Co-living spaces offer flexible, community-focused living arrangements with shared amenities, appealing to young professionals and urban dwellers seeking affordability and social engagement. Multi-family complexes provide larger-scale residential buildings with distinct units, catering to families or individuals preferring privacy and long-term tenancy options. Explore the key differences, benefits, and investment potential of both housing models to make informed real estate decisions.
Why it is important
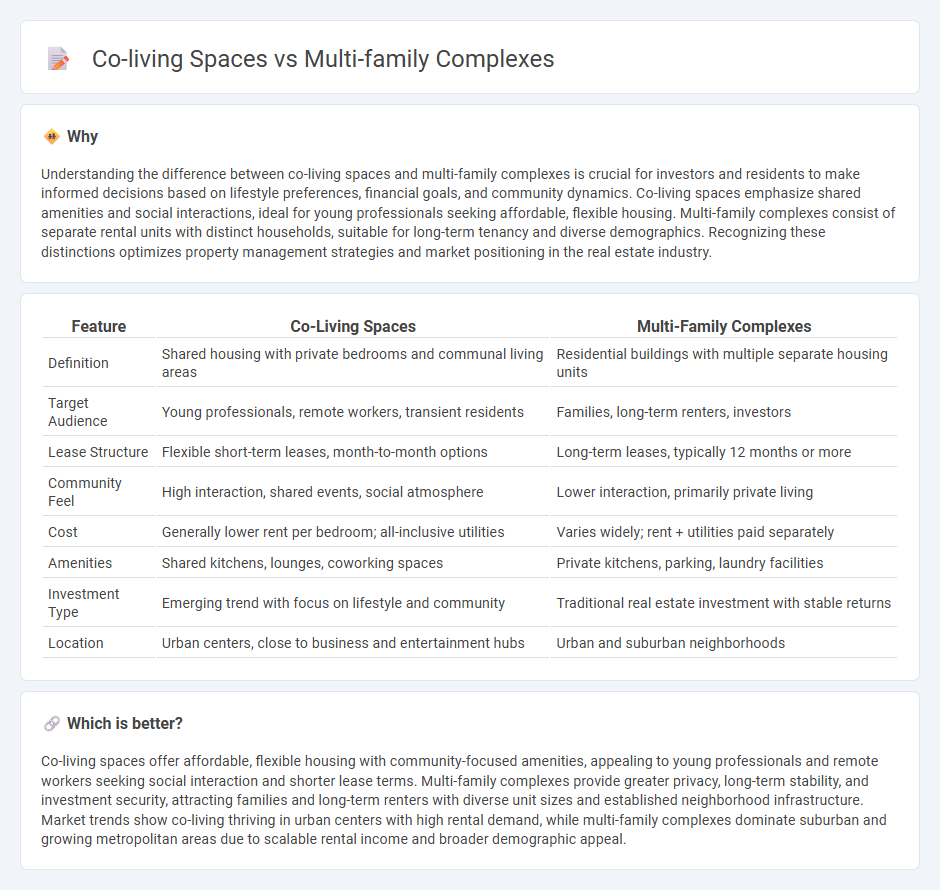
Understanding the difference between co-living spaces and multi-family complexes is crucial for investors and residents to make informed decisions based on lifestyle preferences, financial goals, and community dynamics. Co-living spaces emphasize shared amenities and social interactions, ideal for young professionals seeking affordable, flexible housing. Multi-family complexes consist of separate rental units with distinct households, suitable for long-term tenancy and diverse demographics. Recognizing these distinctions optimizes property management strategies and market positioning in the real estate industry.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Co-Living Spaces | Multi-Family Complexes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared housing with private bedrooms and communal living areas | Residential buildings with multiple separate housing units |
| Target Audience | Young professionals, remote workers, transient residents | Families, long-term renters, investors |
| Lease Structure | Flexible short-term leases, month-to-month options | Long-term leases, typically 12 months or more |
| Community Feel | High interaction, shared events, social atmosphere | Lower interaction, primarily private living |
| Cost | Generally lower rent per bedroom; all-inclusive utilities | Varies widely; rent + utilities paid separately |
| Amenities | Shared kitchens, lounges, coworking spaces | Private kitchens, parking, laundry facilities |
| Investment Type | Emerging trend with focus on lifestyle and community | Traditional real estate investment with stable returns |
| Location | Urban centers, close to business and entertainment hubs | Urban and suburban neighborhoods |
Which is better?
Co-living spaces offer affordable, flexible housing with community-focused amenities, appealing to young professionals and remote workers seeking social interaction and shorter lease terms. Multi-family complexes provide greater privacy, long-term stability, and investment security, attracting families and long-term renters with diverse unit sizes and established neighborhood infrastructure. Market trends show co-living thriving in urban centers with high rental demand, while multi-family complexes dominate suburban and growing metropolitan areas due to scalable rental income and broader demographic appeal.
Connection
Co-living spaces and multi-family complexes are connected through their shared focus on community-oriented housing models designed to optimize space utilization and affordability. Both real estate types cater to increasing urban populations seeking flexible lease terms and shared amenities, driving demand in metropolitan rental markets. Developers prioritize these models for their potential to deliver higher density living while fostering social interaction among residents.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Multi-family complexes are typically owned by institutional investors or real estate investment trusts (REITs), providing centralized management and long-term asset appreciation, while co-living spaces often operate under flexible ownership models including private operators and startup ventures emphasizing community-driven environments. Ownership structure in multi-family complexes often supports scalability and traditional rental income streams, whereas co-living spaces lean toward adaptable leases and shared economies fostering communal living. Explore how these distinct ownership frameworks impact investment returns and resident experiences in depth.
Lease Agreements
Multi-family complexes often feature standardized lease agreements that typically span 12 months, with strict clauses on maintenance responsibilities and pet policies to ensure uniformity across units. Co-living spaces use flexible, shorter-term leases with more communal living rules and shared responsibility agreements tailored to foster community interaction and adaptability. Explore more to understand how lease terms impact your living experience in these housing options.
Amenities Shared
Multi-family complexes often include amenities such as fitness centers, swimming pools, playgrounds, and on-site laundry facilities designed to serve a broad resident base. Co-living spaces prioritize shared amenities like communal kitchens, co-working areas, and social lounges that foster community interaction and collaboration. Explore the differences in shared amenities to determine which living option best suits your lifestyle and preferences.
Source and External Links
Multifamily residential - Multifamily residential, also known as multidwelling unit (MDU), refers to properties with multiple separate housing units for residents, often including apartments and condominiums.
What are the types of multifamily housing? - This article lists four main types of multifamily housing: duplexes, triplexes, garden-style apartments, and high-rise buildings, each offering unique features and challenges.
Multifamily Homes: Types and Trends - Multifamily homes include a variety of structures like apartment buildings, condominiums, townhouses, and mixed-use developments, which are increasingly popular for convenience and amenities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com