Ghost kitchens in retail spaces transform underutilized commercial areas into efficient food production hubs without traditional dining rooms, optimizing urban real estate for high-demand delivery services. Maker spaces, by contrast, utilize retail premises to foster community-driven manufacturing and innovation, offering shared resources for creative entrepreneurs and startups. Explore how these distinct uses of retail real estate are reshaping urban economies and property value.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ghost kitchens in retail spaces versus maker spaces is crucial for real estate investors and developers to maximize property value and attract the right tenants. Ghost kitchens in retail spaces typically benefit from high foot traffic and customer exposure, enhancing commercial viability. Maker spaces, designed for production and innovation, offer flexible leasing options but may lack direct consumer engagement, affecting profitability. Accurate distinction informs strategic planning, zoning decisions, and targeted marketing in commercial real estate development.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Ghost Kitchens in Retail Spaces | Ghost Kitchens in Maker Spaces |
|---|---|---|
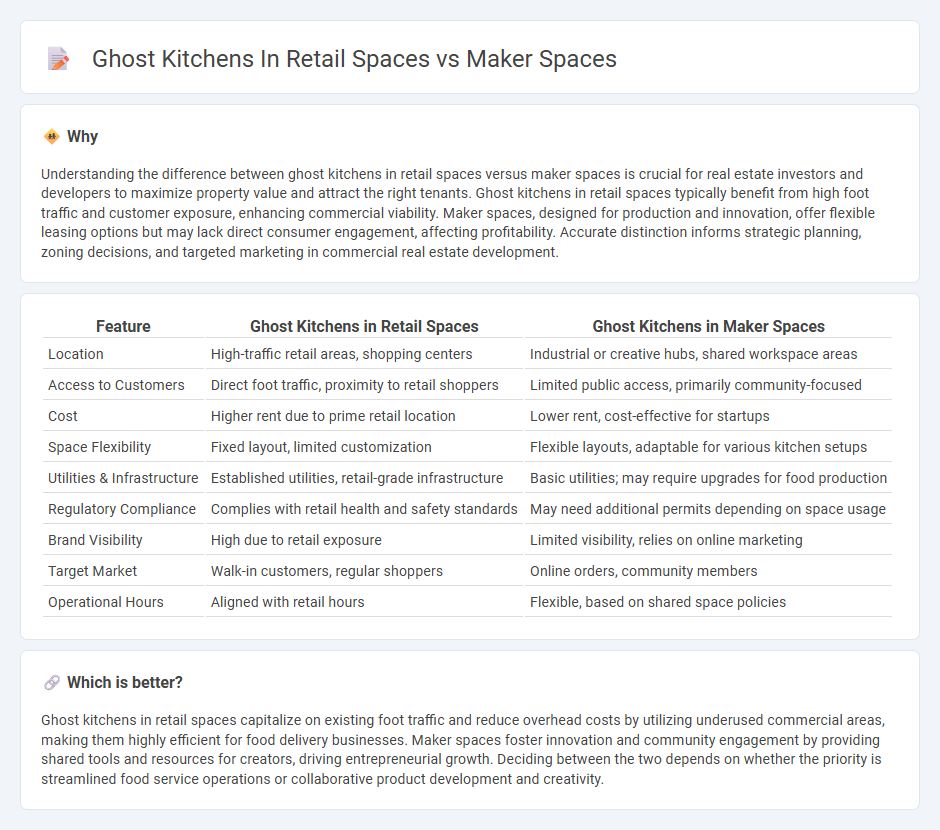
| Location | High-traffic retail areas, shopping centers | Industrial or creative hubs, shared workspace areas |
| Access to Customers | Direct foot traffic, proximity to retail shoppers | Limited public access, primarily community-focused |
| Cost | Higher rent due to prime retail location | Lower rent, cost-effective for startups |
| Space Flexibility | Fixed layout, limited customization | Flexible layouts, adaptable for various kitchen setups |
| Utilities & Infrastructure | Established utilities, retail-grade infrastructure | Basic utilities; may require upgrades for food production |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complies with retail health and safety standards | May need additional permits depending on space usage |
| Brand Visibility | High due to retail exposure | Limited visibility, relies on online marketing |
| Target Market | Walk-in customers, regular shoppers | Online orders, community members |
| Operational Hours | Aligned with retail hours | Flexible, based on shared space policies |
Which is better?
Ghost kitchens in retail spaces capitalize on existing foot traffic and reduce overhead costs by utilizing underused commercial areas, making them highly efficient for food delivery businesses. Maker spaces foster innovation and community engagement by providing shared tools and resources for creators, driving entrepreneurial growth. Deciding between the two depends on whether the priority is streamlined food service operations or collaborative product development and creativity.
Connection
Ghost kitchens in retail spaces leverage available commercial real estate by converting underutilized areas into food preparation hubs, optimizing space efficiency and rental income. Maker spaces share this adaptive reuse trend by transforming traditional retail or industrial properties into collaborative work environments, enhancing property value through diversified tenant use. Both concepts demonstrate evolving real estate strategies focused on maximizing utility and generating alternative revenue streams in urban markets.
Key Terms
Flex Space
Maker spaces and ghost kitchens optimize flex space utilization by catering to evolving consumer and business demands within retail environments; maker spaces support creative enterprises with tools and collaborative areas, while ghost kitchens streamline food delivery operations without dine-in facilities. Both leverage transient occupancy models to maximize revenue per square foot and reduce traditional retail constraints, such as long-term leases and fixed infrastructure. Explore how integrating these innovative concepts can transform retail property value and meet shifting market trends.
Tenant Mix
Maker spaces and ghost kitchens serve distinct tenant mix strategies in retail spaces, with maker spaces attracting creative entrepreneurs and artisans who require hands-on work areas, while ghost kitchens cater to food delivery services needing minimal storefront presence. Maker spaces enhance community engagement and experiential retail, driving foot traffic through workshops and product showcases, whereas ghost kitchens optimize operational efficiency and reduce costs by eliminating dine-in facilities. Explore how these tenant types can redefine retail ecosystems and maximize property value.
Adaptive Reuse
Adaptive reuse transforms underutilized retail spaces into innovative hubs like maker spaces and ghost kitchens, maximizing urban real estate efficiency. Maker spaces foster creativity through shared tools and collaborative environments, promoting community-driven product development, while ghost kitchens optimize food delivery operations, reducing overhead by eliminating dine-in facilities. Explore how adaptive reuse redefines commercial real estate trends by balancing creativity and convenience in repurposed retail environments.
Source and External Links
What is a Makerspace? - A makerspace is a collaborative workspace for making, learning, and sharing, often equipped with various tools like 3D printers and laser cutters, but can also be as simple as using cardboard and art supplies.
What is Making? What is a Makerspace? - A makerspace is a collaborative work space for making and learning, utilizing both high-tech and low-tech tools to foster STEM skills and creativity.
Maker Spaces - Maker spaces are designed to support student collaboration, creativity, and product development through hands-on learning environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com