Nature inclusive design integrates natural elements and ecosystems into built environments, enhancing sustainability and biodiversity in real estate developments. Modular construction employs prefabricated sections assembled on-site, accelerating project timelines and reducing waste while maintaining quality. Discover how these innovative approaches transform modern real estate projects.
Why it is important
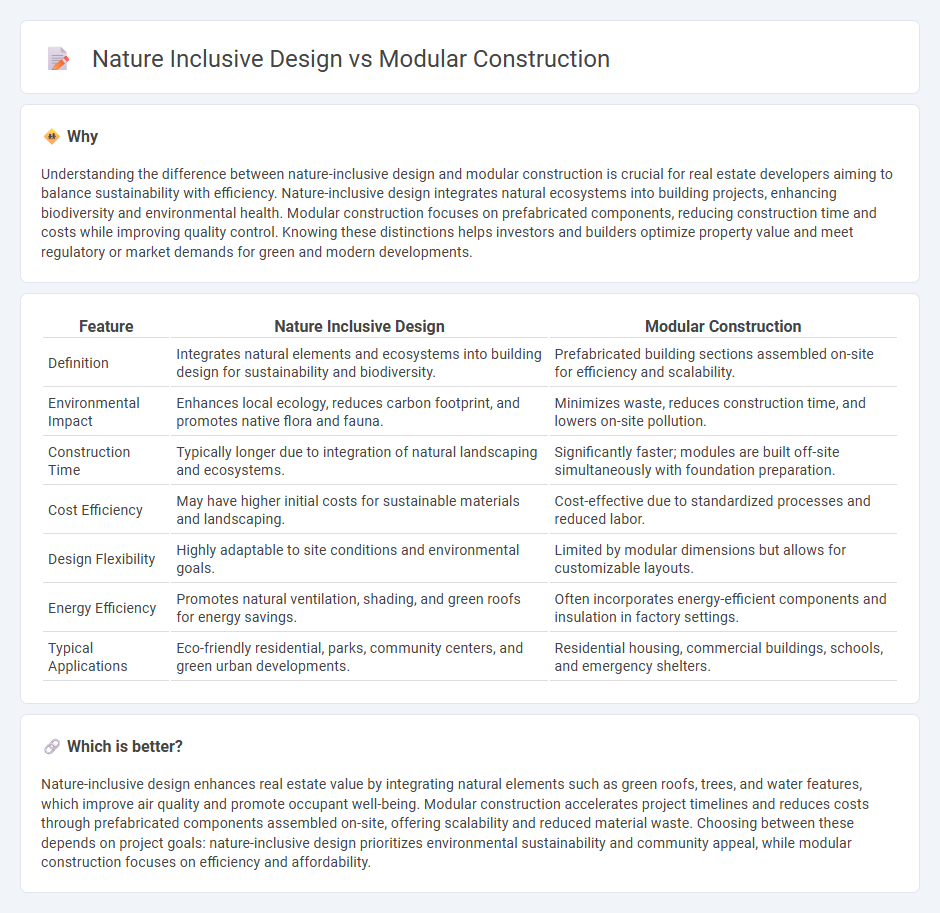
Understanding the difference between nature-inclusive design and modular construction is crucial for real estate developers aiming to balance sustainability with efficiency. Nature-inclusive design integrates natural ecosystems into building projects, enhancing biodiversity and environmental health. Modular construction focuses on prefabricated components, reducing construction time and costs while improving quality control. Knowing these distinctions helps investors and builders optimize property value and meet regulatory or market demands for green and modern developments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Nature Inclusive Design | Modular Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrates natural elements and ecosystems into building design for sustainability and biodiversity. | Prefabricated building sections assembled on-site for efficiency and scalability. |
| Environmental Impact | Enhances local ecology, reduces carbon footprint, and promotes native flora and fauna. | Minimizes waste, reduces construction time, and lowers on-site pollution. |
| Construction Time | Typically longer due to integration of natural landscaping and ecosystems. | Significantly faster; modules are built off-site simultaneously with foundation preparation. |
| Cost Efficiency | May have higher initial costs for sustainable materials and landscaping. | Cost-effective due to standardized processes and reduced labor. |
| Design Flexibility | Highly adaptable to site conditions and environmental goals. | Limited by modular dimensions but allows for customizable layouts. |
| Energy Efficiency | Promotes natural ventilation, shading, and green roofs for energy savings. | Often incorporates energy-efficient components and insulation in factory settings. |
| Typical Applications | Eco-friendly residential, parks, community centers, and green urban developments. | Residential housing, commercial buildings, schools, and emergency shelters. |
Which is better?
Nature-inclusive design enhances real estate value by integrating natural elements such as green roofs, trees, and water features, which improve air quality and promote occupant well-being. Modular construction accelerates project timelines and reduces costs through prefabricated components assembled on-site, offering scalability and reduced material waste. Choosing between these depends on project goals: nature-inclusive design prioritizes environmental sustainability and community appeal, while modular construction focuses on efficiency and affordability.
Connection
Nature-inclusive design integrates natural elements into built environments to enhance sustainability and biodiversity, while modular construction employs prefabricated components for efficient, adaptable building processes. Their connection lies in the ability of modular construction to facilitate the rapid implementation of nature-inclusive features, such as green walls, rooftop gardens, and natural ventilation systems. This synergy promotes eco-friendly developments that reduce environmental impact and support occupant well-being.
Key Terms
Prefabrication
Prefabrication in modular construction enables rapid assembly and precise quality control while minimizing on-site waste, making it a preferred method for scalable building projects. Nature inclusive design incorporates prefabricated elements that support biodiversity and natural ecosystem functions, integrating green roofs, walls, and habitats within the modular components. Explore how advancing prefabrication techniques are revolutionizing sustainable building by harmonizing modular efficiency with nature inclusive design principles.
Biodiversity
Modular construction offers efficient, scalable building solutions that minimize site disturbance while nature inclusive design prioritizes biodiversity by integrating native flora and fauna habitats into the built environment. Emphasizing green roofs, wildlife corridors, and pollinator gardens enhances ecosystem services and supports urban wildlife populations. Explore more about combining modular methods with biodiversity-focused strategies to create sustainable, resilient spaces.
Sustainability
Modular construction minimizes waste by manufacturing components off-site, reducing onsite disturbances and energy consumption, aligning with sustainable building practices. Nature-inclusive design integrates natural ecosystems into architecture, promoting biodiversity and enhancing environmental resilience in urban settings. Explore how these innovative approaches can transform sustainability in modern construction.
Source and External Links
Modular Building - Modular buildings are prefabricated structures composed of sections called modules, often used for temporary or permanent facilities such as schools and housing.
Modular Construction - Modular construction is a process where buildings are constructed off-site under controlled conditions, using the same materials as traditional construction but in less time.
What is Modular Construction? - Modular construction involves assembling building components in a factory, reducing delays from weather and improving sustainability by decreasing energy usage and material waste.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com