Nature-inclusive design integrates green spaces, biodiversity, and sustainable materials to create eco-friendly urban environments that improve air quality and residents' well-being. High-rise urban development prioritizes maximizing land use through vertical construction, addressing housing shortages while potentially limiting natural elements and open spaces. Explore the balance between these approaches to understand their impact on future real estate trends.
Why it is important
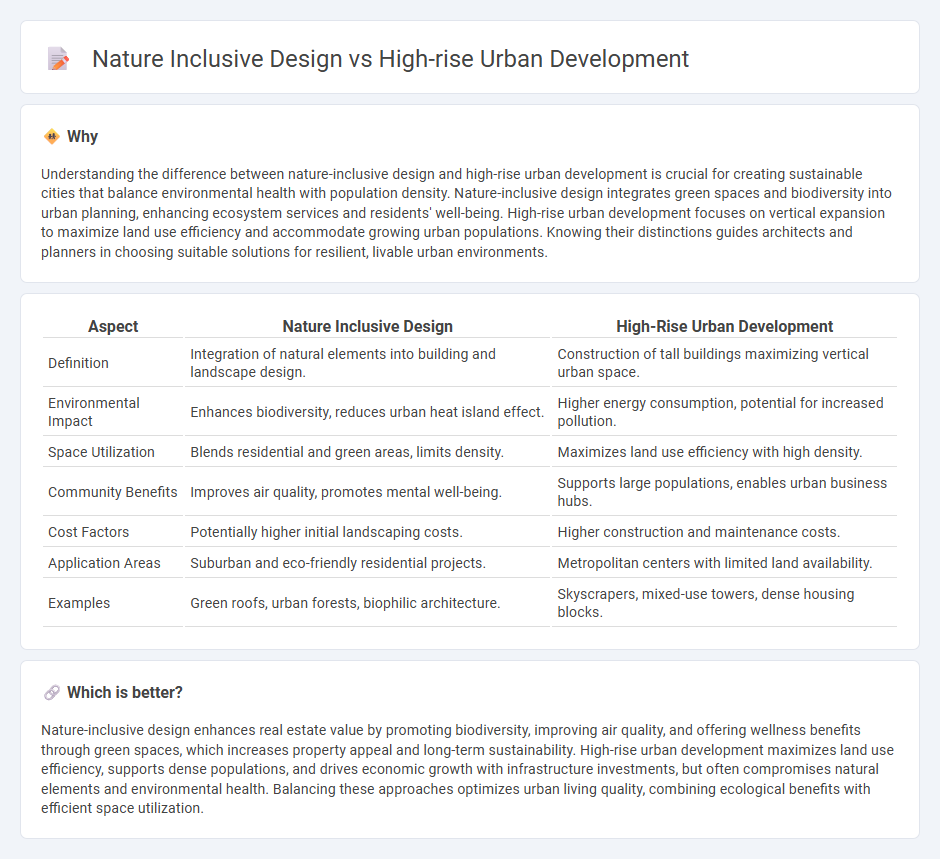
Understanding the difference between nature-inclusive design and high-rise urban development is crucial for creating sustainable cities that balance environmental health with population density. Nature-inclusive design integrates green spaces and biodiversity into urban planning, enhancing ecosystem services and residents' well-being. High-rise urban development focuses on vertical expansion to maximize land use efficiency and accommodate growing urban populations. Knowing their distinctions guides architects and planners in choosing suitable solutions for resilient, livable urban environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Nature Inclusive Design | High-Rise Urban Development |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of natural elements into building and landscape design. | Construction of tall buildings maximizing vertical urban space. |
| Environmental Impact | Enhances biodiversity, reduces urban heat island effect. | Higher energy consumption, potential for increased pollution. |
| Space Utilization | Blends residential and green areas, limits density. | Maximizes land use efficiency with high density. |
| Community Benefits | Improves air quality, promotes mental well-being. | Supports large populations, enables urban business hubs. |
| Cost Factors | Potentially higher initial landscaping costs. | Higher construction and maintenance costs. |
| Application Areas | Suburban and eco-friendly residential projects. | Metropolitan centers with limited land availability. |
| Examples | Green roofs, urban forests, biophilic architecture. | Skyscrapers, mixed-use towers, dense housing blocks. |
Which is better?
Nature-inclusive design enhances real estate value by promoting biodiversity, improving air quality, and offering wellness benefits through green spaces, which increases property appeal and long-term sustainability. High-rise urban development maximizes land use efficiency, supports dense populations, and drives economic growth with infrastructure investments, but often compromises natural elements and environmental health. Balancing these approaches optimizes urban living quality, combining ecological benefits with efficient space utilization.
Connection
Nature inclusive design integrates green spaces, natural light, and biodiversity within high-rise urban developments to enhance environmental sustainability and improve residents' well-being. High-rise buildings incorporating vertical gardens, green roofs, and eco-friendly materials reduce urban heat island effects and support local ecosystems. This synergy fosters healthier urban environments while efficiently utilizing limited city space for real estate growth.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations play a critical role in balancing high-rise urban development with nature-inclusive design by dictating land use, building heights, and green space requirements to promote sustainable cities. Incorporating green infrastructure and biodiversity corridors within zoning laws supports ecological connectivity and enhances urban resilience. Explore how innovative zoning policies can harmonize city growth with environmental stewardship for future urban planning.
Green Infrastructure
High-rise urban development often prioritizes maximizing floor area and density, which can lead to reduced green spaces and increased urban heat island effects. Nature-inclusive design emphasizes integrating green infrastructure such as green roofs, vertical gardens, and permeable pavements to enhance biodiversity, improve air quality, and manage stormwater effectively. Explore innovative green infrastructure strategies to balance urban growth and ecological sustainability in city planning.
Biodiversity Integration
High-rise urban development often challenges biodiversity by reducing natural habitats and altering ecosystems, whereas nature inclusive design prioritizes integrating green spaces and native flora within urban settings to support diverse species. Biodiversity integration involves strategic planning to create ecological corridors, green roofs, and vertical gardens that enhance habitat connectivity and promote urban wildlife. Explore innovative approaches to harmonize urban growth with biodiversity conservation for sustainable city development.
Source and External Links
Going Vertical: Pros and Cons of High-Rise Development - This article explores the benefits and challenges of high-rise development, including efficient use of urban space and regulatory hurdles.
High-rise - a global perspective - This piece discusses global trends in high-rise development, driven by urbanization and land scarcity, with commercial and residential uses dominating these projects.
High-Rise Construction: Benefits, Considerations, and Alternatives - This blog post highlights the benefits of high-rise construction, such as increased density, walkability, and mixed-use capabilities, while also noting considerations and alternatives.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com