Energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume through renewable sources like solar panels and geothermal systems, significantly reducing carbon footprints. Net zero energy buildings balance energy consumption with on-site renewable energy production, aiming for zero net energy use annually. Explore how these sustainable building approaches revolutionize real estate and promote environmental responsibility.
Why it is important
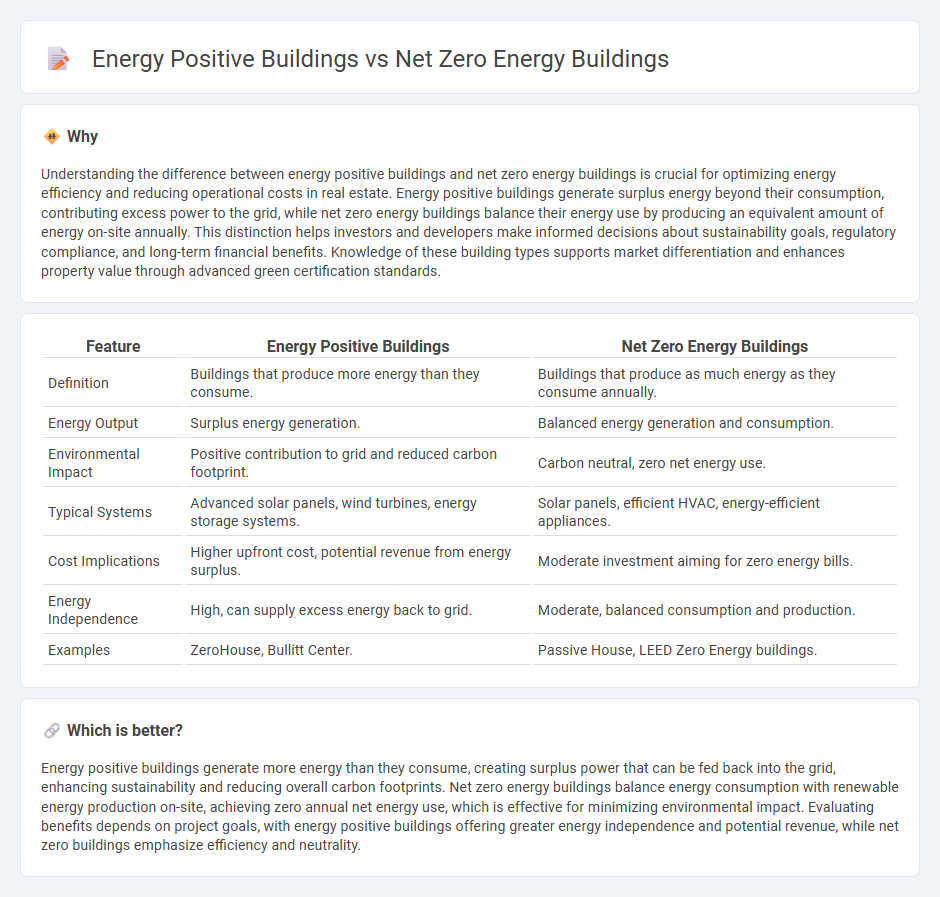
Understanding the difference between energy positive buildings and net zero energy buildings is crucial for optimizing energy efficiency and reducing operational costs in real estate. Energy positive buildings generate surplus energy beyond their consumption, contributing excess power to the grid, while net zero energy buildings balance their energy use by producing an equivalent amount of energy on-site annually. This distinction helps investors and developers make informed decisions about sustainability goals, regulatory compliance, and long-term financial benefits. Knowledge of these building types supports market differentiation and enhances property value through advanced green certification standards.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Energy Positive Buildings | Net Zero Energy Buildings |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buildings that produce more energy than they consume. | Buildings that produce as much energy as they consume annually. |
| Energy Output | Surplus energy generation. | Balanced energy generation and consumption. |
| Environmental Impact | Positive contribution to grid and reduced carbon footprint. | Carbon neutral, zero net energy use. |
| Typical Systems | Advanced solar panels, wind turbines, energy storage systems. | Solar panels, efficient HVAC, energy-efficient appliances. |
| Cost Implications | Higher upfront cost, potential revenue from energy surplus. | Moderate investment aiming for zero energy bills. |
| Energy Independence | High, can supply excess energy back to grid. | Moderate, balanced consumption and production. |
| Examples | ZeroHouse, Bullitt Center. | Passive House, LEED Zero Energy buildings. |
Which is better?
Energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume, creating surplus power that can be fed back into the grid, enhancing sustainability and reducing overall carbon footprints. Net zero energy buildings balance energy consumption with renewable energy production on-site, achieving zero annual net energy use, which is effective for minimizing environmental impact. Evaluating benefits depends on project goals, with energy positive buildings offering greater energy independence and potential revenue, while net zero buildings emphasize efficiency and neutrality.
Connection
Energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume by integrating renewable energy systems such as solar panels and advanced insulation technologies, while net zero energy buildings balance their energy consumption with on-site renewable energy production. Both building types emphasize sustainable design, energy efficiency, and reduced carbon footprints to combat climate change within the real estate sector. The connection lies in their shared goal of minimizing reliance on external energy sources and promoting environmental responsibility in property development.
Key Terms
Energy Consumption
Net zero energy buildings achieve balance by generating as much energy as they consume annually, relying heavily on energy-efficient design and renewable sources like solar panels. Energy positive buildings surpass this balance, producing surplus energy that can be fed back into the grid, contributing to overall energy sustainability. Explore further to understand how these innovations shape the future of sustainable architecture.
On-site Energy Generation
Net zero energy buildings (NZEBs) generate as much energy on-site through solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems as they consume annually, achieving a balance between production and consumption. Energy positive buildings exceed their energy needs with on-site renewable generation, often feeding surplus power back to the grid, contributing to overall energy sustainability. Discover detailed comparisons and technologies driving these innovative building standards to enhance energy efficiency and environmental impact.
Grid Interaction
Net zero energy buildings (NZEBs) achieve a balance between the energy they consume and produce annually, typically interacting with the grid to offset energy deficits through renewable sources like solar panels. Energy positive buildings not only meet their own energy needs but generate surplus electricity, often exporting excess power to the grid, enhancing grid resilience and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Explore how advancements in smart grid technology and energy storage are transforming the interaction between these innovative building types and the power grid.
Source and External Links
Zero-Energy Building - A zero-energy building (ZEB) is a building with net zero energy consumption, achieved by using high-efficiency equipment and renewable energy sources.
Zero Net Energy - This page outlines California's goals for zero net energy buildings, including requirements for new residential and commercial constructions.
Zero Energy Buildings Basics - Zero energy buildings produce at least as much energy as they consume annually by incorporating state-of-the-art energy efficiency and renewable energy technologies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com