Vertical forests enhance urban biodiversity by integrating dense vegetation on building facades, improving air quality and providing natural insulation. Green roofs focus on covering rooftops with plant life to reduce heat islands, manage stormwater, and increase energy efficiency. Explore the benefits and differences of vertical forests and green roofs in transforming sustainable real estate development.
Why it is important
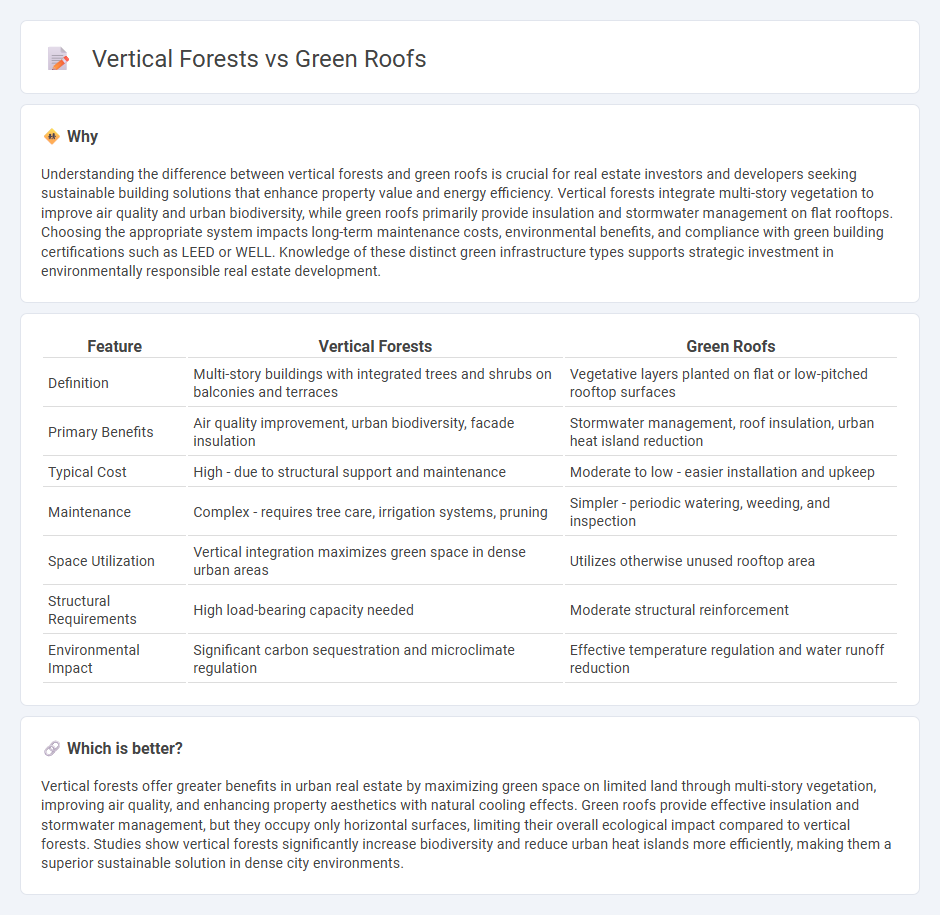
Understanding the difference between vertical forests and green roofs is crucial for real estate investors and developers seeking sustainable building solutions that enhance property value and energy efficiency. Vertical forests integrate multi-story vegetation to improve air quality and urban biodiversity, while green roofs primarily provide insulation and stormwater management on flat rooftops. Choosing the appropriate system impacts long-term maintenance costs, environmental benefits, and compliance with green building certifications such as LEED or WELL. Knowledge of these distinct green infrastructure types supports strategic investment in environmentally responsible real estate development.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Vertical Forests | Green Roofs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multi-story buildings with integrated trees and shrubs on balconies and terraces | Vegetative layers planted on flat or low-pitched rooftop surfaces |
| Primary Benefits | Air quality improvement, urban biodiversity, facade insulation | Stormwater management, roof insulation, urban heat island reduction |
| Typical Cost | High - due to structural support and maintenance | Moderate to low - easier installation and upkeep |
| Maintenance | Complex - requires tree care, irrigation systems, pruning | Simpler - periodic watering, weeding, and inspection |
| Space Utilization | Vertical integration maximizes green space in dense urban areas | Utilizes otherwise unused rooftop area |
| Structural Requirements | High load-bearing capacity needed | Moderate structural reinforcement |
| Environmental Impact | Significant carbon sequestration and microclimate regulation | Effective temperature regulation and water runoff reduction |
Which is better?
Vertical forests offer greater benefits in urban real estate by maximizing green space on limited land through multi-story vegetation, improving air quality, and enhancing property aesthetics with natural cooling effects. Green roofs provide effective insulation and stormwater management, but they occupy only horizontal surfaces, limiting their overall ecological impact compared to vertical forests. Studies show vertical forests significantly increase biodiversity and reduce urban heat islands more efficiently, making them a superior sustainable solution in dense city environments.
Connection
Vertical forests and green roofs both enhance urban biodiversity and air quality by integrating vegetation into building structures. Vertical forests, typically high-rise buildings covered with trees and plants, improve insulation and reduce urban heat islands similarly to green roofs, which use vegetation to manage stormwater and lower rooftop temperatures. These green infrastructure solutions contribute to sustainable real estate development by increasing energy efficiency and promoting healthier living environments.
Key Terms
Biodiversity
Green roofs enhance urban biodiversity by providing habitats for pollinators, birds, and insects, using native plant species to support local ecosystems. Vertical forests incorporate large trees and shrubs on building facades, increasing habitat complexity and improving air quality through increased vegetation density. Explore more to understand how each approach uniquely benefits urban biodiversity and ecological balance.
Energy Efficiency
Green roofs reduce building energy consumption by providing insulation that lowers heating and cooling demands, often cutting energy use by up to 25%. Vertical forests, with their dense foliage and strategic plant placements, enhance energy efficiency by shading facades and improving air quality, leading to reduced reliance on air conditioning. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which option suits your energy goals best.
Urban Heat Island
Green roofs significantly reduce Urban Heat Island (UHI) effects by increasing surface albedo and enhancing evapotranspiration, which cools urban environments through natural processes. Vertical forests contribute to heat mitigation by providing extensive foliage coverage on building facades, improving air quality and shading while promoting biodiversity in dense urban settings. Discover which green infrastructure best combats UHI by exploring detailed comparisons and case studies.
Source and External Links
Green roof - A green roof is a structure covered with vegetation and a growing medium, offering benefits like improved insulation and reduced urban heat island effect.
Advantages and disadvantages of green roofs - This guide explores the benefits and drawbacks of green roofs, including environmental advantages and potential drawbacks.
About Green Roofs - Green roofs mitigate the urban heat island effect and reduce airborne pollutants, contributing to a more sustainable urban environment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com