Agrihoods integrate sustainable agriculture within residential communities, promoting farm-to-table living and environmental stewardship. Cohousing focuses on shared spaces and collaborative living to foster strong social connections and community engagement. Discover the unique benefits and lifestyle features of agrihoods and cohousing to find the ideal residential concept for your needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between agrihoods and cohousing is essential for real estate investors and homebuyers to align property choices with lifestyle preferences and long-term value. Agrihoods combine residential living with sustainable agriculture, promoting community farming and fresh food access. Cohousing emphasizes shared spaces and collaborative living to foster social connections and reduce individual housing costs. Choosing the appropriate model impacts property appeal, market demand, and neighborhood dynamics.
Comparison Table
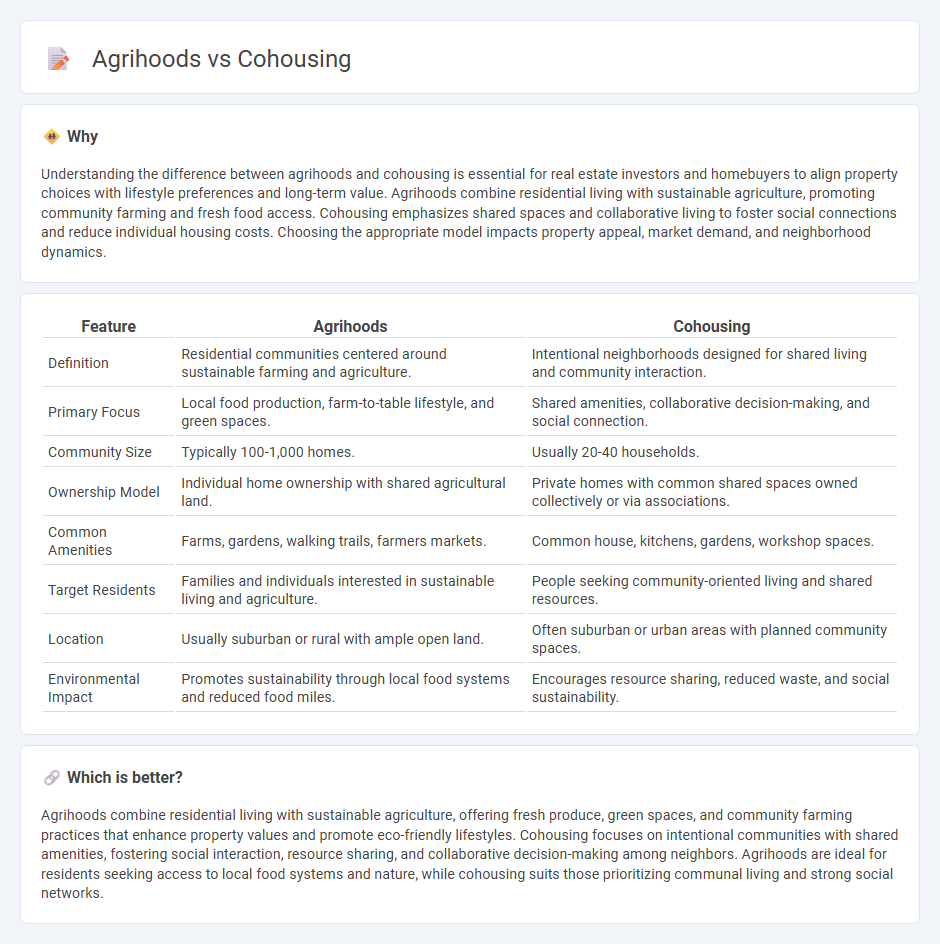
| Feature | Agrihoods | Cohousing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Residential communities centered around sustainable farming and agriculture. | Intentional neighborhoods designed for shared living and community interaction. |
| Primary Focus | Local food production, farm-to-table lifestyle, and green spaces. | Shared amenities, collaborative decision-making, and social connection. |
| Community Size | Typically 100-1,000 homes. | Usually 20-40 households. |
| Ownership Model | Individual home ownership with shared agricultural land. | Private homes with common shared spaces owned collectively or via associations. |
| Common Amenities | Farms, gardens, walking trails, farmers markets. | Common house, kitchens, gardens, workshop spaces. |
| Target Residents | Families and individuals interested in sustainable living and agriculture. | People seeking community-oriented living and shared resources. |
| Location | Usually suburban or rural with ample open land. | Often suburban or urban areas with planned community spaces. |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainability through local food systems and reduced food miles. | Encourages resource sharing, reduced waste, and social sustainability. |
Which is better?
Agrihoods combine residential living with sustainable agriculture, offering fresh produce, green spaces, and community farming practices that enhance property values and promote eco-friendly lifestyles. Cohousing focuses on intentional communities with shared amenities, fostering social interaction, resource sharing, and collaborative decision-making among neighbors. Agrihoods are ideal for residents seeking access to local food systems and nature, while cohousing suits those prioritizing communal living and strong social networks.
Connection
Agrihoods and cohousing are connected through their shared emphasis on community-centered living and sustainable design. Both foster social interaction by integrating shared spaces such as communal gardens or farms, which promote collaboration among residents. This connection enhances real estate value by appealing to buyers seeking environmentally conscious and socially engaging neighborhoods.
Key Terms
Shared Amenities
Cohousing communities emphasize shared amenities such as communal kitchens, common dining areas, and recreational spaces to foster social interaction and collaboration among residents. Agrihoods integrate agricultural elements like community gardens, orchards, and farms into their shared amenities, promoting sustainable living and local food production. Explore how these distinct approaches to shared amenities support community goals and lifestyle preferences.
Community Involvement
Cohousing communities prioritize shared spaces and collaborative decision-making to foster close-knit neighbor relationships, encouraging active community participation in daily life and governance. Agrihoods integrate shared agricultural projects within residential neighborhoods, promoting involvement through farming activities, environmental stewardship, and local food production. Explore how these innovative living models cultivate community bonds through unique engagement opportunities.
Agricultural Integration
Cohousing communities emphasize shared living spaces and social interaction, while agrihoods integrate agricultural elements such as community gardens, farms, and orchards directly into residential neighborhoods for sustainable living. Agrihoods promote local food production and environmental stewardship by embedding agriculture into the community design, enhancing residents' connection to nature and healthy lifestyles. Explore how agrihoods redefine modern neighborhoods by blending agriculture with housing for a sustainable future.
Source and External Links
Cohousing - Wikipedia - Cohousing is an intentional, self-governing, cooperative community where residents live in private homes clustered around shared spaces, fostering social interaction and shared resources while maintaining individual privacy and income.
THE COHOUSING COMPANY - Cohousing features thoughtfully designed neighborhoods with private homes around shared common areas, emphasizing collaborative, social, equal, independent, and self-managed community living that balances privacy and collective harmony.
Beyond Contact-Intergenerational Living in Cohousing Communities - Cohousing communities combine private homes of varying sizes with shared facilities and active social programming, encouraging intergenerational interaction and cooperative self-management in diverse physical forms and settings.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com