Quantum networking leverages quantum entanglement and superposition to enable ultra-secure communication and unprecedented data transfer speeds, surpassing classical network limitations. 5G networking enhances mobile connectivity through high-frequency bands, massive MIMO antennas, and low latency, supporting the Internet of Things and real-time applications. Explore the technological advancements and practical applications differentiating quantum networking from 5G networking for future communication paradigms.
Why it is important
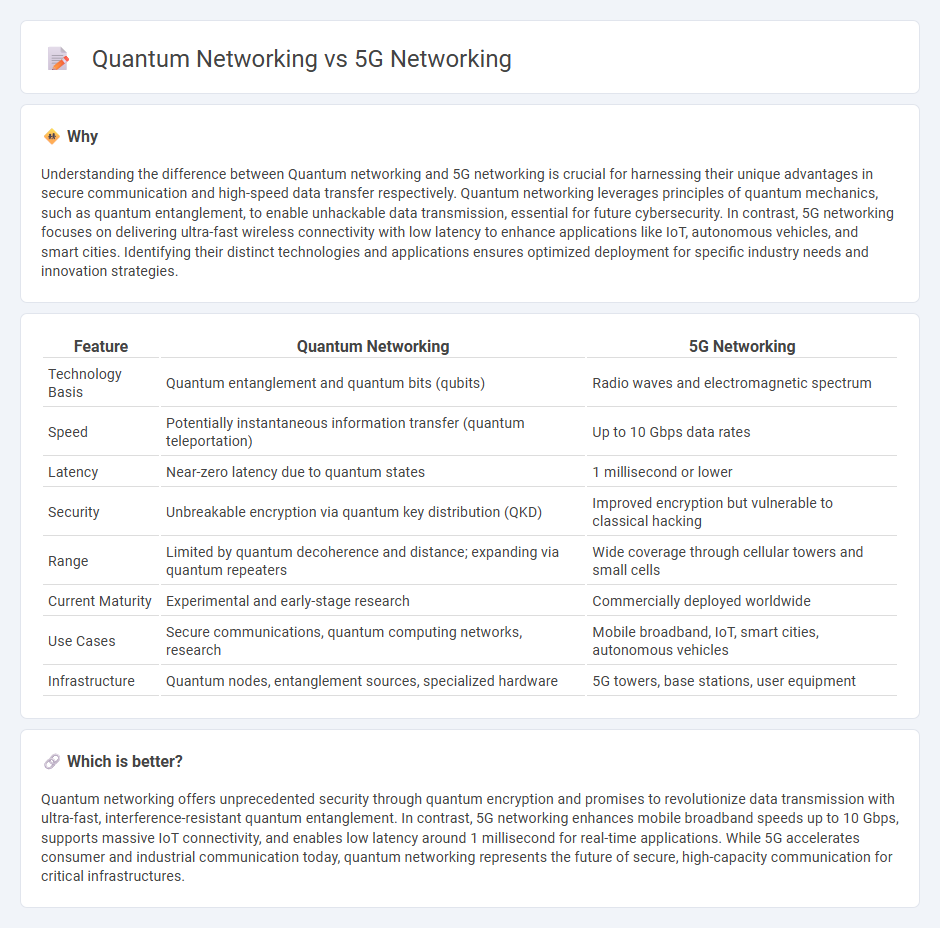
Understanding the difference between Quantum networking and 5G networking is crucial for harnessing their unique advantages in secure communication and high-speed data transfer respectively. Quantum networking leverages principles of quantum mechanics, such as quantum entanglement, to enable unhackable data transmission, essential for future cybersecurity. In contrast, 5G networking focuses on delivering ultra-fast wireless connectivity with low latency to enhance applications like IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities. Identifying their distinct technologies and applications ensures optimized deployment for specific industry needs and innovation strategies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Quantum Networking | 5G Networking |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Basis | Quantum entanglement and quantum bits (qubits) | Radio waves and electromagnetic spectrum |
| Speed | Potentially instantaneous information transfer (quantum teleportation) | Up to 10 Gbps data rates |
| Latency | Near-zero latency due to quantum states | 1 millisecond or lower |
| Security | Unbreakable encryption via quantum key distribution (QKD) | Improved encryption but vulnerable to classical hacking |
| Range | Limited by quantum decoherence and distance; expanding via quantum repeaters | Wide coverage through cellular towers and small cells |
| Current Maturity | Experimental and early-stage research | Commercially deployed worldwide |
| Use Cases | Secure communications, quantum computing networks, research | Mobile broadband, IoT, smart cities, autonomous vehicles |
| Infrastructure | Quantum nodes, entanglement sources, specialized hardware | 5G towers, base stations, user equipment |
Which is better?
