Adaptive reuse transforms existing buildings into functional spaces, maximizing sustainability and preserving architectural heritage. Vertical expansion adds floors to structures, increasing usable area without consuming more land. Explore how each approach impacts urban development and investment potential.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse properties and vertical expansion is crucial in real estate for optimizing investment strategies and maximizing property value. Adaptive reuse transforms existing structures for new purposes, often preserving historical integrity and reducing construction costs. Vertical expansion involves adding floors to existing buildings, increasing usable space and rental income potential. Recognizing these distinctions aids developers, investors, and urban planners in making informed decisions about sustainability, zoning laws, and financial feasibility.
Comparison Table
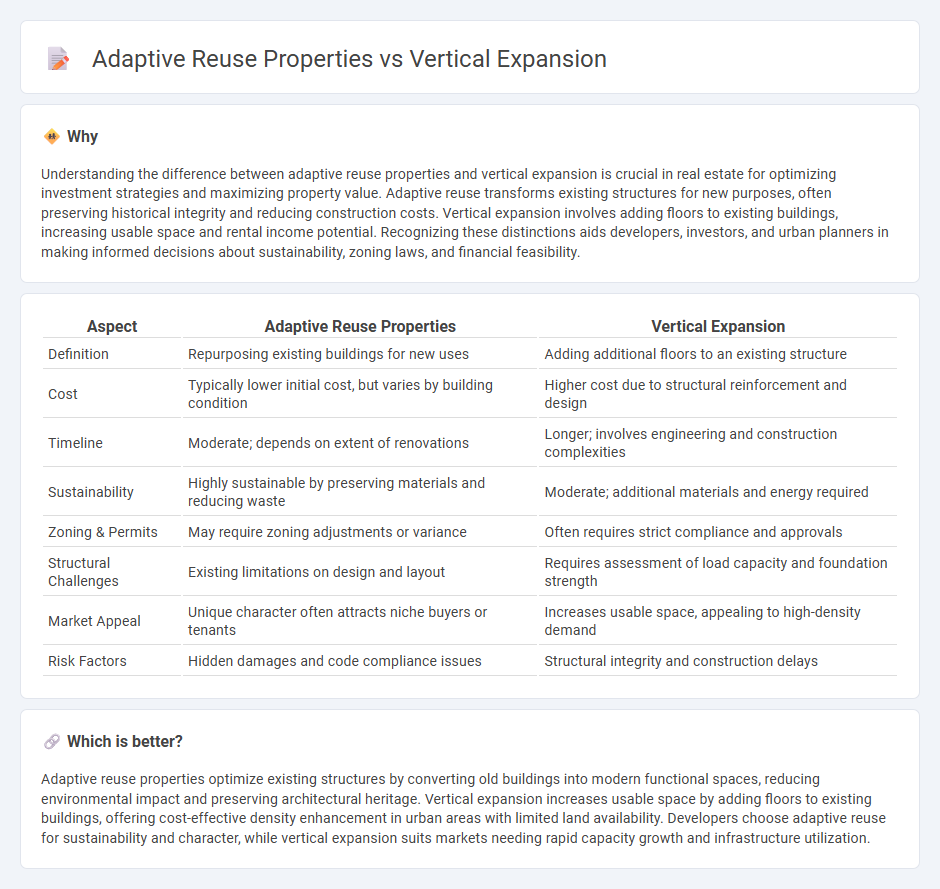
| Aspect | Adaptive Reuse Properties | Vertical Expansion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repurposing existing buildings for new uses | Adding additional floors to an existing structure |
| Cost | Typically lower initial cost, but varies by building condition | Higher cost due to structural reinforcement and design |
| Timeline | Moderate; depends on extent of renovations | Longer; involves engineering and construction complexities |
| Sustainability | Highly sustainable by preserving materials and reducing waste | Moderate; additional materials and energy required |
| Zoning & Permits | May require zoning adjustments or variance | Often requires strict compliance and approvals |
| Structural Challenges | Existing limitations on design and layout | Requires assessment of load capacity and foundation strength |
| Market Appeal | Unique character often attracts niche buyers or tenants | Increases usable space, appealing to high-density demand |
| Risk Factors | Hidden damages and code compliance issues | Structural integrity and construction delays |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse properties optimize existing structures by converting old buildings into modern functional spaces, reducing environmental impact and preserving architectural heritage. Vertical expansion increases usable space by adding floors to existing buildings, offering cost-effective density enhancement in urban areas with limited land availability. Developers choose adaptive reuse for sustainability and character, while vertical expansion suits markets needing rapid capacity growth and infrastructure utilization.
Connection
Adaptive reuse properties maximize existing structures by transforming obsolete buildings into functional real estate, often improving urban density without new land consumption. Vertical expansion enhances these projects by adding floors to existing buildings, increasing usable space and property value while preserving historical facades. Together, they offer sustainable urban development solutions by combining preservation with increased real estate capacity.
Key Terms
Zoning regulations
Zoning regulations critically influence vertical expansion by restricting building heights, floor area ratios (FAR), and setbacks, often limiting the addition of floors in urban areas. Adaptive reuse projects face zoning challenges centered on changing the building's use category, requiring variances or conditional use permits to comply with current land use codes. Explore detailed zoning impacts and strategies to optimize development potential in vertical expansion and adaptive reuse properties.
Structural integrity
Vertical expansion requires thorough assessment of a building's foundational strength and load-bearing capacity to ensure structural integrity under added weight. Adaptive reuse involves reinforcing existing structural elements to accommodate new functions without compromising safety or stability. Explore how engineers balance these challenges to optimize building longevity and safety.
Occupancy permits
Vertical expansion often requires new occupancy permits due to increased floor area and structural changes, adhering strictly to updated building codes and zoning laws. Adaptive reuse properties typically involve modifying existing spaces, which may necessitate permit adjustments to accommodate new uses but often benefit from exemptions or streamlined processes under historic or sustainable development regulations. Explore detailed guidelines and case studies to better understand occupancy permit requirements for both vertical expansions and adaptive reuse projects.
Source and External Links
Horizontal Growth vs. Vertical Growth: What is the Difference? - Vertical expansion is a growth strategy where a business scales by expanding or adding new features to existing products or services within its current market, as opposed to horizontal growth which involves new markets or products.
Vertical Expansion Option - Glossary of CRE Terms - In real estate, vertical expansion refers to the option to increase the height of a building in a future phase, allowing developers to add stories without costly reconstruction upfront, providing flexibility to meet future market demands.
Building Up VS. Building Out - Hourigan Group - Vertical expansion in construction means adding floors or levels atop an existing building, leveraging the strength of the current structure, unlike horizontal expansion which increases footprint at ground level.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com