Vertical farming buildings optimize urban real estate by integrating agricultural production within high-rise structures, maximizing space efficiency and promoting sustainable food systems. Student housing developments focus on providing affordable, convenient living accommodations near educational institutions to support academic success and community engagement. Explore the unique benefits and challenges of these innovative real estate solutions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between vertical farming buildings and student housing is crucial for optimizing land use and investment strategies in real estate. Vertical farming structures focus on controlled-environment agriculture, requiring specific design elements like climate control and hydroponic systems, whereas student housing prioritizes communal living spaces, security, and proximity to educational institutions. Accurate differentiation ensures compliance with zoning laws and enhances property valuation based on intended occupancy. Real estate developers can maximize return on investment and sustainability by aligning building design with purpose-specific infrastructure demands.
Comparison Table
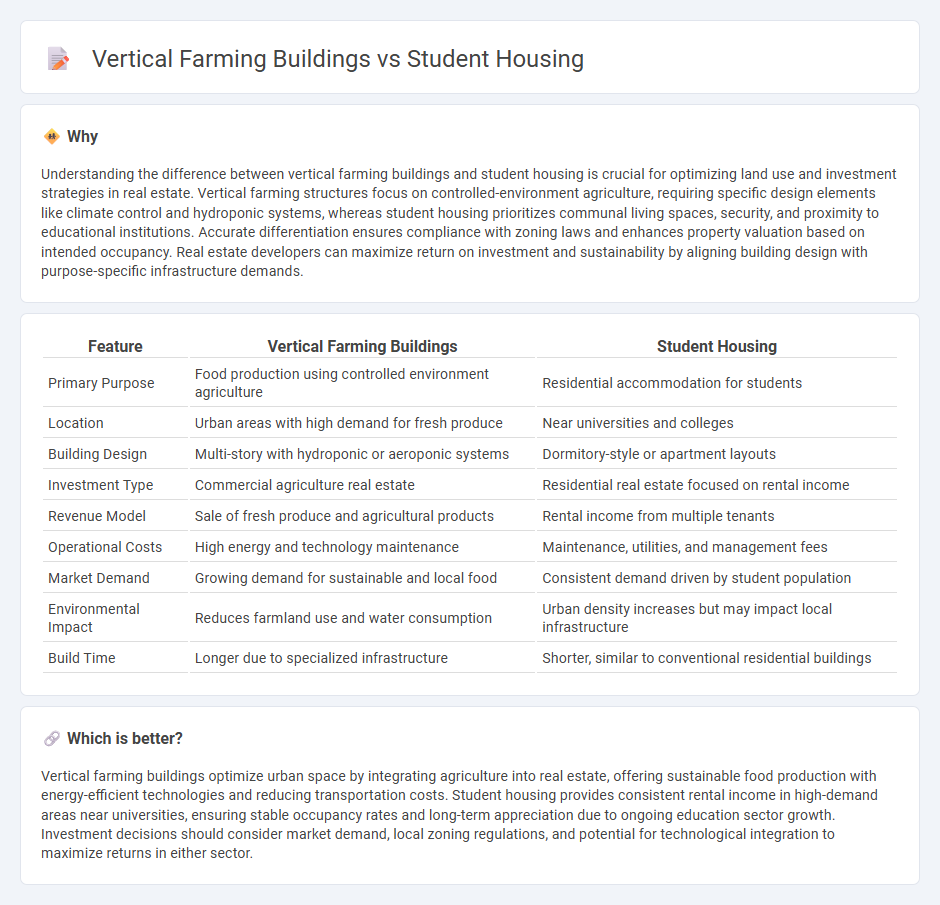
| Feature | Vertical Farming Buildings | Student Housing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Food production using controlled environment agriculture | Residential accommodation for students |
| Location | Urban areas with high demand for fresh produce | Near universities and colleges |
| Building Design | Multi-story with hydroponic or aeroponic systems | Dormitory-style or apartment layouts |
| Investment Type | Commercial agriculture real estate | Residential real estate focused on rental income |
| Revenue Model | Sale of fresh produce and agricultural products | Rental income from multiple tenants |
| Operational Costs | High energy and technology maintenance | Maintenance, utilities, and management fees |
| Market Demand | Growing demand for sustainable and local food | Consistent demand driven by student population |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces farmland use and water consumption | Urban density increases but may impact local infrastructure |
| Build Time | Longer due to specialized infrastructure | Shorter, similar to conventional residential buildings |
Which is better?
Vertical farming buildings optimize urban space by integrating agriculture into real estate, offering sustainable food production with energy-efficient technologies and reducing transportation costs. Student housing provides consistent rental income in high-demand areas near universities, ensuring stable occupancy rates and long-term appreciation due to ongoing education sector growth. Investment decisions should consider market demand, local zoning regulations, and potential for technological integration to maximize returns in either sector.
Connection
Vertical farming buildings and student housing intersect through innovative real estate developments that maximize land use efficiency in urban areas. Incorporating vertical farms within or adjacent to student housing complexes enhances sustainability by providing fresh produce onsite, reducing food supply chains and operational costs. This integration supports eco-friendly living environments, appealing to environmentally conscious students and investors focused on sustainable urban growth.
Key Terms
Occupancy Rate
Student housing complexes typically achieve occupancy rates between 90-95%, driven by consistent demand during academic terms and limited availability. Vertical farming buildings, while emerging, report occupancy based on leased farming plots or leased vertical space, often fluctuating between 70-85% due to market adoption rates and technological scalability. Explore detailed comparative analyses to understand how occupancy dynamics influence investment and operational strategies in both sectors.
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations play a critical role in determining the feasibility and development of both student housing and vertical farming buildings, often dictating land use, building height, and density requirements. Student housing typically faces regulations aimed at residential zoning districts, emphasizing proximity to educational institutions and community impact, whereas vertical farming buildings are often categorized under agricultural or commercial zones with specific considerations for environmental controls and sustainability. Explore how evolving zoning laws impact urban development strategies for student housing and vertical farming projects.
Mixed-Use Development
Mixed-use development combines student housing with vertical farming buildings to enhance urban sustainability and resource efficiency by integrating residential, agricultural, and commercial spaces within the same footprint. This approach maximizes land use, reduces food transportation emissions, and provides students with fresh produce on-site, fostering a healthy, community-oriented lifestyle. Explore how mixed-use developments create innovative urban solutions by blending living spaces and food production.
Source and External Links
Student Housing Tempe | Upto 19% OFF - Offers affordable student housing options in Tempe, with prices starting at $829/month, near Arizona State University.
ASU Off Campus Student Housing & Apartments Tempe, AZ - Provides quality housing for ASU students with amenities like a resort-style pool complex and fitness center.
Arizona State University Off-Campus Housing - Offers over 80 verified off-campus apartments near ASU, aiding students in finding rentals in Tempe.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com