Modular construction involves prefabricating entire building sections in a factory setting before transporting them to the site for assembly, offering speed and quality control. Panelized construction uses factory-built wall panels that are shipped and assembled on-site, allowing for design flexibility and efficient labor use. Explore the advantages and applications of both methods to determine the best fit for your real estate project.
Why it is important
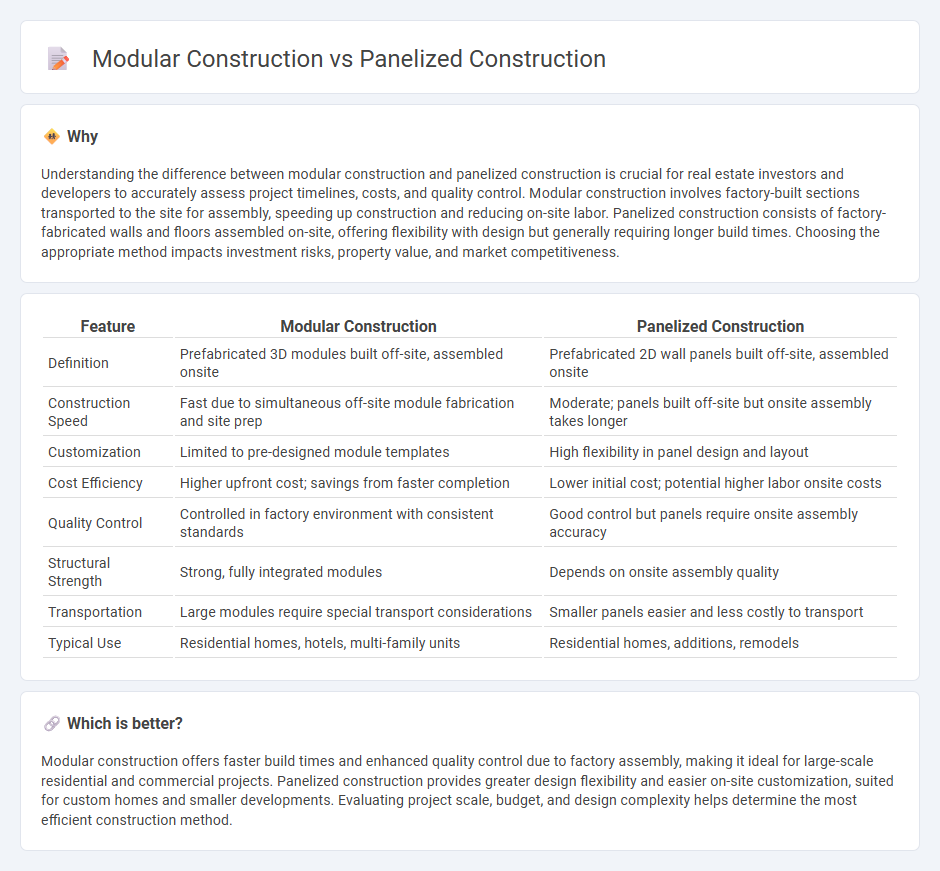
Understanding the difference between modular construction and panelized construction is crucial for real estate investors and developers to accurately assess project timelines, costs, and quality control. Modular construction involves factory-built sections transported to the site for assembly, speeding up construction and reducing on-site labor. Panelized construction consists of factory-fabricated walls and floors assembled on-site, offering flexibility with design but generally requiring longer build times. Choosing the appropriate method impacts investment risks, property value, and market competitiveness.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Modular Construction | Panelized Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prefabricated 3D modules built off-site, assembled onsite | Prefabricated 2D wall panels built off-site, assembled onsite |
| Construction Speed | Fast due to simultaneous off-site module fabrication and site prep | Moderate; panels built off-site but onsite assembly takes longer |
| Customization | Limited to pre-designed module templates | High flexibility in panel design and layout |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher upfront cost; savings from faster completion | Lower initial cost; potential higher labor onsite costs |
| Quality Control | Controlled in factory environment with consistent standards | Good control but panels require onsite assembly accuracy |
| Structural Strength | Strong, fully integrated modules | Depends on onsite assembly quality |
| Transportation | Large modules require special transport considerations | Smaller panels easier and less costly to transport |
| Typical Use | Residential homes, hotels, multi-family units | Residential homes, additions, remodels |
Which is better?
Modular construction offers faster build times and enhanced quality control due to factory assembly, making it ideal for large-scale residential and commercial projects. Panelized construction provides greater design flexibility and easier on-site customization, suited for custom homes and smaller developments. Evaluating project scale, budget, and design complexity helps determine the most efficient construction method.
Connection
Modular construction and panelized construction both streamline real estate development by prefabricating building components off-site, significantly reducing construction time and costs. Modular construction assembles entire room-sized units in factories, while panelized construction involves manufacturing flat panels like walls and floors for on-site assembly. Both methods enhance project efficiency, improve quality control, and increase sustainability in residential and commercial real estate projects.
Key Terms
Prefabrication
Panelized construction involves assembling flat wall panels in a factory setting, which are then transported to the site for installation, streamlining the building process and ensuring quality control. Modular construction consists of fully finished, three-dimensional modules built off-site, enabling faster assembly and reduced on-site labor compared to traditional methods. Explore detailed comparisons between panelized and modular construction methods to optimize your prefabrication strategy.
On-site Assembly
Panelized construction involves delivering pre-fabricated wall panels to the site for on-site assembly, which accelerates the building process and provides flexibility in design. Modular construction consists of fully constructed sections or modules built in a factory and then transported to the site for quick assembly, significantly reducing build time and minimizing on-site labor. Explore further to understand the key differences and advantages of each method for your construction project.
Structural Systems
Panelized construction involves assembling pre-fabricated wall, floor, and roof panels on-site, offering flexibility and reduced construction time with structural elements like wood or steel frames. Modular construction uses fully built and finished 3D units manufactured in factories, enabling precise quality control and faster project completion through integrated structural systems. Explore detailed comparisons and benefits to determine the best structural approach for your construction project.
Source and External Links
Panelization: What It Is and Why Use It - Panelized construction involves fabricating structural elements like walls, floors, and roofs off-site in controlled environments, leading to increased building efficiency, greater accuracy, and reduced waste by assembling two-dimensional panels that are later erected on-site.
Overview of Panelized Construction - Panelized construction means factory-built walls, floors, and roofs transported to the site and lifted into place, usually forming a watertight and airtight building envelope often including structural framing, insulation, and water, vapor, and air control layers.
Panelized Homes: Your Questions Answered - Panelized homes use pre-engineered wall and roof sections made in factory-controlled settings, resulting in higher quality homes with better airtightness and lumber quality compared to traditional stick framing, and can be more cost-effective overall.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com