Energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume, often through solar panels and advanced energy storage systems, reducing reliance on external power grids and lowering carbon footprints. Energy neutral buildings balance their energy consumption with on-site renewable energy production, achieving net-zero energy use and minimizing environmental impact without surplus generation. Explore the key differences and benefits of these sustainable building approaches to enhance your real estate projects.
Why it is important
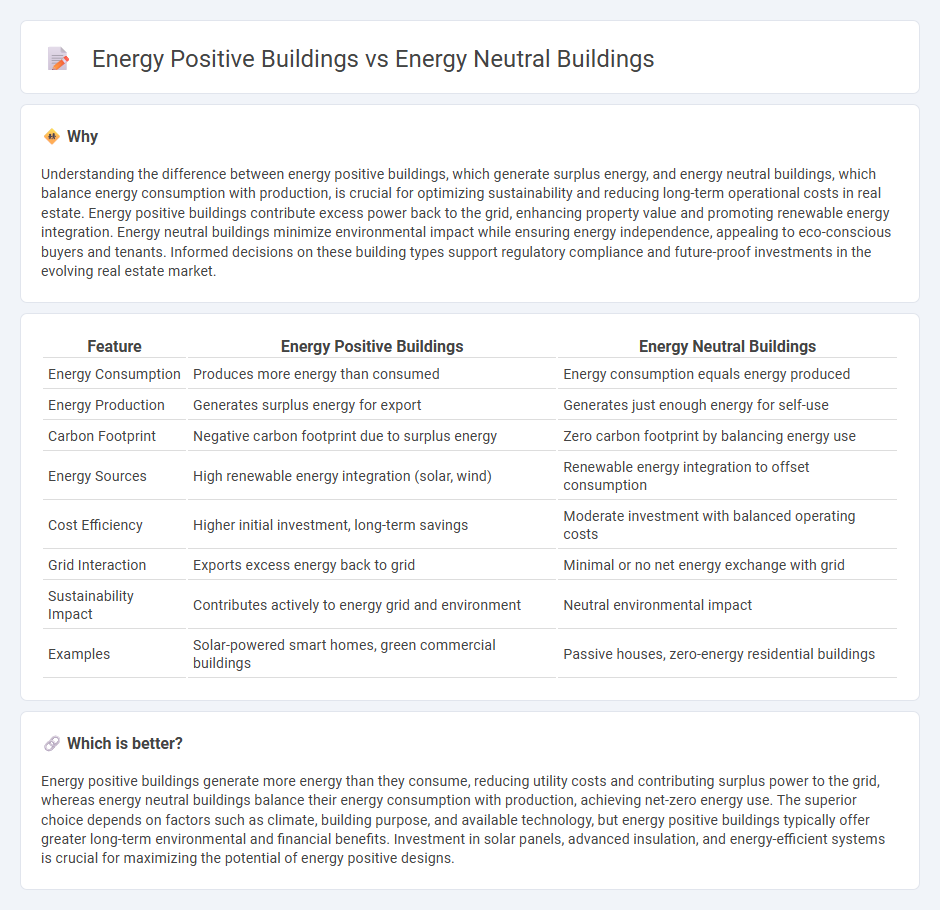
Understanding the difference between energy positive buildings, which generate surplus energy, and energy neutral buildings, which balance energy consumption with production, is crucial for optimizing sustainability and reducing long-term operational costs in real estate. Energy positive buildings contribute excess power back to the grid, enhancing property value and promoting renewable energy integration. Energy neutral buildings minimize environmental impact while ensuring energy independence, appealing to eco-conscious buyers and tenants. Informed decisions on these building types support regulatory compliance and future-proof investments in the evolving real estate market.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Energy Positive Buildings | Energy Neutral Buildings |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | Produces more energy than consumed | Energy consumption equals energy produced |
| Energy Production | Generates surplus energy for export | Generates just enough energy for self-use |
| Carbon Footprint | Negative carbon footprint due to surplus energy | Zero carbon footprint by balancing energy use |
| Energy Sources | High renewable energy integration (solar, wind) | Renewable energy integration to offset consumption |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial investment, long-term savings | Moderate investment with balanced operating costs |
| Grid Interaction | Exports excess energy back to grid | Minimal or no net energy exchange with grid |
| Sustainability Impact | Contributes actively to energy grid and environment | Neutral environmental impact |
| Examples | Solar-powered smart homes, green commercial buildings | Passive houses, zero-energy residential buildings |
Which is better?
Energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume, reducing utility costs and contributing surplus power to the grid, whereas energy neutral buildings balance their energy consumption with production, achieving net-zero energy use. The superior choice depends on factors such as climate, building purpose, and available technology, but energy positive buildings typically offer greater long-term environmental and financial benefits. Investment in solar panels, advanced insulation, and energy-efficient systems is crucial for maximizing the potential of energy positive designs.
Connection
Energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume, while energy neutral buildings balance their energy consumption with on-site production. Both utilize renewable energy technologies, advanced insulation, and efficient systems to minimize environmental impact in real estate development. Integrating these innovations accelerates sustainable building practices, reducing carbon footprints and operational costs in modern properties.
Key Terms
Net Zero Energy
Energy neutral buildings, also known as Net Zero Energy buildings, produce as much energy as they consume annually, achieving a balance through efficient design and renewable energy integration. Energy positive buildings generate surplus energy beyond their consumption, contributing excess power back to the grid or storage systems, enhancing sustainability efforts. Explore the distinctions and benefits of Net Zero Energy concepts to advance eco-friendly construction practices.
Energy Surplus
Energy neutral buildings achieve a balance between the energy they consume and the energy they generate on-site, resulting in zero net energy use. Energy positive buildings go beyond this balance by producing an energy surplus, exporting excess energy back to the grid or storing it for future use. Explore more about how energy surplus impacts sustainability and energy efficiency in modern building designs.
On-site Renewable Generation
Energy neutral buildings achieve a balance between energy consumption and production, relying heavily on on-site renewable generation such as solar panels and wind turbines to offset their energy use. Energy positive buildings generate surplus energy beyond their operational needs, often feeding excess power back into the grid through advanced renewable systems and energy storage solutions. Explore the innovations in on-site renewable technologies to understand how these building types contribute to sustainable urban development.
Source and External Links
Zero-energy building - A zero-energy building achieves net zero energy consumption by balancing energy use with onsite renewable generation, often using grid interconnections for storage.
Nearly-zero energy and zero-emission buildings - According to updated EU regulations, new buildings must be zero-emission by 2028-2030, meaning no onsite fossil fuel emissions and very high energy performance, with any remaining energy demand met by renewables.
Carbon Neutral Buildings - Carbon neutral buildings eliminate greenhouse gas emissions from their operation by maximizing energy efficiency, using all-electric systems, and sourcing zero-emission electricity from onsite or community renewables.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com