Co-living spaces offer flexible, fully furnished accommodations designed for short-term or transitional living, emphasizing community and shared amenities in urban settings. Cooperative housing involves a legally incorporated corporation where residents collectively own and manage the property, providing long-term stability and shared decision-making power. Explore how these housing models cater to different lifestyle needs and investment opportunities.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between co-living spaces and cooperative housing is crucial for making informed real estate decisions based on lifestyle preferences and financial commitments. Co-living spaces typically offer flexible, short-term leases with shared amenities designed for social interaction and affordability. Cooperative housing involves long-term ownership with collective decision-making responsibilities, providing residents with equity and control over the property. Knowing these distinctions helps investors and tenants align their housing choices with their economic goals and community involvement desires.
Comparison Table
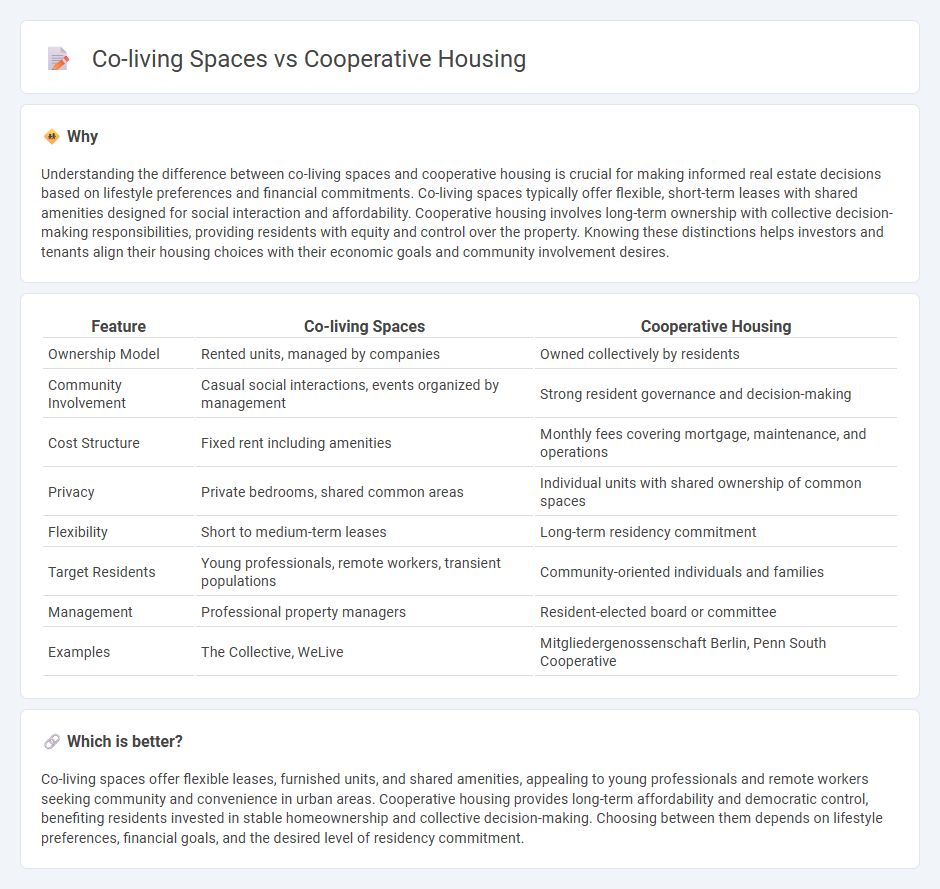
| Feature | Co-living Spaces | Cooperative Housing |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership Model | Rented units, managed by companies | Owned collectively by residents |
| Community Involvement | Casual social interactions, events organized by management | Strong resident governance and decision-making |
| Cost Structure | Fixed rent including amenities | Monthly fees covering mortgage, maintenance, and operations |
| Privacy | Private bedrooms, shared common areas | Individual units with shared ownership of common spaces |
| Flexibility | Short to medium-term leases | Long-term residency commitment |
| Target Residents | Young professionals, remote workers, transient populations | Community-oriented individuals and families |
| Management | Professional property managers | Resident-elected board or committee |
| Examples | The Collective, WeLive | Mitgliedergenossenschaft Berlin, Penn South Cooperative |
Which is better?
Co-living spaces offer flexible leases, furnished units, and shared amenities, appealing to young professionals and remote workers seeking community and convenience in urban areas. Cooperative housing provides long-term affordability and democratic control, benefiting residents invested in stable homeownership and collective decision-making. Choosing between them depends on lifestyle preferences, financial goals, and the desired level of residency commitment.
Connection
Co-living spaces and cooperative housing both emphasize shared living arrangements that foster community engagement and cost efficiency in real estate. These housing models prioritize communal resources and collective decision-making to create affordable and socially supportive environments. By leveraging shared ownership or rental structures, they address urban housing challenges through sustainable and inclusive real estate solutions.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Cooperative housing involves residents collectively owning and managing their property through a legal cooperative corporation, granting shareholders equal voting rights and decision-making power. Co-living spaces typically operate under a rental or lease agreement managed by a third-party company or landlord, without ownership stakes for residents. Explore the key differences in ownership models to determine which housing option aligns with your lifestyle and financial goals.
Governance
Cooperative housing operates under a democratic governance model where residents collectively make decisions through elected boards, ensuring shared responsibility and long-term stability. In contrast, co-living spaces typically feature management-led governance with predefined rules set by property owners or operators, emphasizing flexibility and convenience over resident control. Explore the nuances of governance structures to understand which living arrangement aligns with your community values and lifestyle preferences.
Lease Agreement
Cooperative housing agreements typically require members to purchase shares and sign a proprietary lease, granting exclusive rights to an apartment within the co-op building. Co-living leases are usually straightforward rental agreements with flexible terms, designed for short to medium-term stays and shared common areas. Explore the nuances of these lease agreements to determine which housing model suits your lifestyle and legal needs.
Source and External Links
Housing cooperative - Wikipedia - A housing cooperative is a legal entity owning residential real estate, where members buy shares granting the right to occupy units, pooling resources to lower costs and often participating in selecting residents and managing the community.
Housing Co-ops - Cooperatives for a Better World - Housing co-ops offer residents collective ownership and management of housing, providing more affordable, democratically controlled living alternatives to traditional rentals or condos.
What is a co-op and how do they work? | Rocket Mortgage - In a co-op, residents buy shares in a nonprofit corporation that owns the building rather than individual property, promoting shared responsibility and collaboration in housing management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com