Modular home construction offers factory-built sections assembled on-site with durable materials adhering to local building codes, providing superior energy efficiency and customization compared to traditional mobile homes. Mobile homes, typically manufactured on a chassis and designed for mobility, often have lower initial costs but may face zoning restrictions and depreciate faster. Explore the key differences to determine which housing option best suits your needs and investment goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between modular home construction and mobile home construction is crucial because modular homes are built to meet local building codes and offer higher durability, value retention, and financing options, while mobile homes are constructed to federal HUD standards, typically have lower resale value, and face zoning restrictions. Modular homes are assembled on permanent foundations, unlike mobile homes that are designed for relocation, impacting legal classification and land use. This knowledge affects purchasing decisions, investment potential, and long-term homeownership benefits in the real estate market. Real estate professionals and buyers must differentiate these to accurately assess property value and compliance.
Comparison Table
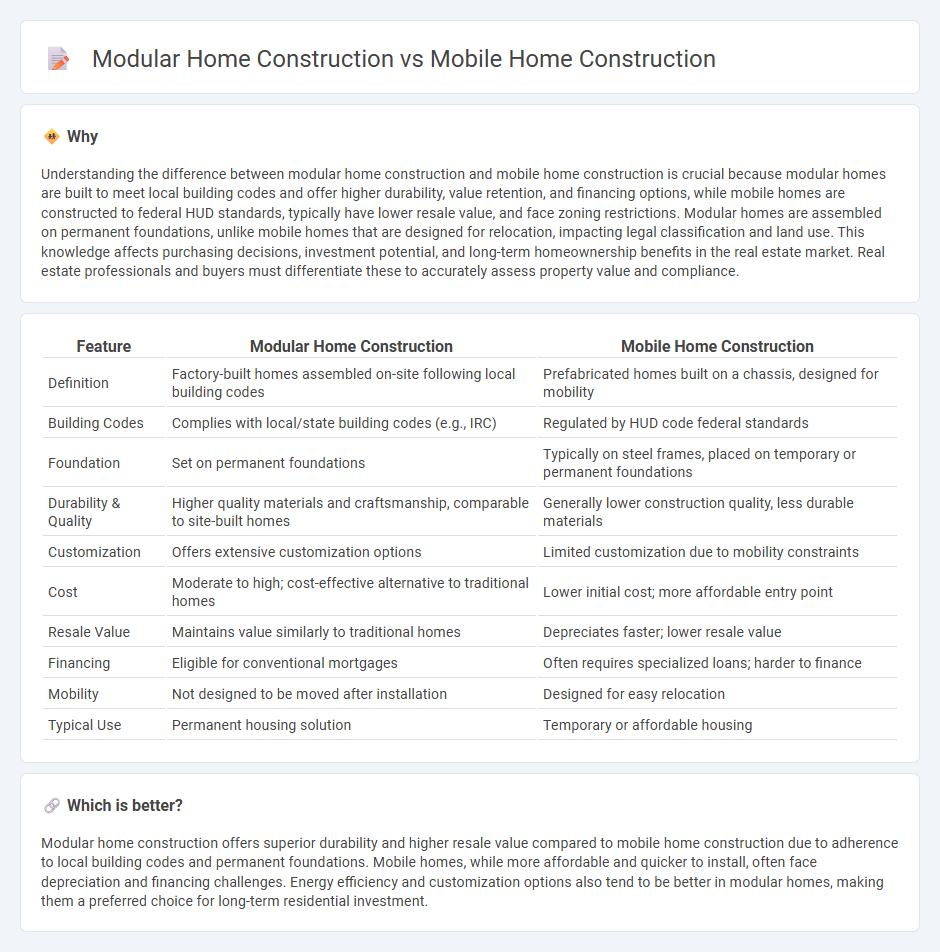
| Feature | Modular Home Construction | Mobile Home Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Factory-built homes assembled on-site following local building codes | Prefabricated homes built on a chassis, designed for mobility |
| Building Codes | Complies with local/state building codes (e.g., IRC) | Regulated by HUD code federal standards |
| Foundation | Set on permanent foundations | Typically on steel frames, placed on temporary or permanent foundations |
| Durability & Quality | Higher quality materials and craftsmanship, comparable to site-built homes | Generally lower construction quality, less durable materials |
| Customization | Offers extensive customization options | Limited customization due to mobility constraints |
| Cost | Moderate to high; cost-effective alternative to traditional homes | Lower initial cost; more affordable entry point |
| Resale Value | Maintains value similarly to traditional homes | Depreciates faster; lower resale value |
| Financing | Eligible for conventional mortgages | Often requires specialized loans; harder to finance |
| Mobility | Not designed to be moved after installation | Designed for easy relocation |
| Typical Use | Permanent housing solution | Temporary or affordable housing |
Which is better?
Modular home construction offers superior durability and higher resale value compared to mobile home construction due to adherence to local building codes and permanent foundations. Mobile homes, while more affordable and quicker to install, often face depreciation and financing challenges. Energy efficiency and customization options also tend to be better in modular homes, making them a preferred choice for long-term residential investment.
Connection
Modular home construction and mobile home construction both utilize factory-built components that are transported to the building site, streamlining the construction process and reducing on-site labor. Modular homes adhere to local building codes similar to traditional homes, while mobile homes, also known as manufactured homes, are built according to federal HUD standards, offering greater mobility. Both methods provide cost-effective, customizable housing solutions that address growing demand in the real estate market.
Key Terms
HUD Code
Mobile home construction adheres to HUD Code regulations, ensuring standardization for transportable factory-built housing units. Modular homes, by contrast, comply with local building codes as they are assembled on-site and typically offer greater customization and structural variety. Explore detailed comparisons and regulatory insights to understand which construction method aligns best with your housing needs.
Building Codes (State/Local)
Mobile home construction is primarily governed by the federal HUD Code, ensuring nationwide standards for safety and durability, while modular home construction must comply with state and local building codes, which can vary significantly. Modular homes are built to meet the same codes as site-built homes, allowing for greater customization and adherence to regional requirements, whereas mobile homes have uniform standards that may not align with local zoning laws. Explore the distinct regulatory frameworks to understand how building codes impact your choice between mobile and modular homes.
Permanent Foundation
Mobile home construction typically involves building units on a steel chassis designed for transport and placement on temporary or semi-permanent foundations, limiting long-term stability and resale value. Modular home construction assembles factory-built sections on a permanent foundation, ensuring structural integrity, compliance with local building codes, and increased durability. Discover more about the benefits of permanent foundations in modular homes to make an informed housing decision.
Source and External Links
How Are Mobile Homes Built? The Anatomy of a ... - Mobile homes are built in factories using a unified structural approach, with 2x4 wall studs, fiberglass insulation, fire-rated interior paneling, prefinished aluminum siding, and a gusseted truss-and-plate roof system integrated with steel anchor bonding for added rigidity and durability.
How are Manufactured Homes Built? - Manufactured homes are constructed on a steel frame in a factory setting, with insulation, flooring, plumbing, and electrical systems installed before walls and roof sections are assembled using a ceiling track system for precise placement and then sealed with insulation and painted finishes.
Mobile Home Construction Process Overview - The construction process starts with an engineered steel I-beam frame and thin concrete decking, followed by modular assembly of wall, roof, and interior components, electrical and plumbing installation, and finishing touches--all completed in a compartmentalized factory environment to ensure consistency and efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com