Modular construction offers faster build times and consistent quality through factory-controlled processes compared to traditional site-built homes, which rely on on-site labor and weather conditions. This method often results in cost savings and reduced environmental impact due to minimized material waste. Explore the advantages and considerations of modular versus site-built homes to determine the best fit for your real estate needs.
Why it is important
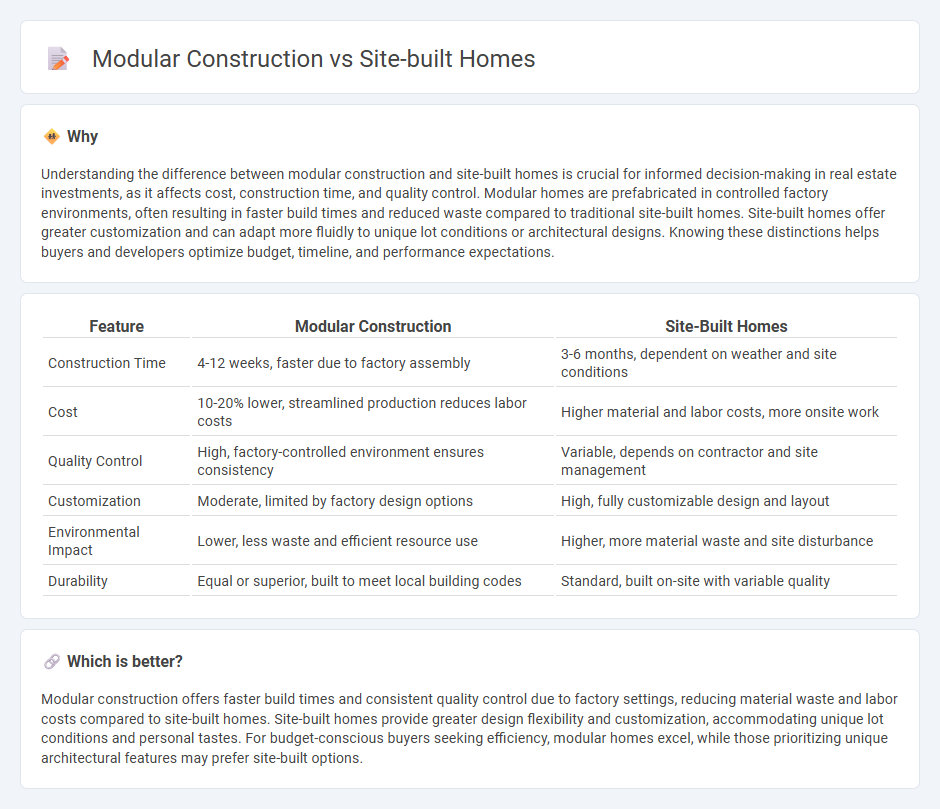
Understanding the difference between modular construction and site-built homes is crucial for informed decision-making in real estate investments, as it affects cost, construction time, and quality control. Modular homes are prefabricated in controlled factory environments, often resulting in faster build times and reduced waste compared to traditional site-built homes. Site-built homes offer greater customization and can adapt more fluidly to unique lot conditions or architectural designs. Knowing these distinctions helps buyers and developers optimize budget, timeline, and performance expectations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Modular Construction | Site-Built Homes |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Time | 4-12 weeks, faster due to factory assembly | 3-6 months, dependent on weather and site conditions |
| Cost | 10-20% lower, streamlined production reduces labor costs | Higher material and labor costs, more onsite work |
| Quality Control | High, factory-controlled environment ensures consistency | Variable, depends on contractor and site management |
| Customization | Moderate, limited by factory design options | High, fully customizable design and layout |
| Environmental Impact | Lower, less waste and efficient resource use | Higher, more material waste and site disturbance |
| Durability | Equal or superior, built to meet local building codes | Standard, built on-site with variable quality |
Which is better?
Modular construction offers faster build times and consistent quality control due to factory settings, reducing material waste and labor costs compared to site-built homes. Site-built homes provide greater design flexibility and customization, accommodating unique lot conditions and personal tastes. For budget-conscious buyers seeking efficiency, modular homes excel, while those prioritizing unique architectural features may prefer site-built options.
Connection
Modular construction and site-built homes are connected through their shared use of traditional building materials and design standards, ensuring structural integrity and compliance with local codes. Modular homes are prefabricated in controlled factory environments, allowing precise measurements and quality control before being transported to the site for assembly, whereas site-built homes are constructed entirely on location. Both methods contribute to the real estate market by offering varied options for homebuyers, balancing efficiency, cost, and customization.
Key Terms
On-site Construction
Site-built homes rely on traditional on-site construction, where every phase of building occurs directly at the property location, often resulting in longer project timelines and exposure to weather delays. Modular construction involves fabricating prefabricated sections in a factory setting with controlled conditions, which are then transported to the site for assembly, significantly reducing on-site labor and construction time. Explore further to understand the efficiency and cost implications of on-site construction in both methods.
Factory-built
Factory-built homes streamline construction with controlled environments, reducing weather-related delays and enhancing material efficiency. These modular units undergo rigorous quality inspections before transport, ensuring consistent standards and faster on-site assembly compared to traditional site-built homes. Explore how factory-built methods revolutionize housing affordability and sustainability.
Building Codes
Site-built homes must strictly comply with local building codes enforced by municipal inspectors throughout the construction process, ensuring adherence to structural, electrical, and safety standards. Modular construction requires factories to meet the International Residential Code (IRC) and state-specific regulations before modules are transported and assembled onsite, with final inspections confirming code compliance. Explore the detailed differences between these building approaches to understand their regulatory frameworks better.
Source and External Links
Site-built homes: What you need to know - This article provides an overview of site-built homes, including their construction process and design flexibility, highlighting how they differ from other types of homes.
Comparison of the Costs of Manufactured and Site-Built Housing - This report compares the costs of manufactured housing with site-built homes, highlighting the financial advantages of manufactured housing.
Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies - A research center that studies housing trends, including information on site-built homes and their economic implications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com