Adaptive reuse projects transform obsolete buildings into functional spaces, preserving architectural heritage while reducing material waste. Urban infill focuses on developing vacant or underutilized land within existing urban areas to increase density and optimize infrastructure. Explore the benefits and challenges of these real estate strategies to enhance sustainable urban growth.
Why it is important
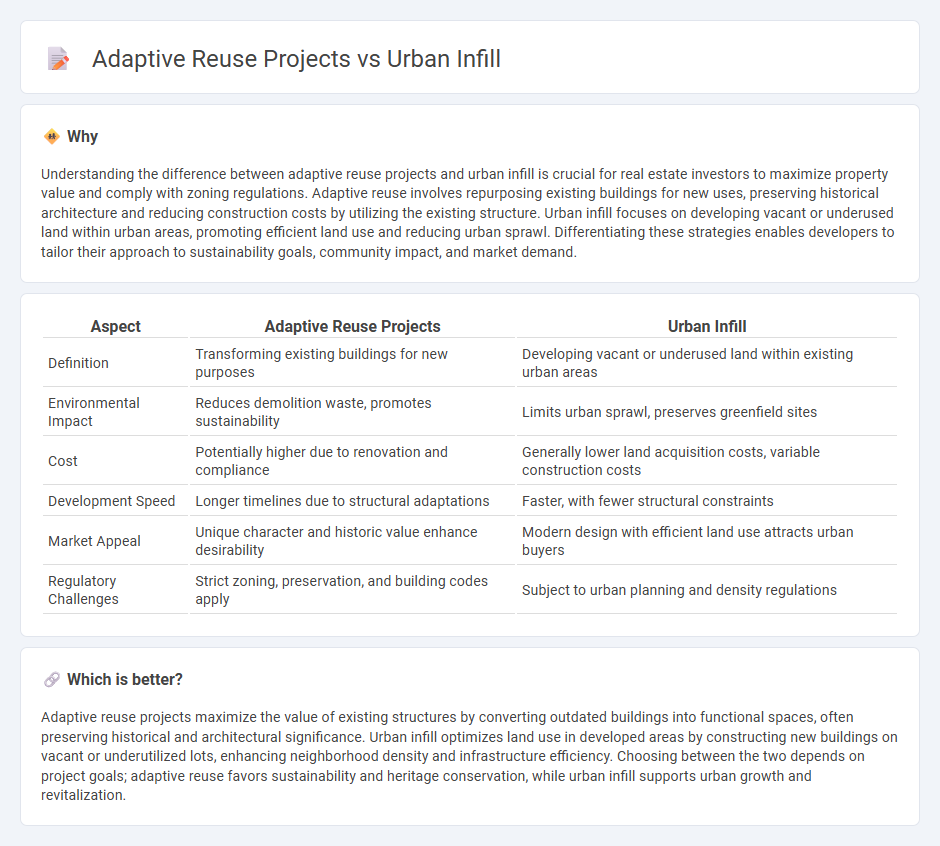
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse projects and urban infill is crucial for real estate investors to maximize property value and comply with zoning regulations. Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing buildings for new uses, preserving historical architecture and reducing construction costs by utilizing the existing structure. Urban infill focuses on developing vacant or underused land within urban areas, promoting efficient land use and reducing urban sprawl. Differentiating these strategies enables developers to tailor their approach to sustainability goals, community impact, and market demand.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Adaptive Reuse Projects | Urban Infill |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transforming existing buildings for new purposes | Developing vacant or underused land within existing urban areas |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces demolition waste, promotes sustainability | Limits urban sprawl, preserves greenfield sites |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to renovation and compliance | Generally lower land acquisition costs, variable construction costs |
| Development Speed | Longer timelines due to structural adaptations | Faster, with fewer structural constraints |
| Market Appeal | Unique character and historic value enhance desirability | Modern design with efficient land use attracts urban buyers |
| Regulatory Challenges | Strict zoning, preservation, and building codes apply | Subject to urban planning and density regulations |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse projects maximize the value of existing structures by converting outdated buildings into functional spaces, often preserving historical and architectural significance. Urban infill optimizes land use in developed areas by constructing new buildings on vacant or underutilized lots, enhancing neighborhood density and infrastructure efficiency. Choosing between the two depends on project goals; adaptive reuse favors sustainability and heritage conservation, while urban infill supports urban growth and revitalization.
Connection
Adaptive reuse projects and urban infill are connected through their shared goal of maximizing land use efficiency by repurposing underutilized buildings within existing urban areas. Both strategies support sustainable development by reducing urban sprawl, preserving cultural heritage, and revitalizing neighborhoods with increased density and improved infrastructure. Data from real estate markets shows that properties involved in adaptive reuse and urban infill often experience higher value appreciation due to their prime locations and enhanced community appeal.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations significantly influence urban infill and adaptive reuse projects by dictating land use, building height, density, and parking requirements within city limits. Urban infill often faces challenges like strict zoning codes and floor area ratio limits that restrict new construction density, while adaptive reuse benefits from more flexible zoning allowances aimed at preserving historic structures. Explore how zoning policies impact your next project's feasibility and design options.
Building Codes
Urban infill projects often require compliance with current building codes that address new construction standards, energy efficiency, and zoning regulations, ensuring seamless integration within existing urban fabrics. Adaptive reuse projects must navigate building codes designed for existing structures, including challenges related to structural upgrades, fire safety, and accessibility modifications to meet contemporary requirements. Explore the nuances and compliance strategies of urban infill and adaptive reuse in building codes to optimize project outcomes.
Site Selection
Site selection in urban infill projects prioritizes underutilized or vacant parcels within existing urban fabrics to maximize land efficiency and infrastructure use. Adaptive reuse site selection centers on existing structures with historical, architectural, or cultural significance, aiming to preserve embodied energy and community identity. Explore the critical factors that influence choosing the ideal site for these sustainable urban development strategies.
Source and External Links
What is Urban Infill? | Definition, Key Components & Examples - This webpage provides a comprehensive overview of urban infill, including its definition, key components, and examples of how it enhances urban vitality.
Urban Infill - 2030 Palette - This site discusses urban infill as an opportunity to grow within existing infrastructure, enhancing walkable areas and reducing pressure on rural spaces.
Infill - Wikipedia - This Wikipedia page defines infill as the rededication of urban land to new construction, highlighting its role in reusing underutilized spaces and combating urban sprawl.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com