Vertical farming buildings maximize urban space by integrating agriculture into high-rise structures, enhancing sustainability and reducing food transportation costs. Industrial warehouses prioritize large-scale storage and distribution logistics, often requiring expansive, single-floor layouts for efficient goods handling. Explore how these real estate sectors redefine space utilization and economic potential.
Why it is important
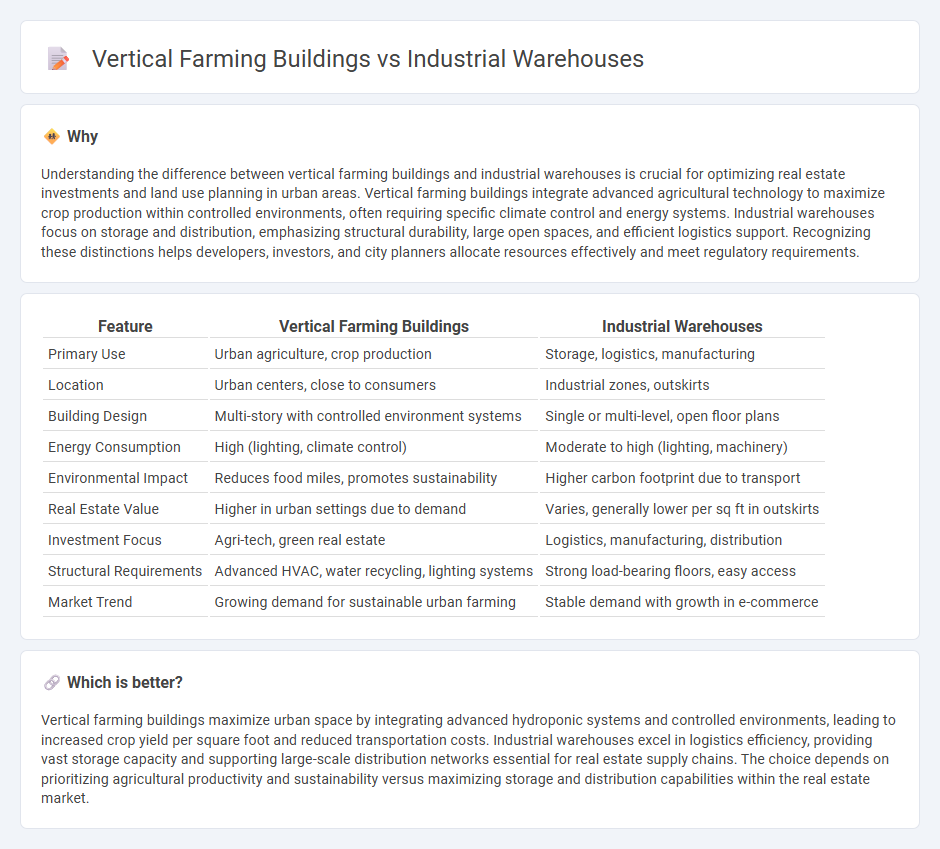
Understanding the difference between vertical farming buildings and industrial warehouses is crucial for optimizing real estate investments and land use planning in urban areas. Vertical farming buildings integrate advanced agricultural technology to maximize crop production within controlled environments, often requiring specific climate control and energy systems. Industrial warehouses focus on storage and distribution, emphasizing structural durability, large open spaces, and efficient logistics support. Recognizing these distinctions helps developers, investors, and city planners allocate resources effectively and meet regulatory requirements.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Vertical Farming Buildings | Industrial Warehouses |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Urban agriculture, crop production | Storage, logistics, manufacturing |
| Location | Urban centers, close to consumers | Industrial zones, outskirts |
| Building Design | Multi-story with controlled environment systems | Single or multi-level, open floor plans |
| Energy Consumption | High (lighting, climate control) | Moderate to high (lighting, machinery) |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces food miles, promotes sustainability | Higher carbon footprint due to transport |
| Real Estate Value | Higher in urban settings due to demand | Varies, generally lower per sq ft in outskirts |
| Investment Focus | Agri-tech, green real estate | Logistics, manufacturing, distribution |
| Structural Requirements | Advanced HVAC, water recycling, lighting systems | Strong load-bearing floors, easy access |
| Market Trend | Growing demand for sustainable urban farming | Stable demand with growth in e-commerce |
Which is better?
Vertical farming buildings maximize urban space by integrating advanced hydroponic systems and controlled environments, leading to increased crop yield per square foot and reduced transportation costs. Industrial warehouses excel in logistics efficiency, providing vast storage capacity and supporting large-scale distribution networks essential for real estate supply chains. The choice depends on prioritizing agricultural productivity and sustainability versus maximizing storage and distribution capabilities within the real estate market.
Connection
Vertical farming buildings and industrial warehouses share structural and logistical similarities, including large open floor plans, high ceilings, and advanced climate control systems designed to optimize space and environmental conditions. Both facilities leverage cutting-edge technology such as automation, IoT sensors, and energy-efficient LED lighting to maximize operational efficiency and productivity. The integration of these features supports scalability and sustainability in urban agriculture and industrial storage solutions.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations for industrial warehouses typically permit large-scale storage and manufacturing operations in designated industrial zones, emphasizing compliance with safety, noise, and environmental standards. Vertical farming buildings often require special zoning considerations due to their hybrid nature, combining agricultural production with commercial real estate, leading to potential challenges in securing permits within urban areas. Explore detailed zoning requirements to understand how these regulations impact the development and operation of both industrial warehouses and vertical farms.
Ceiling Height
Industrial warehouses typically feature ceiling heights ranging from 24 to 36 feet to accommodate large machinery, storage racks, and efficient air circulation, optimizing space for bulk goods and logistics operations. Vertical farming buildings prioritize lower ceiling heights, often between 12 to 20 feet, to enhance controlled environment agriculture by optimizing light distribution, climate control, and energy efficiency for plant growth. Explore how ceiling height influences operational efficiency and design in both industrial warehouses and vertical farming facilities.
HVAC Systems
Industrial warehouses rely on robust HVAC systems designed for large-scale ventilation and temperature control to support storage and manufacturing processes. Vertical farming buildings require specialized HVAC solutions that maintain precise humidity, temperature, and CO2 levels to optimize plant growth and maximize yield efficiency. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how HVAC innovations drive performance in these contrasting environments.
Source and External Links
Industrial, Manufacturing & Warehouse | Wichita, KS - This webpage outlines incentives and programs for industrial and manufacturing developments in Wichita, including tax abatements and revenue bonds.
Wichita, KS Industrial & Warehouse Space for Rent - This platform offers a variety of industrial and warehouse spaces for rent in Wichita, providing detailed listings and local market statistics.
Wichita, KS Industrial & Warehouse Spaces for Sale - This webpage provides a selection of industrial warehouses available for purchase in Wichita, allowing users to filter by neighborhood and price range.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com