently for AI-driven tasks like similarity search and machine learning. Explore more to understand how each database type supports scalability in diverse application scenarios.
Source and External Links
Object database - Wikipedia - An object database or object-oriented database is a database management system where information is represented as objects like in object-oriented programming, differing from relational databases by using objects rather than tables.
Top 9 Object-Oriented Database Examples 2024 - Daily.dev - Object-oriented databases store data as objects with properties and methods, aligning closely with object-oriented programming and are used in domains like CAD, multimedia, and scientific research, featuring direct object access and distinct query languages from relational databases.
What is an object database? - Aerospike - Object databases integrate object-oriented programming concepts to efficiently manage complex data, with examples including db4o, ObjectDB, Versant, GemStone/S, and ZODB, each suited for different languages and enterprise needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com