Modular construction leverages prefabricated sections to accelerate build times, reduce costs, and minimize waste, making it a practical solution for efficient real estate development. Passive house construction focuses on superior insulation, airtightness, and energy-efficient systems to achieve minimal energy consumption and enhanced indoor comfort. Explore our detailed comparison to understand which method aligns best with your sustainable building goals.
Why it is important
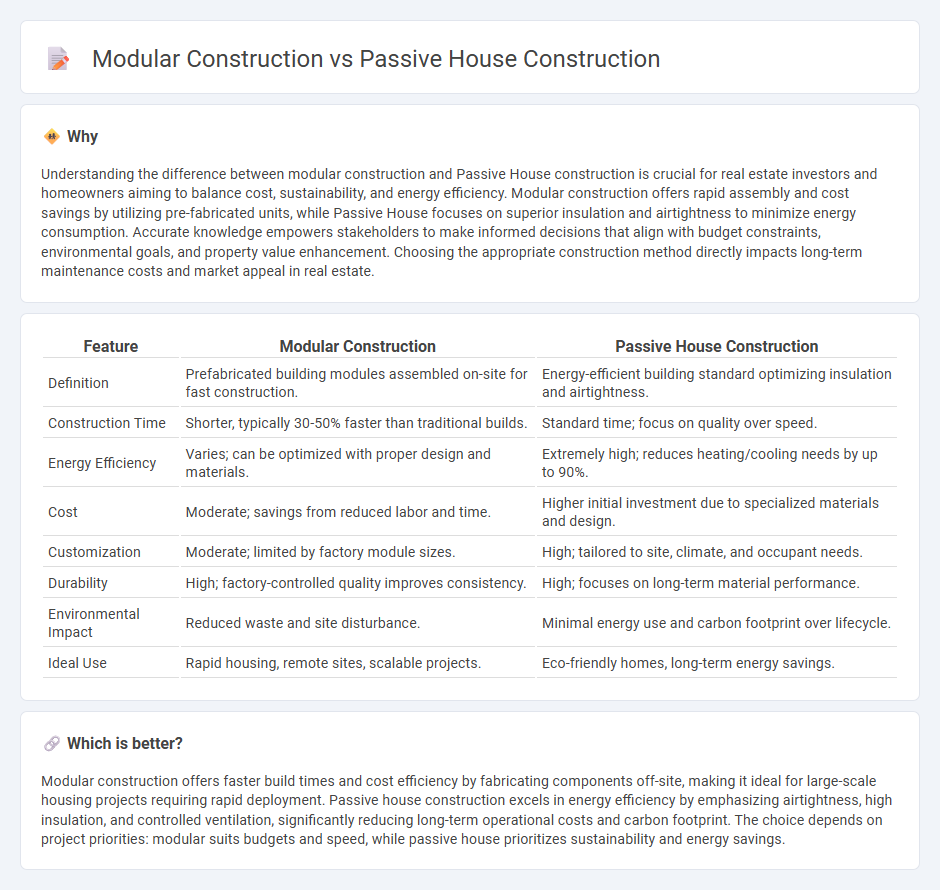
Understanding the difference between modular construction and Passive House construction is crucial for real estate investors and homeowners aiming to balance cost, sustainability, and energy efficiency. Modular construction offers rapid assembly and cost savings by utilizing pre-fabricated units, while Passive House focuses on superior insulation and airtightness to minimize energy consumption. Accurate knowledge empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions that align with budget constraints, environmental goals, and property value enhancement. Choosing the appropriate construction method directly impacts long-term maintenance costs and market appeal in real estate.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Modular Construction | Passive House Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prefabricated building modules assembled on-site for fast construction. | Energy-efficient building standard optimizing insulation and airtightness. |
| Construction Time | Shorter, typically 30-50% faster than traditional builds. | Standard time; focus on quality over speed. |
| Energy Efficiency | Varies; can be optimized with proper design and materials. | Extremely high; reduces heating/cooling needs by up to 90%. |
| Cost | Moderate; savings from reduced labor and time. | Higher initial investment due to specialized materials and design. |
| Customization | Moderate; limited by factory module sizes. | High; tailored to site, climate, and occupant needs. |
| Durability | High; factory-controlled quality improves consistency. | High; focuses on long-term material performance. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced waste and site disturbance. | Minimal energy use and carbon footprint over lifecycle. |
| Ideal Use | Rapid housing, remote sites, scalable projects. | Eco-friendly homes, long-term energy savings. |
Which is better?
Modular construction offers faster build times and cost efficiency by fabricating components off-site, making it ideal for large-scale housing projects requiring rapid deployment. Passive house construction excels in energy efficiency by emphasizing airtightness, high insulation, and controlled ventilation, significantly reducing long-term operational costs and carbon footprint. The choice depends on project priorities: modular suits budgets and speed, while passive house prioritizes sustainability and energy savings.
Connection
Modular construction enhances Passive House standards by enabling precise factory-controlled fabrication of highly insulated, airtight building components that improve energy efficiency. The integration of modular building techniques with Passive House principles reduces construction waste, shortens build times, and ensures consistent quality in thermal performance. This synergy supports sustainable real estate development by lowering operational costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Key Terms
Energy Efficiency
Passive house construction maximizes energy efficiency through airtight building envelopes, superior insulation, and heat recovery ventilation systems, which significantly reduce heating and cooling demands. Modular construction, while efficient in reducing construction time and waste, may not inherently meet passive house standards unless specifically designed with energy-efficient materials and techniques. Explore detailed comparisons of passive house and modular construction to optimize energy use in your next building project.
Prefabrication
Passive house construction emphasizes high energy efficiency and airtight design using prefabricated components to ensure consistent quality and thermal performance. Modular construction involves assembling factory-built sections, enabling faster build times and reduced on-site labor, often incorporating prefabricated elements compatible with passive house standards. Discover how combining prefabrication with these construction methods can optimize sustainability and efficiency.
Thermal Insulation
Passive house construction excels in thermal insulation by utilizing high-performance materials such as triple-glazed windows, dense wall insulation, and airtight building envelopes to minimize heat loss and optimize energy efficiency. Modular construction can incorporate similar insulation techniques but often faces challenges ensuring seamless thermal barriers between prefabricated units, potentially reducing overall performance. Discover how combining innovative insulation strategies in both methods can create superior energy-efficient homes.
Source and External Links
Passive House - A voluntary standard for energy efficiency in buildings, focusing on reducing energy consumption through techniques like superinsulation and passive solar design.
What is Passive House? - A performance-based building certification that significantly reduces energy use for space heating and cooling, promoting a healthier and more comfortable living environment.
Passive House: An In-Depth Guide - Provides detailed insights into the construction and benefits of Passive Houses, including energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the long term.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com