Adaptive reuse transforms old buildings into functional spaces by preserving architectural heritage and reducing environmental impact, while urban renewal involves comprehensive redevelopment to revitalize entire neighborhoods, often including demolition and new construction. Both strategies address real estate challenges by enhancing property value and fostering sustainable urban growth. Discover the benefits and applications of adaptive reuse and urban renewal in modern real estate development.
Why it is important
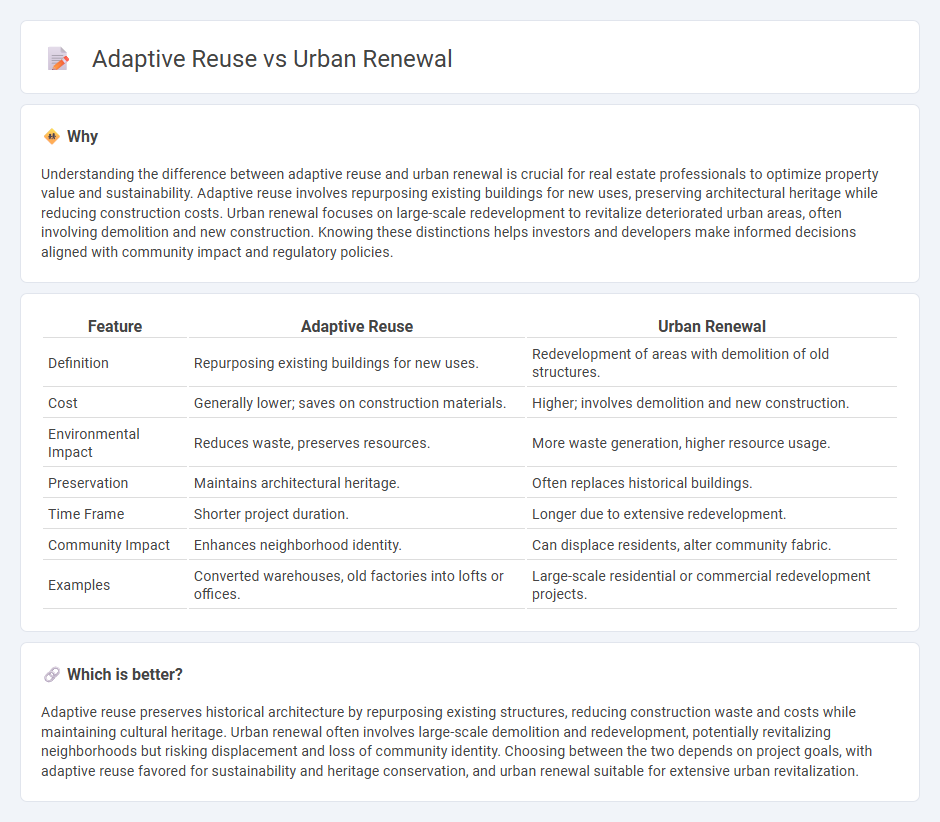
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse and urban renewal is crucial for real estate professionals to optimize property value and sustainability. Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing buildings for new uses, preserving architectural heritage while reducing construction costs. Urban renewal focuses on large-scale redevelopment to revitalize deteriorated urban areas, often involving demolition and new construction. Knowing these distinctions helps investors and developers make informed decisions aligned with community impact and regulatory policies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Adaptive Reuse | Urban Renewal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repurposing existing buildings for new uses. | Redevelopment of areas with demolition of old structures. |
| Cost | Generally lower; saves on construction materials. | Higher; involves demolition and new construction. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste, preserves resources. | More waste generation, higher resource usage. |
| Preservation | Maintains architectural heritage. | Often replaces historical buildings. |
| Time Frame | Shorter project duration. | Longer due to extensive redevelopment. |
| Community Impact | Enhances neighborhood identity. | Can displace residents, alter community fabric. |
| Examples | Converted warehouses, old factories into lofts or offices. | Large-scale residential or commercial redevelopment projects. |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse preserves historical architecture by repurposing existing structures, reducing construction waste and costs while maintaining cultural heritage. Urban renewal often involves large-scale demolition and redevelopment, potentially revitalizing neighborhoods but risking displacement and loss of community identity. Choosing between the two depends on project goals, with adaptive reuse favored for sustainability and heritage conservation, and urban renewal suitable for extensive urban revitalization.
Connection
Adaptive reuse transforms outdated or underutilized buildings into functional spaces, directly contributing to urban renewal by revitalizing neighborhoods and preserving architectural heritage. These practices enhance real estate value by attracting investment, increasing property demand, and promoting sustainable development within urban environments. Urban renewal benefits from adaptive reuse as it stimulates economic growth, reduces urban sprawl, and supports community revitalization through innovative real estate solutions.
Key Terms
Revitalization
Urban renewal aims to revitalize declining areas through large-scale redevelopment projects, often involving demolition and new construction to boost economic growth and community appeal. Adaptive reuse focuses on preserving and repurposing existing structures, maintaining historical and cultural value while updating spaces for modern uses to enhance neighborhood vitality. Discover how these strategies uniquely contribute to sustainable urban revitalization and community development.
Historic preservation
Urban renewal often involves large-scale demolition and reconstruction that can threaten historic landmarks, whereas adaptive reuse preserves the architectural integrity of heritage buildings by repurposing them for modern use. Historic preservation benefits from adaptive reuse as it maintains cultural significance and supports sustainable development by reducing waste and conserving resources. Explore how adaptive reuse can transform historic preservation efforts in urban settings for a deeper understanding.
Zoning
Urban renewal often involves comprehensive rezoning to facilitate large-scale redevelopment projects aimed at revitalizing underutilized areas, whereas adaptive reuse typically works within existing zoning frameworks to convert historic or obsolete buildings into functional spaces, preserving cultural heritage. Zoning regulations play a pivotal role in determining allowable land uses, density, and building codes, directly impacting the feasibility and design of both urban renewal and adaptive reuse projects. Explore zoning strategies to optimize redevelopment potential and sustainable urban growth.
Source and External Links
Urban Renewal | EBSCO Research Starters - Urban renewal is a process aimed at revitalizing urban and rural areas by renovating existing structures or constructing new ones, often with a focus on economic revitalization and improving living conditions.
Urban Renewal - Wikipedia - Urban renewal involves revitalizing urban areas through the clearance of blighted areas and development of new housing, businesses, and other projects, with goals including economic revitalization, social regeneration, and environmental sustainability.
What Is Urban Renewal? | Planopedia - Planetizen - Urban renewal policies focus on improving the attractiveness and property values of specific areas through initiatives like "slum clearance" and redevelopment, as initially established by the Housing Act of 1949.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com