Opportunity Zone investing offers significant tax benefits by incentivizing investments in designated economically-distressed areas, allowing for capital gains deferral and potential exclusion. Triple Net Lease (NNN) properties provide stable, passive income through long-term leases where tenants cover property expenses, making them attractive for conservative investors seeking predictable cash flow. Explore these distinct real estate strategies to determine which aligns best with your investment goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Opportunity Zone investing and Triple Net Lease is crucial for real estate investors to optimize tax benefits and risk management. Opportunity Zones offer significant capital gains tax incentives by investing in designated low-income areas, promoting economic growth. Triple Net Lease properties provide stable, long-term income with tenants responsible for expenses such as taxes, insurance, and maintenance. Investors must align their financial goals with the distinct benefits and obligations of each strategy to maximize returns and minimize liabilities.
Comparison Table
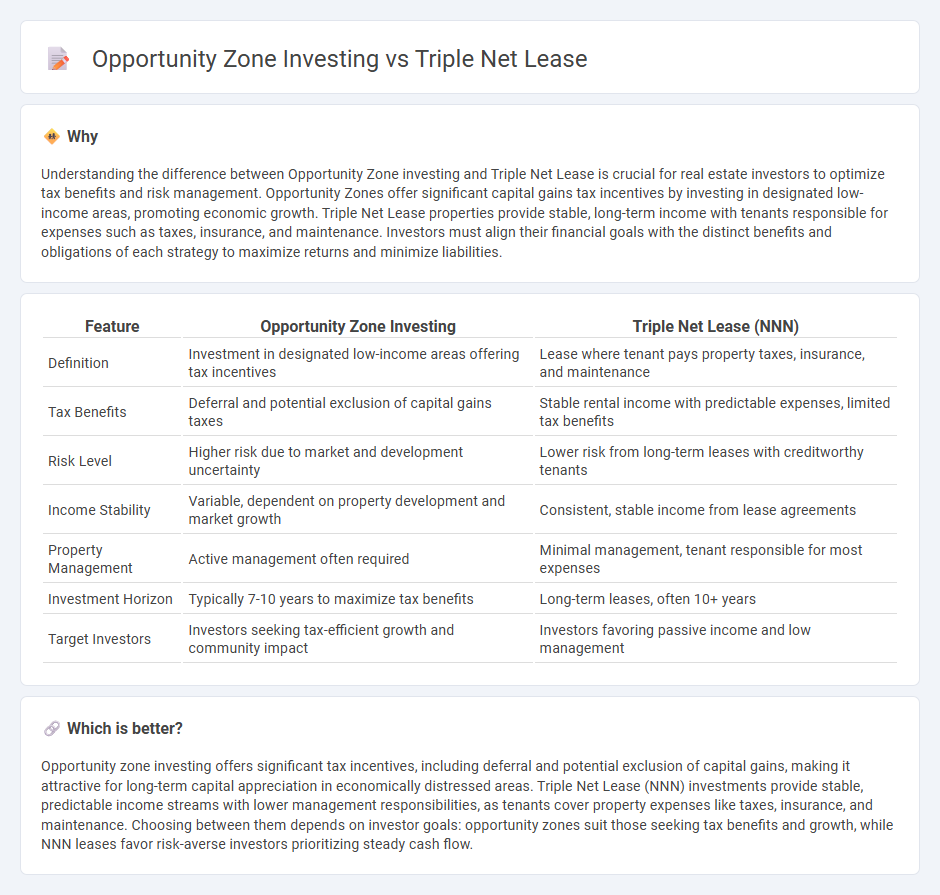
| Feature | Opportunity Zone Investing | Triple Net Lease (NNN) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in designated low-income areas offering tax incentives | Lease where tenant pays property taxes, insurance, and maintenance |
| Tax Benefits | Deferral and potential exclusion of capital gains taxes | Stable rental income with predictable expenses, limited tax benefits |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to market and development uncertainty | Lower risk from long-term leases with creditworthy tenants |
| Income Stability | Variable, dependent on property development and market growth | Consistent, stable income from lease agreements |
| Property Management | Active management often required | Minimal management, tenant responsible for most expenses |
| Investment Horizon | Typically 7-10 years to maximize tax benefits | Long-term leases, often 10+ years |
| Target Investors | Investors seeking tax-efficient growth and community impact | Investors favoring passive income and low management |
Which is better?
Opportunity zone investing offers significant tax incentives, including deferral and potential exclusion of capital gains, making it attractive for long-term capital appreciation in economically distressed areas. Triple Net Lease (NNN) investments provide stable, predictable income streams with lower management responsibilities, as tenants cover property expenses like taxes, insurance, and maintenance. Choosing between them depends on investor goals: opportunity zones suit those seeking tax benefits and growth, while NNN leases favor risk-averse investors prioritizing steady cash flow.
Connection
Opportunity zone investing leverages tax incentives for properties in designated low-income areas, enhancing long-term capital gains benefits. Triple Net Lease (NNN) properties, often found in these zones, provide stable, predictable income through tenant-responsible expenses for taxes, insurance, and maintenance. Combining opportunity zone investing with triple net leases creates a powerful strategy for real estate investors seeking tax advantages and steady cash flow.
Key Terms
Operating Expenses
Triple net lease properties shift operating expenses such as property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs to the tenant, minimizing landlord financial risk and stabilizing cash flow. Opportunity zone investing offers tax incentives to investors, but operating expenses remain the responsibility of the property owner, affecting overall returns. Explore how operating expenses impact investment strategies in both models to optimize financial outcomes.
Tax Deferral
Triple net lease investments offer predictable income streams with property tax, insurance, and maintenance costs typically borne by tenants, allowing investors to benefit from steady cash flow while maximizing tax-deductible expenses. Opportunity zone investing provides significant tax deferral advantages by allowing investors to defer capital gains taxes until the earlier of the asset sale or December 31, 2026, with potential for partial exclusion if held beyond five years. Explore the benefits and tax implications of these strategies to enhance your investment portfolio.
Property Management
Triple net lease properties typically require minimal property management since tenants handle taxes, insurance, and maintenance, reducing landlord responsibilities and operational costs. Opportunity zone investments often involve active property management to meet redevelopment goals and comply with regulatory requirements, which can lead to higher hands-on involvement but potentially greater returns. Explore detailed strategies to optimize property management in both investment types for informed decision-making.
Source and External Links
What Is A Triple Net Lease (NNN) | Definition & Examples - DoorLoop - A triple net lease (NNN) is a commercial lease where the tenant pays base rent plus all operating expenses, including property taxes, insurance, and maintenance, effectively shifting most property-related costs and responsibilities from the landlord to the tenant.
triple net lease | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - In a triple net lease, the lessee covers rent, utilities, insurance, maintenance, and taxes, reducing financial risk for landlords and often resulting in lower base rent but with the tenant shouldering potential cost fluctuations and long-term lease agreements.
Benefits and Drawbacks of a Triple Net Lease (NNN) in Commercial Real Estate - The triple net lease structure benefits landlords with low overhead and steady income, while tenants gain freedom to customize and potentially negotiate lower rents but must manage property-related expenses and maintenance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com