Walkability premium refers to the increased property value in neighborhoods where amenities and services are accessible on foot, reflecting consumer demand for convenience and reduced car dependence. Zoning regulations influence walkability by determining land use, density, and street design, which can either enhance or diminish a community's pedestrian friendliness. Explore how these factors interact to shape urban development and real estate investment opportunities.
Why it is important
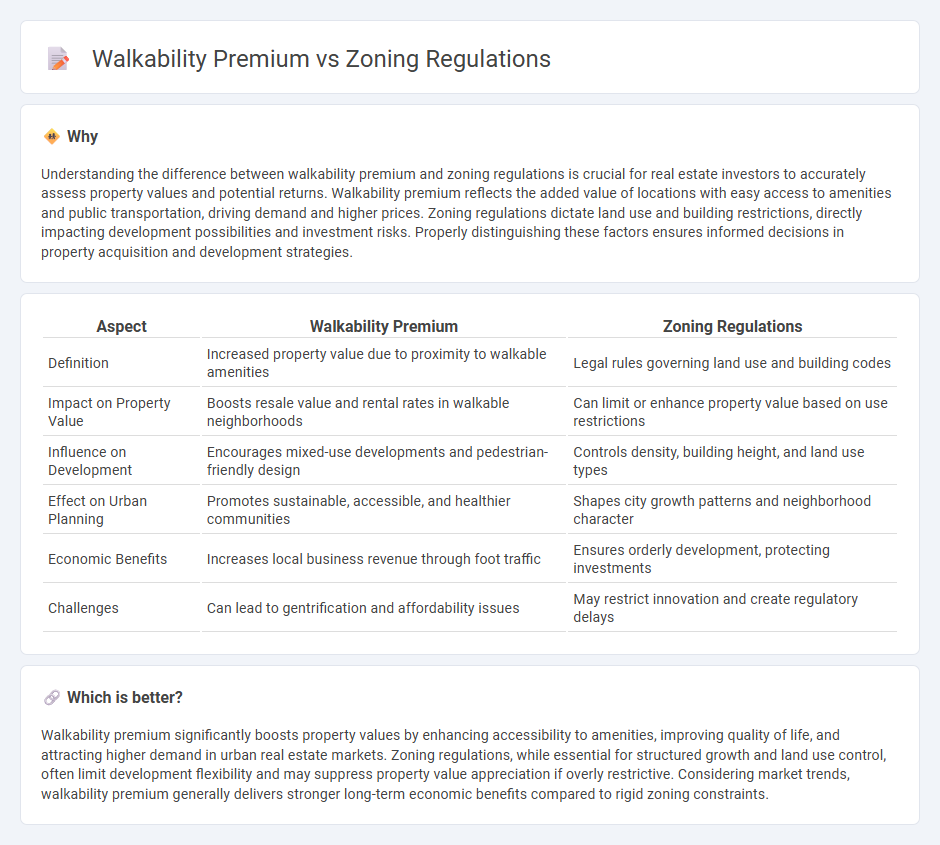
Understanding the difference between walkability premium and zoning regulations is crucial for real estate investors to accurately assess property values and potential returns. Walkability premium reflects the added value of locations with easy access to amenities and public transportation, driving demand and higher prices. Zoning regulations dictate land use and building restrictions, directly impacting development possibilities and investment risks. Properly distinguishing these factors ensures informed decisions in property acquisition and development strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Walkability Premium | Zoning Regulations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increased property value due to proximity to walkable amenities | Legal rules governing land use and building codes |
| Impact on Property Value | Boosts resale value and rental rates in walkable neighborhoods | Can limit or enhance property value based on use restrictions |
| Influence on Development | Encourages mixed-use developments and pedestrian-friendly design | Controls density, building height, and land use types |
| Effect on Urban Planning | Promotes sustainable, accessible, and healthier communities | Shapes city growth patterns and neighborhood character |
| Economic Benefits | Increases local business revenue through foot traffic | Ensures orderly development, protecting investments |
| Challenges | Can lead to gentrification and affordability issues | May restrict innovation and create regulatory delays |
Which is better?
Walkability premium significantly boosts property values by enhancing accessibility to amenities, improving quality of life, and attracting higher demand in urban real estate markets. Zoning regulations, while essential for structured growth and land use control, often limit development flexibility and may suppress property value appreciation if overly restrictive. Considering market trends, walkability premium generally delivers stronger long-term economic benefits compared to rigid zoning constraints.
Connection
Walkability premium significantly influences real estate values, as properties in highly walkable neighborhoods consistently command higher prices due to increased demand for convenience and accessibility. Zoning regulations shape this premium by determining land use, density, and mixed-use developments that enhance pedestrian-friendly environments. Adjusting zoning laws to promote walkability supports sustainable urban growth and maximizes property investment returns.
Key Terms
Land Use
Zoning regulations directly impact land use by dictating permissible building types, densities, and land functions, shaping urban form and pedestrian environments. Walkability premium refers to the added value properties gain due to proximity to walkable amenities and transit, often influenced by zoning that encourages mixed-use developments and reduced parking requirements. Explore how strategic zoning reforms can enhance land use efficiency and maximize walkability premiums in urban planning.
Mixed-Use Development
Zoning regulations significantly influence walkability premiums by determining land use distribution, density, and design standards in mixed-use developments, which integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces. Higher walkability premiums are often found in areas where mixed-use zoning promotes pedestrian-friendly infrastructure, reduced car dependence, and increased accessibility to daily amenities. Explore how optimizing zoning policies can enhance walkability and drive economic value in mixed-use communities.
Transit-Oriented Development
Zoning regulations directly influence the walkability premium by determining land use density, mixed-use developments, and pedestrian infrastructure essential for Transit-Oriented Development (TOD). TOD leverages high-density zoning near transit hubs to increase walkability, reduce car dependency, and enhance property values through increased accessibility. Explore how integrating zoning policies with transit planning can maximize walkability benefits and urban sustainability.
Source and External Links
What are zoning laws and how do they work? - Zoning laws regulate types of buildings allowed on properties, their expansion, residential, commercial, industrial, historic, and agricultural uses, and set standards like building height and setbacks to organize city development.
Residential Zoning Laws and Regulations Washington, DC - Washington, DC's residential zoning laws regulate building height, lot occupancy, parking, and setbacks to maintain neighborhood character and appropriate density in residential zones.
Zoning | Rockville, MD - Official Website - Rockville's zoning ordinance defines land use, density, building size and height, parking, and landscaping requirements to protect community welfare and shape city development.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com