Build-to-rent homes offer purpose-built rental properties designed for long-term tenants, often featuring modern amenities and professional management, contrasting with affordable housing aimed at low-income families with subsidized rents and government support. These models address different segments of the housing market, with build-to-rent focusing on rental convenience and investment returns, while affordable housing prioritizes accessibility and social equity. Explore the distinct benefits and challenges of build-to-rent homes versus affordable housing to understand their impact on urban development.
Why it is important
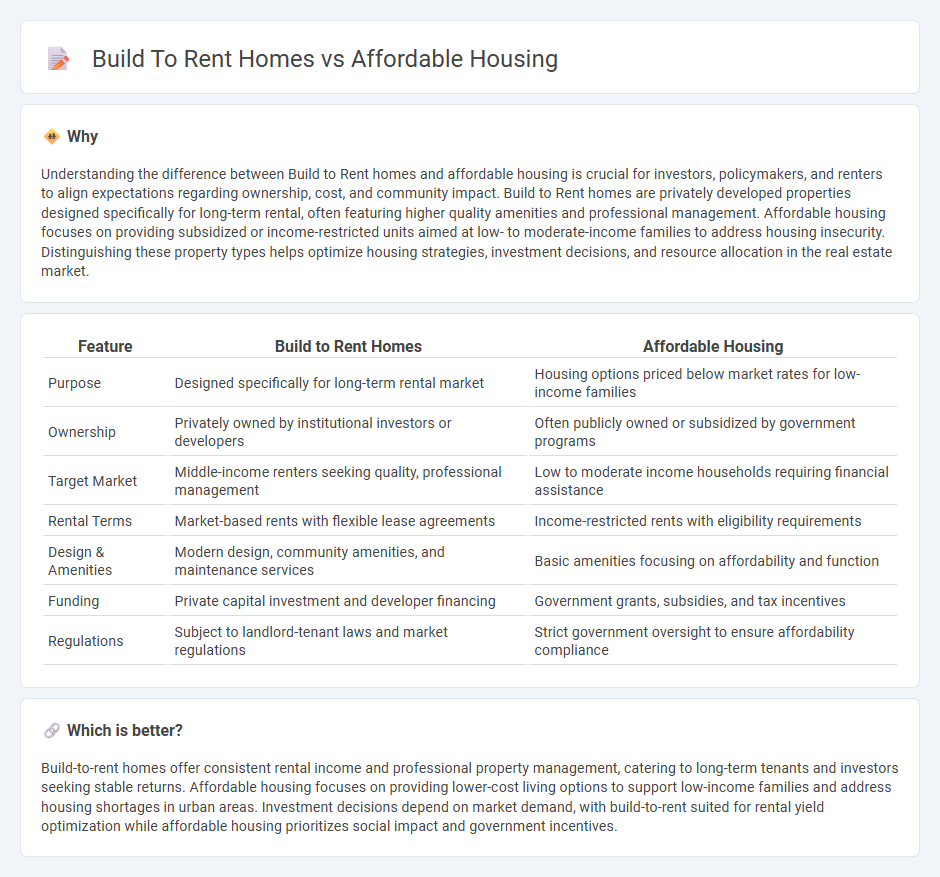
Understanding the difference between Build to Rent homes and affordable housing is crucial for investors, policymakers, and renters to align expectations regarding ownership, cost, and community impact. Build to Rent homes are privately developed properties designed specifically for long-term rental, often featuring higher quality amenities and professional management. Affordable housing focuses on providing subsidized or income-restricted units aimed at low- to moderate-income families to address housing insecurity. Distinguishing these property types helps optimize housing strategies, investment decisions, and resource allocation in the real estate market.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Build to Rent Homes | Affordable Housing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Designed specifically for long-term rental market | Housing options priced below market rates for low-income families |
| Ownership | Privately owned by institutional investors or developers | Often publicly owned or subsidized by government programs |
| Target Market | Middle-income renters seeking quality, professional management | Low to moderate income households requiring financial assistance |
| Rental Terms | Market-based rents with flexible lease agreements | Income-restricted rents with eligibility requirements |
| Design & Amenities | Modern design, community amenities, and maintenance services | Basic amenities focusing on affordability and function |
| Funding | Private capital investment and developer financing | Government grants, subsidies, and tax incentives |
| Regulations | Subject to landlord-tenant laws and market regulations | Strict government oversight to ensure affordability compliance |
Which is better?
Build-to-rent homes offer consistent rental income and professional property management, catering to long-term tenants and investors seeking stable returns. Affordable housing focuses on providing lower-cost living options to support low-income families and address housing shortages in urban areas. Investment decisions depend on market demand, with build-to-rent suited for rental yield optimization while affordable housing prioritizes social impact and government incentives.
Connection
Build-to-rent homes increase affordable housing supply by providing professionally managed rental properties with stable long-term occupancy, addressing demand in high-cost markets. These developments optimize land use and construction efficiency to lower overall housing costs while maintaining quality standards. By integrating community amenities and scalable designs, build-to-rent models support sustainable, inclusive neighborhoods that meet diverse affordability needs.
Key Terms
Rent Control
Rent control policies significantly impact both affordable housing and build-to-rent (BTR) developments by limiting rent increases, thereby enhancing housing accessibility for low- to moderate-income tenants. Affordable housing programs often integrate rent control to maintain long-term affordability, whereas BTR homes balance rent regulation with investor returns to encourage sustainable property management. Explore further to understand how rent control shapes these housing sectors and influences market dynamics.
Institutional Investment
Institutional investment in affordable housing centers on long-term community impact and social equity, providing stable rental options for low-to-moderate income families. Build-to-rent homes attract institutional investors by offering scalable, predictable cash flows through professionally managed single-family rental communities designed for middle-income tenants. Explore how institutional investment strategies shape the future of housing affordability and rental markets.
Income Eligibility
Affordable housing typically targets low to moderate-income households with strict income eligibility criteria based on area median income (AMI) percentages, often ranging from 30% to 80% AMI. Build-to-rent homes focus on providing rental options without stringent income limits, catering to a broader market but often at higher price points than traditional affordable housing. Explore more to understand how income eligibility shapes your housing opportunities.
Source and External Links
What is Affordable Housing? - National League of Cities - Defines affordable housing as housing where the occupant pays no more than 30% of their gross income for housing costs, including utilities.
State Housing Initiative Program (SHIP) | Clay County, FL - Provides down payment aid, home repairs, and special needs housing to support safe and affordable homes for income-eligible residents in Clay County.
Affordable Housing Now Available - Jacksonville, Florida - Offers various affordable housing options, including Project Based Vouchers and specific programs like the HUD VASH Program for veterans.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com