Build-to-rent homes offer a dedicated residential community designed for long-term tenants, providing consistent income streams and streamlined property management for investors. Mixed-use developments combine residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within a single project, fostering vibrant communities and diversified revenue opportunities. Discover the key benefits and considerations of each approach to determine the best fit for your real estate investment goals.
Why it is important
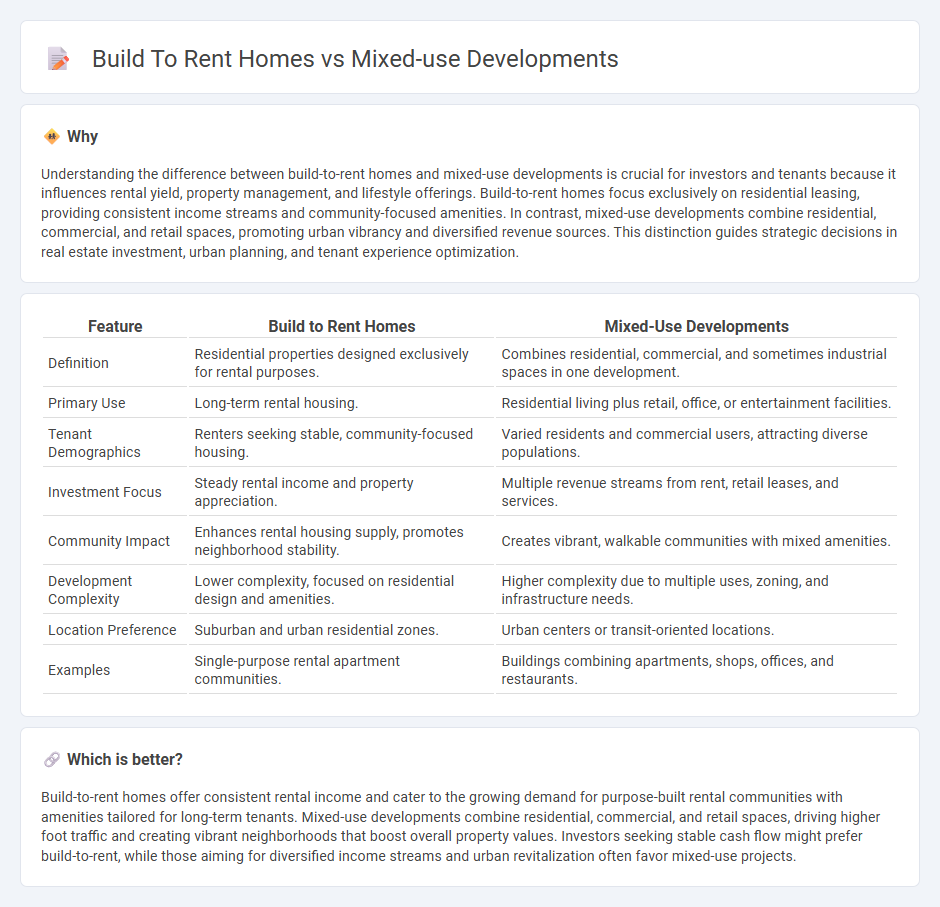
Understanding the difference between build-to-rent homes and mixed-use developments is crucial for investors and tenants because it influences rental yield, property management, and lifestyle offerings. Build-to-rent homes focus exclusively on residential leasing, providing consistent income streams and community-focused amenities. In contrast, mixed-use developments combine residential, commercial, and retail spaces, promoting urban vibrancy and diversified revenue sources. This distinction guides strategic decisions in real estate investment, urban planning, and tenant experience optimization.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Build to Rent Homes | Mixed-Use Developments |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Residential properties designed exclusively for rental purposes. | Combines residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial spaces in one development. |
| Primary Use | Long-term rental housing. | Residential living plus retail, office, or entertainment facilities. |
| Tenant Demographics | Renters seeking stable, community-focused housing. | Varied residents and commercial users, attracting diverse populations. |
| Investment Focus | Steady rental income and property appreciation. | Multiple revenue streams from rent, retail leases, and services. |
| Community Impact | Enhances rental housing supply, promotes neighborhood stability. | Creates vibrant, walkable communities with mixed amenities. |
| Development Complexity | Lower complexity, focused on residential design and amenities. | Higher complexity due to multiple uses, zoning, and infrastructure needs. |
| Location Preference | Suburban and urban residential zones. | Urban centers or transit-oriented locations. |
| Examples | Single-purpose rental apartment communities. | Buildings combining apartments, shops, offices, and restaurants. |
Which is better?
Build-to-rent homes offer consistent rental income and cater to the growing demand for purpose-built rental communities with amenities tailored for long-term tenants. Mixed-use developments combine residential, commercial, and retail spaces, driving higher foot traffic and creating vibrant neighborhoods that boost overall property values. Investors seeking stable cash flow might prefer build-to-rent, while those aiming for diversified income streams and urban revitalization often favor mixed-use projects.
Connection
Build-to-rent homes and mixed-use developments are connected through their shared goal of creating integrated living environments that combine residential units with commercial, retail, and recreational spaces. These developments enhance community engagement and provide convenient access to amenities, increasing the value and appeal of rental properties. Real estate investors prioritize mixed-use build-to-rent projects for their potential to generate stable, long-term rental income while fostering vibrant, self-sustained neighborhoods.
Key Terms
Zoning
Mixed-use developments integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within a single zoning classification, promoting urban density and walkability. Build to rent homes typically fall under residential zoning, focusing on community-specific amenities and long-term tenant retention. Discover how zoning regulations impact the planning and investment strategies for each property type.
Ownership Structure
Mixed-use developments combine residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial spaces under a single property management model, often featuring a diverse ownership structure with multiple stakeholders including investors, developers, and sometimes individual unit owners. Build-to-rent homes typically involve single-owner models where a professional landlord or investment firm controls the entire property portfolio, ensuring consistent management and tenant experience. Explore the detailed distinctions between ownership structures to understand the impact on investment potential and community dynamics.
Tenant Demographics
Mixed-use developments attract diverse tenant demographics including young professionals, families, and retirees seeking convenience and amenities such as retail, office spaces, and entertainment within walking distance. Build-to-rent homes primarily appeal to long-term renters valuing community-oriented living and single-family home features, often attracting families and middle-income individuals. Explore more to understand how tenant demographics shape these residential models.
Source and External Links
Supporting Active Living Through Mixed-Use Developments - Mixed-use developments combine multiple uses such as residential, commercial, and civic spaces either vertically (e.g., retail on the ground floor with apartments above) or horizontally (different uses within walking distance), promoting physical activity, economic opportunity, and a variety of housing options within communities.
Benefits of Mixed-Use Development in Urban Areas - Mixed-use development integrates residential, commercial, cultural, retail, and sometimes industrial spaces in one area to optimize land use, enhance accessibility, foster vibrant communities, and reduce the need for long-distance travel.
8 Different Types of Mixed-Use Development - Mixed-use developments include several types such as vertical (multiple uses stacked in one building) and horizontal (multiple uses in one neighborhood), live-work setups, and transit-oriented developments, all designed to create dynamic, walkable, and sustainable urban environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com