Energy-positive buildings generate more energy than they consume, significantly reducing carbon footprints compared to conventional buildings that rely heavily on fossil fuels. These sustainable structures integrate advanced technologies such as solar panels, energy-efficient insulation, and smart energy management systems to optimize performance. Discover how energy-positive buildings can transform urban landscapes and create a greener future.
Why it is important
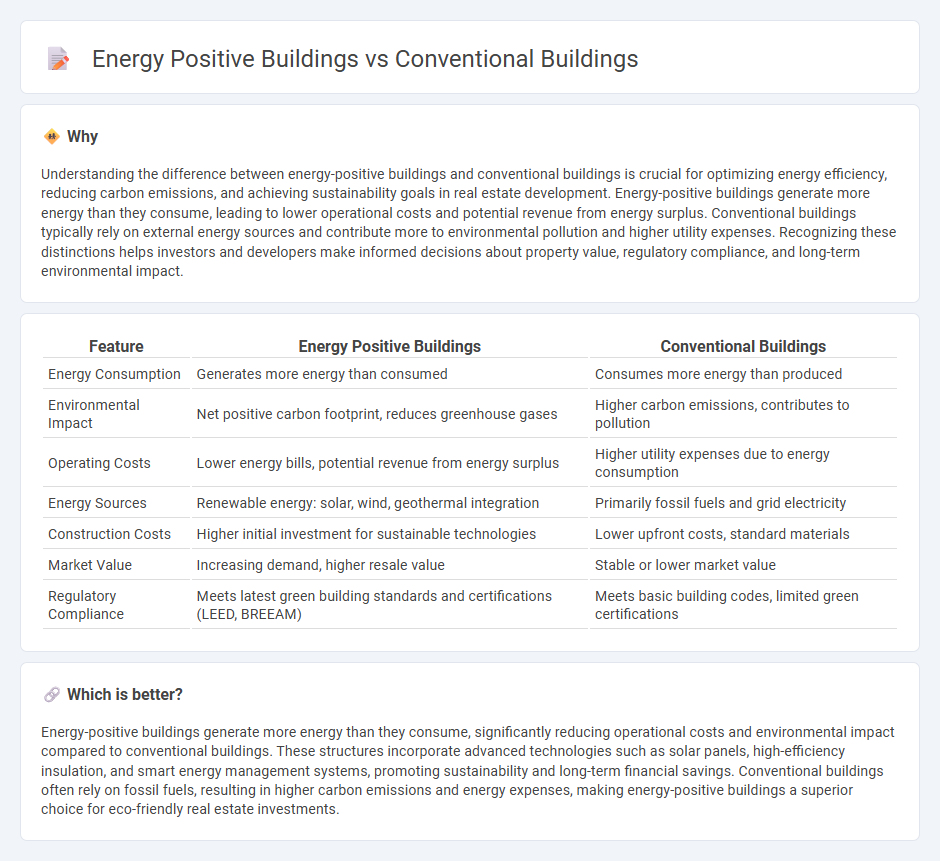
Understanding the difference between energy-positive buildings and conventional buildings is crucial for optimizing energy efficiency, reducing carbon emissions, and achieving sustainability goals in real estate development. Energy-positive buildings generate more energy than they consume, leading to lower operational costs and potential revenue from energy surplus. Conventional buildings typically rely on external energy sources and contribute more to environmental pollution and higher utility expenses. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors and developers make informed decisions about property value, regulatory compliance, and long-term environmental impact.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Energy Positive Buildings | Conventional Buildings |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | Generates more energy than consumed | Consumes more energy than produced |
| Environmental Impact | Net positive carbon footprint, reduces greenhouse gases | Higher carbon emissions, contributes to pollution |
| Operating Costs | Lower energy bills, potential revenue from energy surplus | Higher utility expenses due to energy consumption |
| Energy Sources | Renewable energy: solar, wind, geothermal integration | Primarily fossil fuels and grid electricity |
| Construction Costs | Higher initial investment for sustainable technologies | Lower upfront costs, standard materials |
| Market Value | Increasing demand, higher resale value | Stable or lower market value |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets latest green building standards and certifications (LEED, BREEAM) | Meets basic building codes, limited green certifications |
Which is better?
Energy-positive buildings generate more energy than they consume, significantly reducing operational costs and environmental impact compared to conventional buildings. These structures incorporate advanced technologies such as solar panels, high-efficiency insulation, and smart energy management systems, promoting sustainability and long-term financial savings. Conventional buildings often rely on fossil fuels, resulting in higher carbon emissions and energy expenses, making energy-positive buildings a superior choice for eco-friendly real estate investments.
Connection
Energy positive buildings integrate advanced sustainable technologies that significantly reduce energy consumption compared to conventional buildings, often generating surplus energy through renewable sources like solar panels. This connection highlights the shift in real estate development towards environmentally responsible construction that enhances property value and lowers operational costs. The relationship between these building types underscores the growing demand for energy efficiency and sustainability in modern real estate markets.
Key Terms
Energy Efficiency
Conventional buildings often rely on fossil fuels and inefficient systems, leading to higher energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Energy positive buildings incorporate renewable energy technologies and advanced insulation to generate more energy than they consume, significantly improving energy efficiency. Explore how energy positive buildings transform sustainable architecture and reduce environmental impact.
Net Energy Production
Conventional buildings typically consume more energy than they produce, relying heavily on external sources for heating, cooling, and electricity. Energy positive buildings integrate renewable energy systems such as solar panels and efficient insulation to generate surplus energy, contributing net positive energy to the grid. Explore how these innovations transform energy consumption patterns and promote sustainability in the built environment.
Building Codes/Standards
Conventional buildings adhere to traditional building codes that typically focus on minimum energy efficiency requirements, often resulting in higher energy consumption and carbon emissions. Energy-positive buildings exceed these standards by incorporating advanced technologies and materials that generate more energy than they consume, aligning with progressive codes like LEED Zero or Passive House standards. Explore innovative building codes and standards that drive the transition from conventional to energy-positive construction for sustainable development.
Source and External Links
Pre-Engineered or Conventional Buildings - Tata Blue Scope Steel - Conventional buildings are traditional structures made from steel, brick, and cement, fabricated and assembled on-site through welding and cutting, requiring detailed design and consultant input for construction.
What are the Differences Between Post Frame Buildings and Conventional Framed Buildings? - Conventional framed buildings use a continuous foundation requiring more excavation and concrete, making them costlier and longer to build compared to alternative post frame methods, and they rely on smaller dimensional lumber for structural framing.
Conventional Building Construction - New Belle Construction - Conventional construction uses traditional materials like wood framing and follows a standard construction process to build durable commercial and industrial buildings uniquely designed from the ground up with a focus on integrity and long-term partnerships.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com