Vertical farming real estate maximizes urban space by integrating agricultural production within high-rise buildings, offering sustainable solutions for food security and reducing transportation emissions. Mixed-use developments combine residential, commercial, and recreational spaces to create vibrant communities that enhance walkability and economic growth. Explore the benefits and challenges of these innovative real estate models to understand their impact on urban living and investment opportunities.
Why it is important
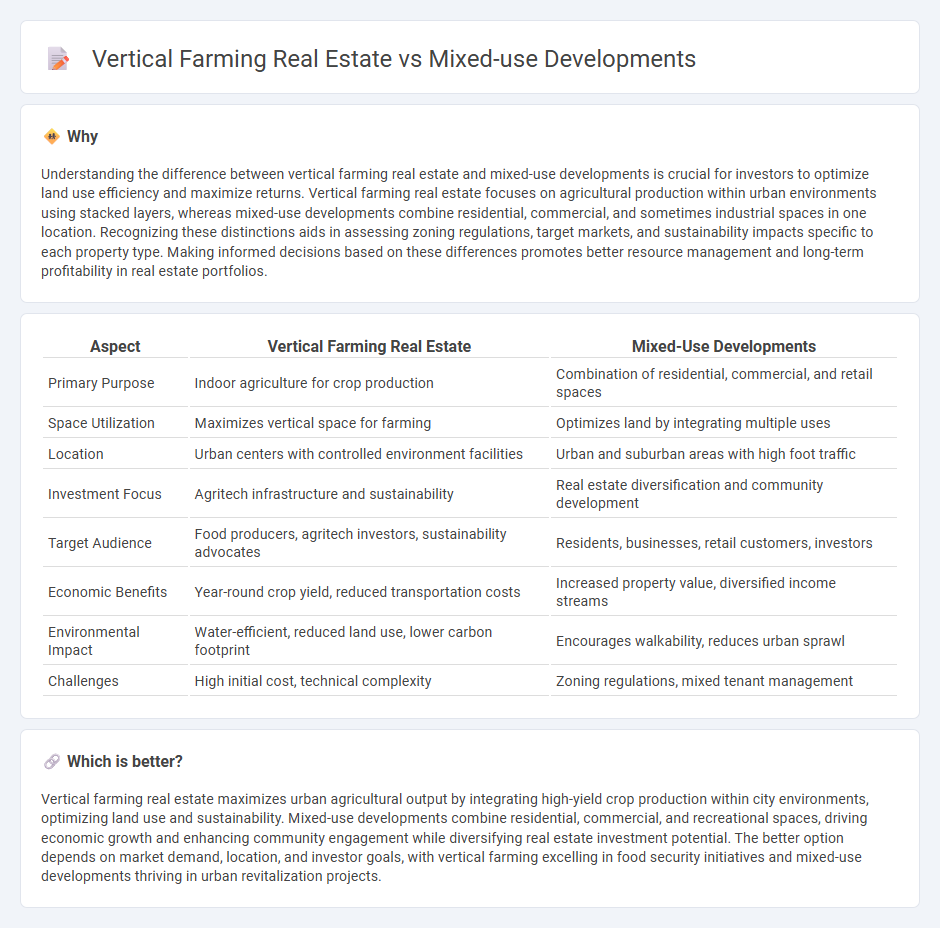
Understanding the difference between vertical farming real estate and mixed-use developments is crucial for investors to optimize land use efficiency and maximize returns. Vertical farming real estate focuses on agricultural production within urban environments using stacked layers, whereas mixed-use developments combine residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial spaces in one location. Recognizing these distinctions aids in assessing zoning regulations, target markets, and sustainability impacts specific to each property type. Making informed decisions based on these differences promotes better resource management and long-term profitability in real estate portfolios.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Vertical Farming Real Estate | Mixed-Use Developments |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Indoor agriculture for crop production | Combination of residential, commercial, and retail spaces |
| Space Utilization | Maximizes vertical space for farming | Optimizes land by integrating multiple uses |
| Location | Urban centers with controlled environment facilities | Urban and suburban areas with high foot traffic |
| Investment Focus | Agritech infrastructure and sustainability | Real estate diversification and community development |
| Target Audience | Food producers, agritech investors, sustainability advocates | Residents, businesses, retail customers, investors |
| Economic Benefits | Year-round crop yield, reduced transportation costs | Increased property value, diversified income streams |
| Environmental Impact | Water-efficient, reduced land use, lower carbon footprint | Encourages walkability, reduces urban sprawl |
| Challenges | High initial cost, technical complexity | Zoning regulations, mixed tenant management |
Which is better?
Vertical farming real estate maximizes urban agricultural output by integrating high-yield crop production within city environments, optimizing land use and sustainability. Mixed-use developments combine residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, driving economic growth and enhancing community engagement while diversifying real estate investment potential. The better option depends on market demand, location, and investor goals, with vertical farming excelling in food security initiatives and mixed-use developments thriving in urban revitalization projects.
Connection
Vertical farming real estate integrates agricultural production into urban settings, optimizing space within mixed-use developments that combine residential, commercial, and industrial functions. These developments enhance sustainability by reducing transportation costs and carbon footprints while fostering local food systems. Incorporating vertical farms into mixed-use projects increases property value and promotes innovative urban planning focused on environmental resilience and community well-being.
Key Terms
Zoning regulations
Zoning regulations play a critical role in shaping mixed-use developments and vertical farming real estate, influencing land use, building heights, and permissible activities within designated areas. Mixed-use projects often require flexible zoning to accommodate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, while vertical farming demands specific agricultural zoning adaptations to support controlled environment agriculture and infrastructure needs. Explore the detailed zoning requirements and regulatory updates to better understand their impact on these innovative real estate sectors.
Space utilization
Mixed-use developments maximize space utilization by integrating residential, commercial, and recreational areas within a single footprint, enhancing urban density and reducing commute times. Vertical farming real estate optimizes vertical space for agricultural production, allowing high-yield crop growth in urban environments while minimizing land use and water consumption. Explore the transformative potential of these innovative space-saving solutions for sustainable urban planning.
Revenue streams
Mixed-use developments generate diverse revenue streams through residential leases, retail rentals, office spaces, and hospitality services, maximizing income by capitalizing on varied tenant types and consumer foot traffic. Vertical farming real estate primarily derives revenue from agricultural produce sales, technology leasing, and potential energy savings, offering sustainable and innovative income sources in urban environments. Explore the detailed comparison of revenue potentials and investment opportunities in both sectors to optimize your real estate portfolio.
Source and External Links
Supporting Active Living Through Mixed-Use Developments - Mixed-use developments combine residential, commercial, and civic spaces within walkable distances, supporting active living, increasing housing variety, and offering social, economic, and health benefits by integrating multiple land uses within one area.
Benefits of Mixed-Use Development in Urban Areas - McClure - These developments optimize space by combining residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial uses, fostering vibrant, accessible, and community-oriented urban environments where people can live, work, and play without extensive travel.
Mixed-use development - Wikipedia - Mixed-use development blends multiple functions such as residential, commercial, cultural, and institutional uses into a physically integrated space, which can be part of a building, a neighborhood, or enforced through zoning policy to create pedestrian-friendly urban environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com