Modular home construction involves building sections of a house in a factory setting before transporting and assembling them on-site, ensuring high quality control and faster completion times compared to traditional methods. Pre-fabricated homes consist of factory-made components that are quickly assembled on location, often resulting in cost savings and reduced waste but with less customization than modular homes. Discover the key differences and benefits of each method to determine the best choice for your real estate investment.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between modular home construction and pre-fabricated home construction is crucial for real estate investors and buyers to make informed decisions regarding cost, build time, and customization options. Modular homes are built in sections in a factory and assembled on-site, offering higher quality control and structural integrity compared to traditional pre-fabricated homes that are often made in panels. Understanding these distinctions affects property value, financing options, and insurance rates, all essential factors in the real estate market. Accurate knowledge can lead to better negotiation power and long-term satisfaction with the investment.
Comparison Table
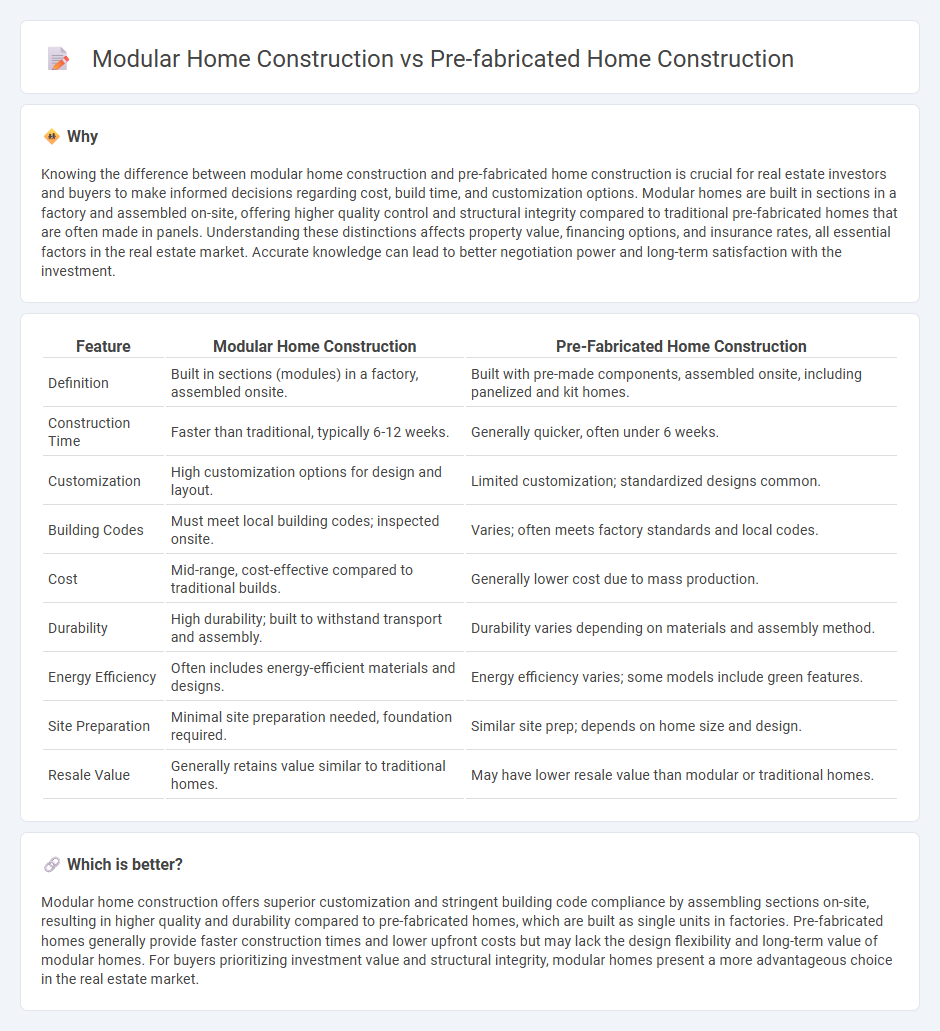
| Feature | Modular Home Construction | Pre-Fabricated Home Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Built in sections (modules) in a factory, assembled onsite. | Built with pre-made components, assembled onsite, including panelized and kit homes. |
| Construction Time | Faster than traditional, typically 6-12 weeks. | Generally quicker, often under 6 weeks. |
| Customization | High customization options for design and layout. | Limited customization; standardized designs common. |
| Building Codes | Must meet local building codes; inspected onsite. | Varies; often meets factory standards and local codes. |
| Cost | Mid-range, cost-effective compared to traditional builds. | Generally lower cost due to mass production. |
| Durability | High durability; built to withstand transport and assembly. | Durability varies depending on materials and assembly method. |
| Energy Efficiency | Often includes energy-efficient materials and designs. | Energy efficiency varies; some models include green features. |
| Site Preparation | Minimal site preparation needed, foundation required. | Similar site prep; depends on home size and design. |
| Resale Value | Generally retains value similar to traditional homes. | May have lower resale value than modular or traditional homes. |
Which is better?
Modular home construction offers superior customization and stringent building code compliance by assembling sections on-site, resulting in higher quality and durability compared to pre-fabricated homes, which are built as single units in factories. Pre-fabricated homes generally provide faster construction times and lower upfront costs but may lack the design flexibility and long-term value of modular homes. For buyers prioritizing investment value and structural integrity, modular homes present a more advantageous choice in the real estate market.
Connection
Modular home construction and pre-fabricated home construction both involve manufacturing building components off-site in controlled factory environments to ensure higher quality and faster assembly. Modular homes are a subset of pre-fabricated homes, consisting of multiple sections or modules built separately and then transported to the site for assembly. This connection allows for reduced construction time, lower costs, and minimized on-site disruptions compared to traditional building methods.
Key Terms
Factory-Built
Factory-built homes, including pre-fabricated and modular construction, streamline the building process by manufacturing sections in controlled environments to reduce waste and improve quality consistency. Pre-fabricated homes typically involve assembling flat components on-site, while modular homes consist of pre-assembled modules transported and joined on location, offering faster build times and enhanced structural integrity. Explore the benefits and distinctions of factory-built home options to determine the best fit for your housing needs.
On-Site Assembly
Pre-fabricated home construction often involves assembling large sections or panels on-site, which can reduce build time but may require more extensive customization during installation. Modular home construction delivers fully-built modules to the site, allowing for quicker and more efficient on-site assembly with less disruption and higher quality control. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which on-site assembly method best suits your project needs.
Building Codes
Pre-fabricated home construction and modular home construction both adhere to building codes, with pre-fabricated homes often following local and regional standards during on-site assembly, while modular homes are constructed according to stringent national or international building codes in factory settings. Modular homes benefit from controlled factory environments, ensuring consistent compliance with codes such as the International Residential Code (IRC), reducing on-site inspection challenges compared to traditional prefab methods. Explore more about how building codes impact the construction quality and compliance of these innovative housing solutions.
Source and External Links
A Comprehensive Guide for Building Modular Homes - Modular homes are prefabricated in factory-built modules transported to the site and assembled on permanent foundations, complying with strict building codes, distinguishing them from other types of prefabricated structures such as panelized or mobile homes.
Prefab Homes - Prefabricated homes include panelized walls, roofs, and floors built off-site to reduce framing time by 60% on site, delivered ready for quick assembly with all necessary components included.
Modular Home Floorplans | Modular Home Layouts - The process involves site preparation, permitting, and professional assembly of factory-built modules to ensure compliance with local codes and quality customization options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com