Quantum networking offers unprecedented security through quantum encryption and promises to revolutionize data transmission with ultra-fast, interference-resistant quantum entanglement. In contrast, 5G networking enhances mobile broadband speeds up to 10 Gbps, supports massive IoT connectivity, and enables low latency around 1 millisecond for real-time applications. While 5G accelerates consumer and industrial communication today, quantum networking represents the future of secure, high-capacity communication for critical infrastructures.
Connection
Quantum networking leverages principles of quantum mechanics to enable ultra-secure communication through quantum key distribution, while 5G networking provides the high-speed, low-latency infrastructure necessary for supporting advanced data transmission. The integration of quantum networking with 5G technology enhances cybersecurity in communication networks by enabling secure quantum encryption over existing 5G infrastructures. This synergy accelerates the development of next-generation internet, combining quantum communication's security benefits with 5G's connectivity and bandwidth advantages.
Key Terms
Latency
5G networking offers ultra-low latency typically around 1 millisecond, enabling real-time applications such as autonomous driving and remote surgery with minimal delay. Quantum networking aims to revolutionize latency by leveraging quantum entanglement for near-instantaneous communication over long distances, potentially reducing delays to nearly zero. Explore the future of connectivity by learning more about how these technologies transform low-latency communication.
Entanglement
5G networking relies on advanced radio waves and massive MIMO technology to deliver ultra-fast, low-latency connectivity, while quantum networking leverages quantum entanglement to enable instantaneous state transfer between distant particles, promising unbreakable encryption and novel communication paradigms. The core advantage of entanglement in quantum networking is its ability to establish secure quantum key distribution, beyond the capabilities of classical 5G networks. Explore the future of communication technologies and understand how entanglement is poised to revolutionize networking security and speed.
Bandwidth
5G networking offers bandwidths typically ranging from 100 Mbps to several Gbps, supporting high-speed data transmission for mobile and IoT devices, whereas quantum networking promises exponentially higher capacity by leveraging qubits for data encoding and transmission through quantum entanglement. Quantum networks aim to revolutionize communication by enabling ultra-secure and instantaneous data transfer, surpassing classical bandwidth limitations inherent in 5G. Explore further to understand how these technologies will reshape future connectivity and data exchange paradigms.
Source and External Links
What Is 5G? Everything You Need To Know About 5G Networks - 5G is the fifth generation of wireless network technology that operates on multiple frequency bands, uses OFDM for efficient data encoding, supports more connected devices with faster speeds, and enables network slicing to create multiple virtual networks within one physical 5G network.
What is 5G? - 5G Technology Explained - AWS - 5G technology enhances cellular networks with higher speeds, lower latency, more consistent connections, uses small cell sites for better coverage, and allows mobile operators to deploy multiple independent virtual networks via network slicing customized for different service needs.
What is 5G? - IBM - 5G improves on 4G by expanding bandwidth into low, mid and high-band spectrums, applying adaptive coding schemes to reduce errors dynamically, and supporting download speeds up to 10 Gbps with the ability to connect many devices simultaneously within cellular "cells".
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com