Agrihoods integrate sustainable agriculture and community living, blending residential spaces with active farms to enhance local food production and environmental stewardship. Urban infill focuses on developing vacant or underutilized parcels within existing urban areas to increase density, improve infrastructure efficiency, and reduce urban sprawl. Explore the benefits and challenges of agrihoods compared to urban infill to determine which real estate model suits evolving lifestyle and sustainability goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between agrihoods and urban infill is crucial for real estate investors and buyers as it influences property value, lifestyle, and community dynamics. Agrihoods integrate agricultural elements with residential living, promoting sustainability and local food production, appealing to eco-conscious buyers. Urban infill focuses on developing vacant or underused urban land, enhancing city density and access to amenities, attracting those seeking convenience and vibrant neighborhoods. Differentiating these helps stakeholders make informed decisions aligned with their investment goals and lifestyle preferences.
Comparison Table
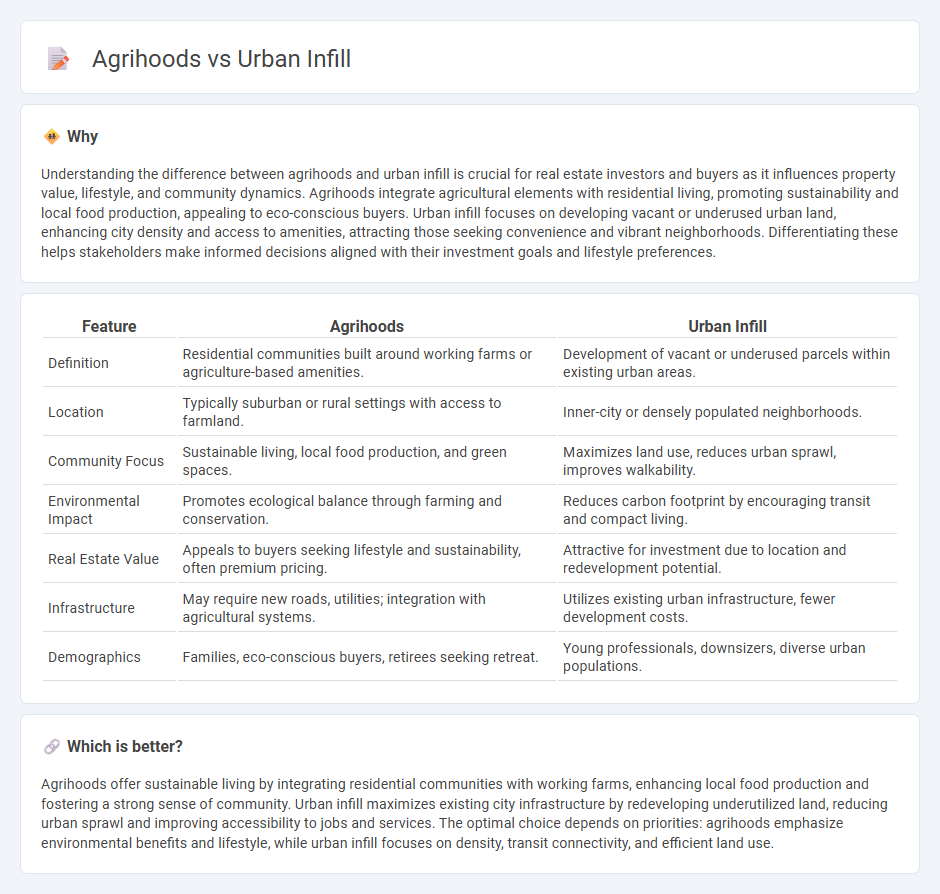
| Feature | Agrihoods | Urban Infill |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Residential communities built around working farms or agriculture-based amenities. | Development of vacant or underused parcels within existing urban areas. |
| Location | Typically suburban or rural settings with access to farmland. | Inner-city or densely populated neighborhoods. |
| Community Focus | Sustainable living, local food production, and green spaces. | Maximizes land use, reduces urban sprawl, improves walkability. |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes ecological balance through farming and conservation. | Reduces carbon footprint by encouraging transit and compact living. |
| Real Estate Value | Appeals to buyers seeking lifestyle and sustainability, often premium pricing. | Attractive for investment due to location and redevelopment potential. |
| Infrastructure | May require new roads, utilities; integration with agricultural systems. | Utilizes existing urban infrastructure, fewer development costs. |
| Demographics | Families, eco-conscious buyers, retirees seeking retreat. | Young professionals, downsizers, diverse urban populations. |
Which is better?
Agrihoods offer sustainable living by integrating residential communities with working farms, enhancing local food production and fostering a strong sense of community. Urban infill maximizes existing city infrastructure by redeveloping underutilized land, reducing urban sprawl and improving accessibility to jobs and services. The optimal choice depends on priorities: agrihoods emphasize environmental benefits and lifestyle, while urban infill focuses on density, transit connectivity, and efficient land use.
Connection
Agrihoods and urban infill both focus on sustainable real estate development by integrating green spaces and community farming within residential areas. Agrihoods enhance urban infill projects by providing local food production and recreational amenities that increase property values and community engagement. This synergy promotes environmentally friendly living and efficient land use in growing metropolitan regions.
Key Terms
Density
Urban infill developments maximize land use by increasing residential density within existing city limits, promoting walkability and reducing urban sprawl. Agrihoods integrate agricultural spaces into suburban communities, offering lower density with a focus on sustainable living and local food production. Explore how density influences lifestyle and environmental impact in both urban infill and agrihood models.
Land Use
Urban infill maximizes land use by redeveloping underutilized parcels within existing urban areas, promoting higher density and reducing urban sprawl. Agrihoods integrate agricultural land use into residential communities, prioritizing open green spaces and local food production over maximum land density. Explore the benefits and challenges of each approach to better understand their impact on sustainable land use planning.
Sustainability
Urban infill promotes sustainability by reducing urban sprawl, preserving natural habitats, and optimizing existing infrastructure in densely populated areas. Agrihoods integrate agriculture with residential neighborhoods, fostering local food production, enhancing biodiversity, and promoting eco-friendly living. Explore how these innovative community designs contribute to sustainable development and environmental resilience.
Source and External Links
Urban Infill - Urban infill involves developing vacant or underused land within existing urban areas to enhance density and community vitality.
Urban Infill - Urban infill provides opportunities for growth within existing infrastructure, promoting mixed-use development and reducing pressure on rural areas.
Infill - Infill is the rededication of land in urban environments for new construction, aiming to efficiently use existing infrastructure and counter urban sprawl.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com