Adaptive reuse properties transform existing buildings for new purposes, preserving historical architecture while maximizing resource efficiency and sustainability. Mixed-use developments combine residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within a single project to create vibrant, walkable communities that enhance urban living experiences. Explore the benefits and challenges of both strategies to discover the most effective approach for modern real estate projects.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse properties and mixed-use developments is crucial for investors and developers to maximize property value and meet market demands effectively. Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing buildings for new uses, preserving historical elements while reducing construction costs and environmental impact. Mixed-use development integrates residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within a single project to promote community engagement and increase economic activity. Accurate knowledge helps stakeholders optimize investment strategies, zoning compliance, and sustainability goals.
Comparison Table
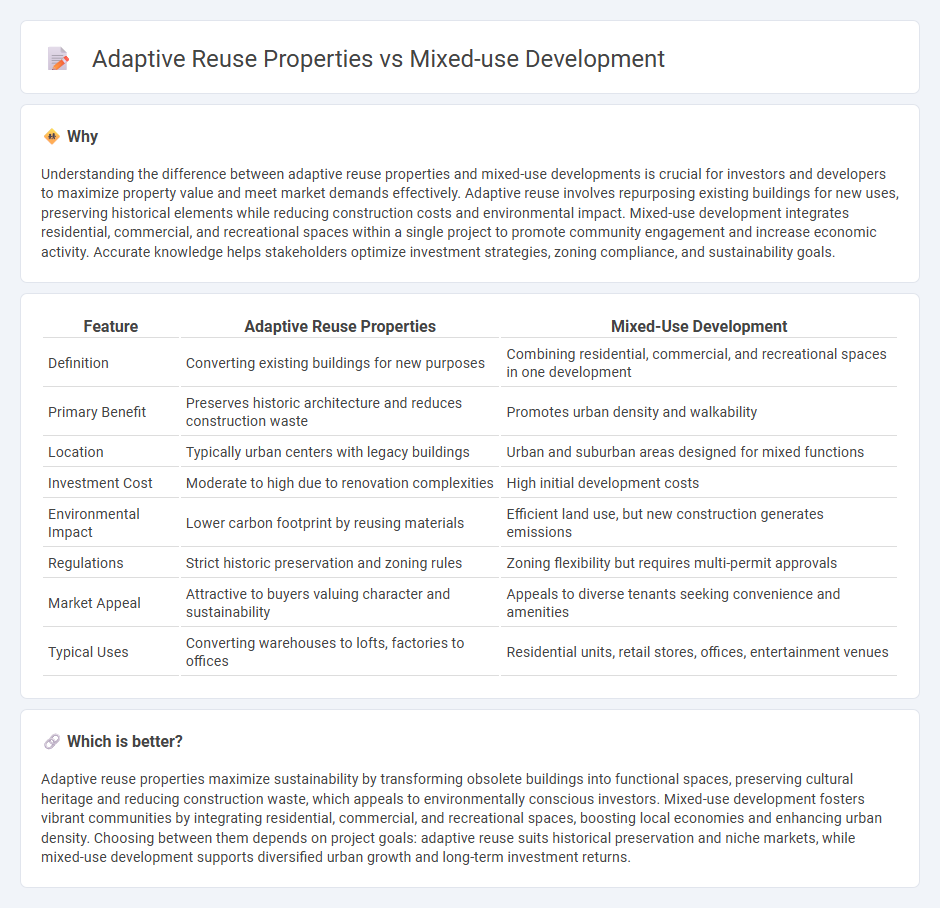
| Feature | Adaptive Reuse Properties | Mixed-Use Development |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Converting existing buildings for new purposes | Combining residential, commercial, and recreational spaces in one development |
| Primary Benefit | Preserves historic architecture and reduces construction waste | Promotes urban density and walkability |
| Location | Typically urban centers with legacy buildings | Urban and suburban areas designed for mixed functions |
| Investment Cost | Moderate to high due to renovation complexities | High initial development costs |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint by reusing materials | Efficient land use, but new construction generates emissions |
| Regulations | Strict historic preservation and zoning rules | Zoning flexibility but requires multi-permit approvals |
| Market Appeal | Attractive to buyers valuing character and sustainability | Appeals to diverse tenants seeking convenience and amenities |
| Typical Uses | Converting warehouses to lofts, factories to offices | Residential units, retail stores, offices, entertainment venues |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse properties maximize sustainability by transforming obsolete buildings into functional spaces, preserving cultural heritage and reducing construction waste, which appeals to environmentally conscious investors. Mixed-use development fosters vibrant communities by integrating residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, boosting local economies and enhancing urban density. Choosing between them depends on project goals: adaptive reuse suits historical preservation and niche markets, while mixed-use development supports diversified urban growth and long-term investment returns.
Connection
Adaptive reuse properties and mixed-use development intersect by transforming underutilized or obsolete buildings into multifunctional spaces that combine residential, commercial, and recreational uses. This approach enhances urban sustainability by maximizing existing infrastructure, reducing urban sprawl, and preserving historical architectural elements. Real estate developers leverage adaptive reuse projects within mixed-use developments to increase property values, attract diverse tenants, and stimulate local economic growth.
Key Terms
Zoning
Mixed-use developments typically require comprehensive zoning approvals to integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within a single project, promoting urban density and multifunctionality. Adaptive reuse properties often navigate zoning variances to repurpose existing structures while maintaining the original building footprint and historical characteristics. Explore detailed zoning requirements and strategies to optimize your property investment.
Urban Revitalization
Mixed-use developments integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces to create vibrant, walkable urban environments, enhancing local economies and reducing urban sprawl. Adaptive reuse properties transform existing structures, preserving historical architecture while meeting modern needs, contributing to sustainable urban revitalization. Explore detailed strategies and benefits to understand how both approaches shape resilient cities.
Building Codes
Mixed-use developments must comply with multiple building codes addressing residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial standards within a single structure, ensuring safety, accessibility, and fire protection for varied occupancy types. Adaptive reuse properties require careful navigation of existing building codes and historical preservation regulations, often necessitating upgrades to meet modern safety and energy efficiency standards while retaining original architectural elements. Explore detailed code requirements and compliance strategies to optimize project outcomes in both development types.
Source and External Links
Supporting Active Living Through Mixed-Use Developments - Mixed-use development is an alternative to single-use zoning, combining multiple uses such as residential, commercial, and civic spaces within a site to support walking, economic opportunity, and diverse housing options.
Benefits of Mixed-Use Development in Urban Areas - Mixed-use development integrates residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial spaces within a single area, optimizing land use, promoting vibrant communities, and offering convenience through reduced travel distances.
Mixed-use development - Wikipedia - Mixed-use development blends multiple functions, like residential, commercial, cultural, or institutional uses, into a physical and functionally integrated space, applied at the building, block, or city scale.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com