Agrihood communities integrate agriculture and residential living, offering sustainability through farm-to-table access and green open spaces, whereas urban infill developments focus on revitalizing city areas by utilizing vacant or underused parcels to increase density and reduce urban sprawl. These two real estate strategies cater to different lifestyle preferences, with agrihoods appealing to those seeking community-supported agriculture and natural surroundings, and urban infill attracting residents desiring proximity to city amenities and public transit. Explore the unique benefits and investment opportunities within agrihood communities and urban infill developments to determine the best fit for your real estate goals.
Why it is important
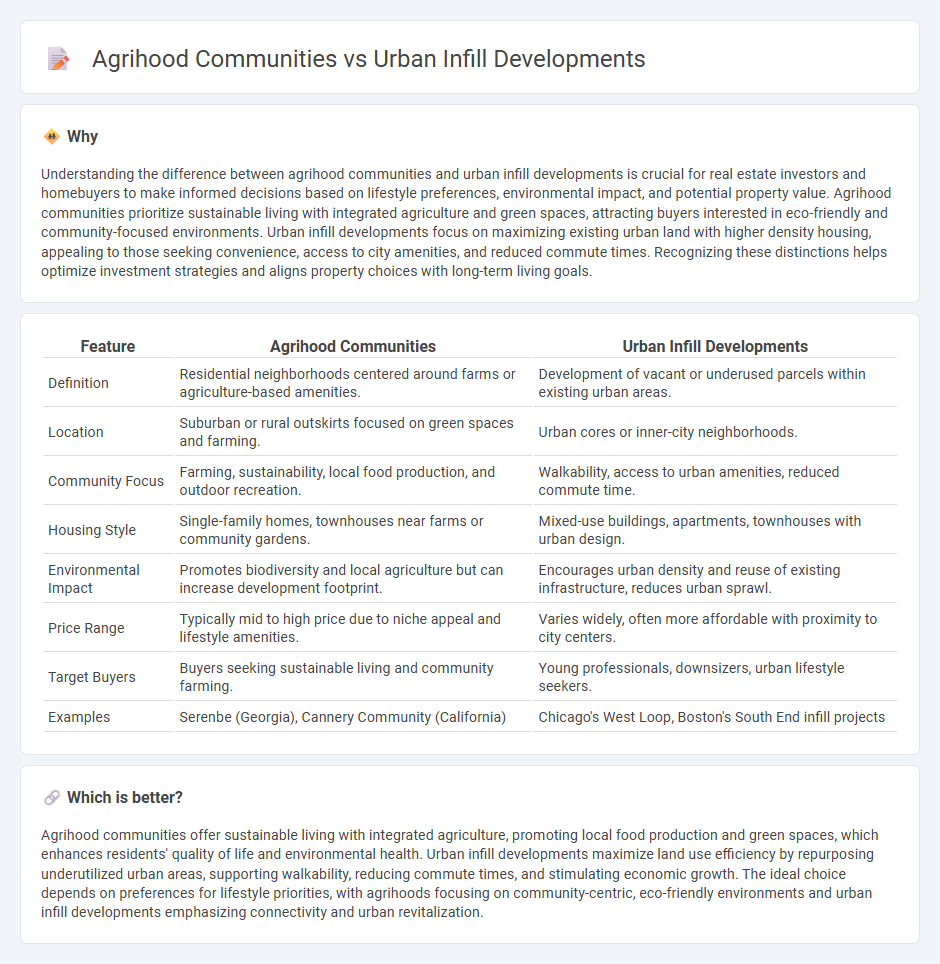
Understanding the difference between agrihood communities and urban infill developments is crucial for real estate investors and homebuyers to make informed decisions based on lifestyle preferences, environmental impact, and potential property value. Agrihood communities prioritize sustainable living with integrated agriculture and green spaces, attracting buyers interested in eco-friendly and community-focused environments. Urban infill developments focus on maximizing existing urban land with higher density housing, appealing to those seeking convenience, access to city amenities, and reduced commute times. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize investment strategies and aligns property choices with long-term living goals.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Agrihood Communities | Urban Infill Developments |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Residential neighborhoods centered around farms or agriculture-based amenities. | Development of vacant or underused parcels within existing urban areas. |
| Location | Suburban or rural outskirts focused on green spaces and farming. | Urban cores or inner-city neighborhoods. |
| Community Focus | Farming, sustainability, local food production, and outdoor recreation. | Walkability, access to urban amenities, reduced commute time. |
| Housing Style | Single-family homes, townhouses near farms or community gardens. | Mixed-use buildings, apartments, townhouses with urban design. |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes biodiversity and local agriculture but can increase development footprint. | Encourages urban density and reuse of existing infrastructure, reduces urban sprawl. |
| Price Range | Typically mid to high price due to niche appeal and lifestyle amenities. | Varies widely, often more affordable with proximity to city centers. |
| Target Buyers | Buyers seeking sustainable living and community farming. | Young professionals, downsizers, urban lifestyle seekers. |
| Examples | Serenbe (Georgia), Cannery Community (California) | Chicago's West Loop, Boston's South End infill projects |
Which is better?
Agrihood communities offer sustainable living with integrated agriculture, promoting local food production and green spaces, which enhances residents' quality of life and environmental health. Urban infill developments maximize land use efficiency by repurposing underutilized urban areas, supporting walkability, reducing commute times, and stimulating economic growth. The ideal choice depends on preferences for lifestyle priorities, with agrihoods focusing on community-centric, eco-friendly environments and urban infill developments emphasizing connectivity and urban revitalization.
Connection
Agrihood communities and urban infill developments both prioritize sustainable living by integrating green spaces and local food production within residential areas. These real estate strategies enhance community engagement, promote walkability, and reduce environmental impact by revitalizing underutilized land or creating new, agriculture-focused neighborhoods. Combining agrihood agriculture with urban infill supports healthier lifestyles and addresses urban sprawl through efficient land use and access to fresh food.
Key Terms
**Urban Infill Developments:**
Urban infill developments maximize land use efficiency by transforming underutilized city spaces into vibrant residential or mixed-use areas, enhancing walkability and reducing urban sprawl. These projects support sustainable growth by integrating public transit access, promoting local economies, and preserving greenfield sites outside the city. Explore how urban infill developments reshape modern living environments and contribute to smarter city planning.
Density
Urban infill developments maximize land use efficiency by increasing housing density within existing city boundaries, reducing urban sprawl and promoting sustainable growth. Agrihood communities, in contrast, integrate residential units with agricultural spaces but typically maintain lower density to preserve open farmland and communal green areas. Explore the benefits and challenges of each approach to understand the impact of density on community design and lifestyle.
Mixed-use
Urban infill developments optimize land use by integrating residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within existing city infrastructure, enhancing walkability and reducing vehicle dependence. Agrihood communities combine residential living with active agricultural elements like farms and community gardens, promoting local food production while often incorporating mixed-use amenities such as retail and educational spaces. Explore the benefits and challenges of mixed-use strategies in these development models to understand their impact on community sustainability and lifestyle.
Source and External Links
Key Success Factors of Urban Infill Development - This article discusses the concept of urban infill development, focusing on its benefits and challenges in promoting efficient land use and community development.
What Is Infill Development? | Planopedia - Infill development is an alternative to urban sprawl, utilizing underused urban land to enhance density, reduce travel distances, and improve local amenities.
What is Urban Infill? | Definition, Key Components & Examples - Urban infill involves developing vacant or underused urban parcels to optimize land use, enhance community vitality, and promote sustainable mixed-use developments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com