Retrofitting buildings for net zero energy focuses on integrating renewable energy sources and enhancing energy efficiency to achieve zero net carbon emissions. LEED certification evaluates overall sustainability, including resource management, indoor environmental quality, and energy performance, but does not guarantee net zero energy use. Explore the key differences and benefits of retrofit strategies versus LEED certification to optimize your real estate investments.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between retrofit for net zero and LEED certification is crucial in real estate as it impacts energy efficiency, cost savings, and environmental compliance. Net zero retrofits focus on achieving zero net energy consumption by balancing energy produced and consumed, crucial for sustainable building operation. LEED certification emphasizes a broad set of sustainable design and construction practices, affecting market value and tenant appeal. Clear knowledge guides investment decisions and regulatory adherence in real estate development and management.
Comparison Table
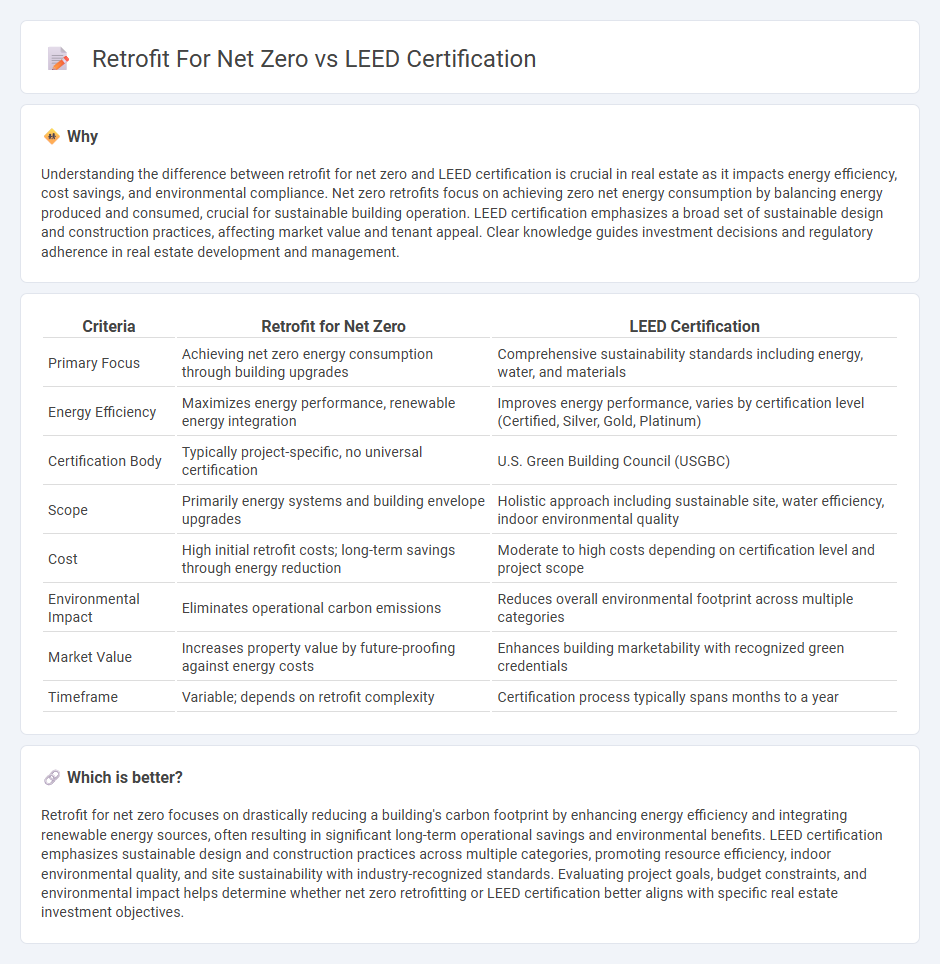
| Criteria | Retrofit for Net Zero | LEED Certification |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Achieving net zero energy consumption through building upgrades | Comprehensive sustainability standards including energy, water, and materials |
| Energy Efficiency | Maximizes energy performance, renewable energy integration | Improves energy performance, varies by certification level (Certified, Silver, Gold, Platinum) |
| Certification Body | Typically project-specific, no universal certification | U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) |
| Scope | Primarily energy systems and building envelope upgrades | Holistic approach including sustainable site, water efficiency, indoor environmental quality |
| Cost | High initial retrofit costs; long-term savings through energy reduction | Moderate to high costs depending on certification level and project scope |
| Environmental Impact | Eliminates operational carbon emissions | Reduces overall environmental footprint across multiple categories |
| Market Value | Increases property value by future-proofing against energy costs | Enhances building marketability with recognized green credentials |
| Timeframe | Variable; depends on retrofit complexity | Certification process typically spans months to a year |
Which is better?
Retrofit for net zero focuses on drastically reducing a building's carbon footprint by enhancing energy efficiency and integrating renewable energy sources, often resulting in significant long-term operational savings and environmental benefits. LEED certification emphasizes sustainable design and construction practices across multiple categories, promoting resource efficiency, indoor environmental quality, and site sustainability with industry-recognized standards. Evaluating project goals, budget constraints, and environmental impact helps determine whether net zero retrofitting or LEED certification better aligns with specific real estate investment objectives.
Connection
Retrofitting buildings for net zero energy efficiency significantly enhances the likelihood of achieving LEED certification by incorporating sustainable design elements such as improved insulation, energy-efficient HVAC systems, and renewable energy sources. LEED certification evaluates environmental performance, making energy retrofits that reduce carbon emissions and optimize resource use essential for meeting its stringent criteria. Integrating net zero strategies supports LEED's credits related to energy optimization, indoor environmental quality, and sustainable sites, creating a direct link between retrofit projects and certification success.
Key Terms
Energy Efficiency
LEED certification evaluates buildings based on comprehensive sustainability criteria, including energy efficiency, water conservation, and indoor environmental quality, promoting reduced environmental impact through design and construction practices. Retrofit for net zero targets transforming existing structures to achieve net-zero energy consumption by integrating advanced energy-saving technologies, renewable energy systems, and improved insulation. Explore the benefits and strategic approaches of LEED certification and net-zero retrofitting to optimize energy performance in your building projects.
Sustainability
LEED certification emphasizes sustainable building practices through energy-efficient design, resource conservation, and reduced environmental impact, setting benchmarks for green construction. Retrofitting existing buildings for net zero focuses on upgrading insulation, installing renewable energy systems, and optimizing energy use to achieve zero carbon emissions over time. Explore more about how sustainable building certifications and net zero retrofits can transform the future of eco-friendly construction.
Building Performance
LEED certification establishes rigorous sustainability standards emphasizing energy efficiency, water savings, and indoor environmental quality to enhance building performance. Retrofit strategies for net zero focus on upgrading existing structures with advanced technologies like high-performance insulation, renewable energy systems, and smart controls to achieve net-zero energy consumption. Explore detailed comparisons to understand the impact on building performance and sustainability goals.
Source and External Links
LEED Certification: Meaning and Requirements - This article explains LEED certification, which promotes sustainable building practices by recognizing projects that achieve high levels of environmental sustainability and energy efficiency.
What Is LEED Certification? - LEED certification acknowledges buildings and communities that meet specific sustainability and energy efficiency standards, contributing to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and improved operational efficiency.
LEED - LEED is a widely used green building certification program that assesses environmental impacts and offers various levels of certification, from Certified to Platinum, based on points earned in different sustainability categories.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com