Vertical gardens maximize limited urban space by growing plants upward on walls, enhancing air quality and aesthetic appeal in city environments. Urban farming involves cultivating food crops within city limits using techniques like rooftop gardens and community plots, promoting local food production and sustainability. Discover more about how these innovative green solutions transform urban living and contribute to environmental well-being.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between vertical gardens and urban farming is crucial for optimizing space use and crop selection in real estate development. Vertical gardens primarily enhance aesthetic appeal and air quality with ornamental plants, while urban farming focuses on producing edible crops for sustainable food sources. This distinction directly impacts property value, maintenance costs, and community engagement strategies. Accurate knowledge helps investors and developers make informed decisions about integrating green infrastructure to maximize environmental and economic benefits.
Comparison Table
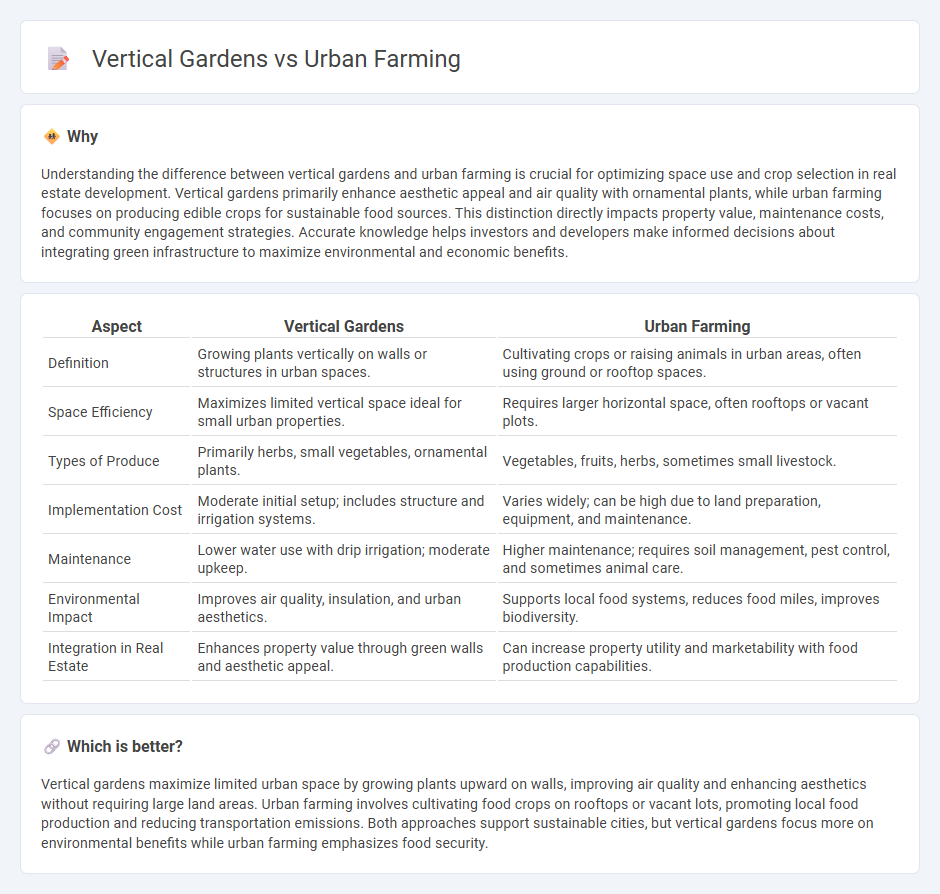
| Aspect | Vertical Gardens | Urban Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growing plants vertically on walls or structures in urban spaces. | Cultivating crops or raising animals in urban areas, often using ground or rooftop spaces. |
| Space Efficiency | Maximizes limited vertical space ideal for small urban properties. | Requires larger horizontal space, often rooftops or vacant plots. |
| Types of Produce | Primarily herbs, small vegetables, ornamental plants. | Vegetables, fruits, herbs, sometimes small livestock. |
| Implementation Cost | Moderate initial setup; includes structure and irrigation systems. | Varies widely; can be high due to land preparation, equipment, and maintenance. |
| Maintenance | Lower water use with drip irrigation; moderate upkeep. | Higher maintenance; requires soil management, pest control, and sometimes animal care. |
| Environmental Impact | Improves air quality, insulation, and urban aesthetics. | Supports local food systems, reduces food miles, improves biodiversity. |
| Integration in Real Estate | Enhances property value through green walls and aesthetic appeal. | Can increase property utility and marketability with food production capabilities. |
Which is better?
Vertical gardens maximize limited urban space by growing plants upward on walls, improving air quality and enhancing aesthetics without requiring large land areas. Urban farming involves cultivating food crops on rooftops or vacant lots, promoting local food production and reducing transportation emissions. Both approaches support sustainable cities, but vertical gardens focus more on environmental benefits while urban farming emphasizes food security.
Connection
Vertical gardens and urban farming are interconnected approaches transforming urban real estate by maximizing limited space through vertical planting techniques. These green installations enhance property value, improve air quality, and support sustainable living within dense city environments. Integrating vertical gardens into urban farming promotes food production and biodiversity, making cities more resilient and eco-friendly.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Urban farming often faces stricter zoning regulations due to land use classifications and restrictions on agricultural activities within city limits, whereas vertical gardens typically encounter fewer regulatory hurdles as they are classified under landscaping or aesthetic enhancements. Zoning laws may limit the scale and type of crops grown in urban farms but generally permit vertical gardens on building facades or rooftops without special permits. Explore local zoning codes further to understand compliance requirements for both urban farming and vertical garden projects.
Land Use Efficiency
Urban farming maximizes land use by transforming rooftops, vacant lots, and small plots into productive agricultural spaces, often integrating crops with community needs. Vertical gardens optimize limited ground space by stacking plants upwards, enhancing crop density and yield per square foot, especially in densely populated areas. Explore more about how these innovative approaches revolutionize land use efficiency in city environments.
Building Integration
Urban farming integrates agriculture into city landscapes, utilizing rooftops, balconies, and vacant lots for growing food directly within urban environments. Vertical gardens enhance building integration by transforming walls and facades into green spaces, improving air quality and energy efficiency while maximizing limited space. Discover how combining both methods revolutionizes sustainable urban living and boosts local food production.
Source and External Links
Urban agriculture - Urban agriculture involves cultivating and processing food in city areas, supported by community-based projects like shared gardens, rooftop farms, and centralized resources for food production.
What Is Urban Farming? Understanding Urban Agriculture - Urban farming is the practice of growing crops or livestock within cities, offering benefits such as local food production, efficient use of space with methods like vertical farming, and enhancing community ties.
Urban Agriculture - Urban agriculture includes various farm types in metropolitan areas, such as community gardens, institutional farms, and small commercial operations, often focusing on education and local food access.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com