Nature-inclusive design integrates natural ecosystems into urban planning, promoting biodiversity and sustainable living spaces. Suburban sprawl, characterized by low-density, car-dependent development, often leads to habitat fragmentation and increased environmental impact. Explore how balancing development and conservation can redefine future real estate projects.
Why it is important
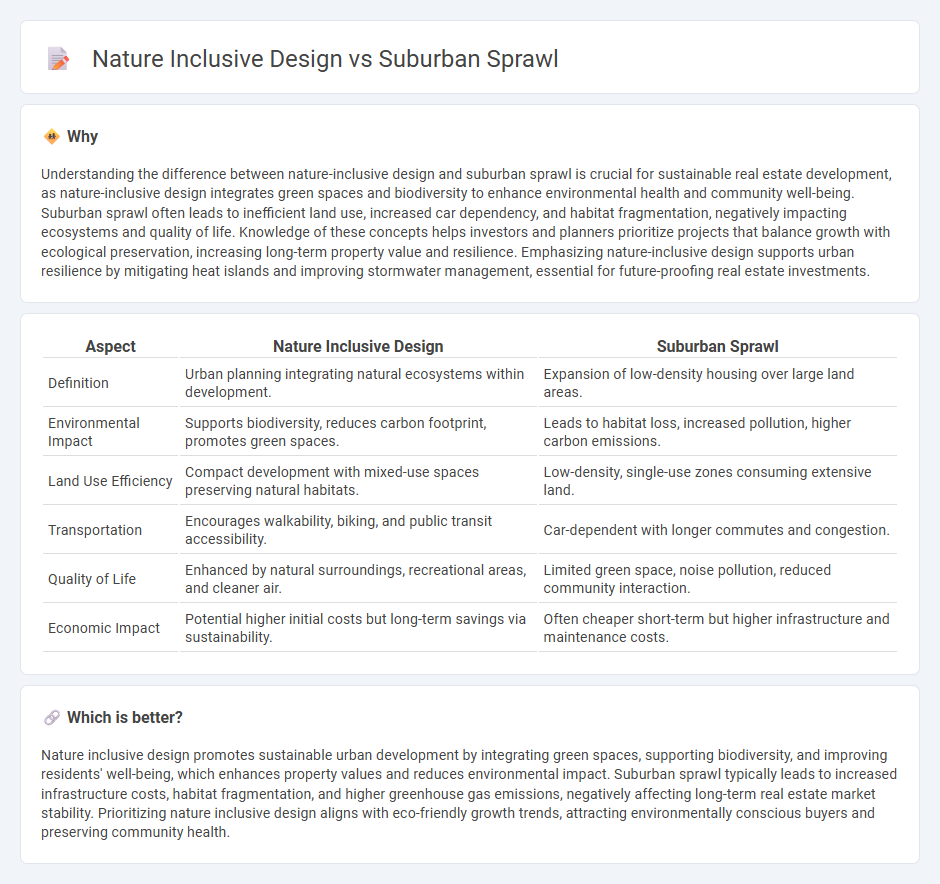
Understanding the difference between nature-inclusive design and suburban sprawl is crucial for sustainable real estate development, as nature-inclusive design integrates green spaces and biodiversity to enhance environmental health and community well-being. Suburban sprawl often leads to inefficient land use, increased car dependency, and habitat fragmentation, negatively impacting ecosystems and quality of life. Knowledge of these concepts helps investors and planners prioritize projects that balance growth with ecological preservation, increasing long-term property value and resilience. Emphasizing nature-inclusive design supports urban resilience by mitigating heat islands and improving stormwater management, essential for future-proofing real estate investments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Nature Inclusive Design | Suburban Sprawl |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Urban planning integrating natural ecosystems within development. | Expansion of low-density housing over large land areas. |
| Environmental Impact | Supports biodiversity, reduces carbon footprint, promotes green spaces. | Leads to habitat loss, increased pollution, higher carbon emissions. |
| Land Use Efficiency | Compact development with mixed-use spaces preserving natural habitats. | Low-density, single-use zones consuming extensive land. |
| Transportation | Encourages walkability, biking, and public transit accessibility. | Car-dependent with longer commutes and congestion. |
| Quality of Life | Enhanced by natural surroundings, recreational areas, and cleaner air. | Limited green space, noise pollution, reduced community interaction. |
| Economic Impact | Potential higher initial costs but long-term savings via sustainability. | Often cheaper short-term but higher infrastructure and maintenance costs. |
Which is better?
Nature inclusive design promotes sustainable urban development by integrating green spaces, supporting biodiversity, and improving residents' well-being, which enhances property values and reduces environmental impact. Suburban sprawl typically leads to increased infrastructure costs, habitat fragmentation, and higher greenhouse gas emissions, negatively affecting long-term real estate market stability. Prioritizing nature inclusive design aligns with eco-friendly growth trends, attracting environmentally conscious buyers and preserving community health.
Connection
Nature inclusive design mitigates the environmental impact of suburban sprawl by integrating green spaces, biodiversity corridors, and sustainable infrastructure within expanding residential areas. This approach enhances ecosystem services, improves air and water quality, and promotes healthier living environments amid sprawling developments. Implementing nature inclusive principles in suburban planning helps balance urban growth with the preservation of natural habitats.
Key Terms
Land Use Planning
Land use planning that emphasizes nature-inclusive design integrates green spaces and biodiversity within suburban developments, reducing environmental impact and enhancing ecosystem services. In contrast, suburban sprawl often leads to fragmented habitats, increased carbon emissions, and inefficient resource use due to unchecked expansion. Explore how strategic land use planning can balance growth with ecological preservation for sustainable communities.
Biodiversity Conservation
Suburban sprawl often leads to habitat fragmentation and loss of biodiversity due to widespread land development and impervious surfaces. Nature-inclusive design integrates green corridors, native vegetation, and wetland preservation, supporting ecosystems and species diversity within urban landscapes. Explore effective strategies and case studies on biodiversity conservation through nature-inclusive urban planning.
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations significantly influence suburban sprawl by often prioritizing low-density, single-use developments that expand urban footprints into natural habitats. Nature-inclusive design calls for adaptive zoning laws promoting mixed-use spaces, green corridors, and sustainable land use to preserve biodiversity and enhance ecosystem services. Explore how innovative zoning reforms can balance growth with ecological integrity to create resilient communities.
Source and External Links
The Definition of Suburban Sprawl - Suburban sprawl refers to the spread of urbanized areas into rural landscapes, characterized by low-density homes and new road networks.
Suburban Sprawl - Suburban sprawl is the rapid expansion of residential areas into previously undeveloped land, marked by low-density housing and reliance on automobiles.
Urban Sprawl - Urban sprawl is the rapid expansion of cities, often characterized by low-density residential housing and increased reliance on private automobiles for transportation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com