Modular home construction offers fast assembly and cost efficiency through pre-fabricated building sections, while insulated concrete form (ICF) construction provides superior energy efficiency and structural durability using interlocking foam blocks filled with concrete. Both methods significantly reduce construction time compared to traditional building, with ICF homes excelling in insulation and soundproofing qualities. Explore the benefits and differences between these innovative construction techniques to determine which fits your real estate investment goals.
Why it is important
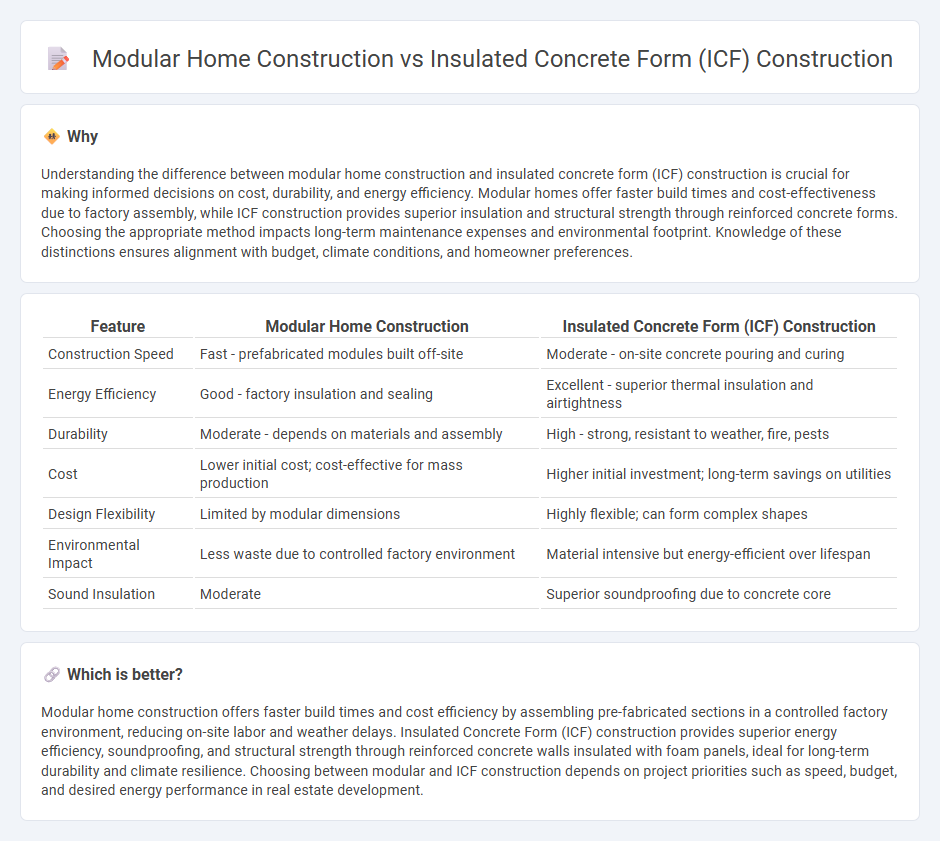
Understanding the difference between modular home construction and insulated concrete form (ICF) construction is crucial for making informed decisions on cost, durability, and energy efficiency. Modular homes offer faster build times and cost-effectiveness due to factory assembly, while ICF construction provides superior insulation and structural strength through reinforced concrete forms. Choosing the appropriate method impacts long-term maintenance expenses and environmental footprint. Knowledge of these distinctions ensures alignment with budget, climate conditions, and homeowner preferences.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Modular Home Construction | Insulated Concrete Form (ICF) Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Speed | Fast - prefabricated modules built off-site | Moderate - on-site concrete pouring and curing |
| Energy Efficiency | Good - factory insulation and sealing | Excellent - superior thermal insulation and airtightness |
| Durability | Moderate - depends on materials and assembly | High - strong, resistant to weather, fire, pests |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; cost-effective for mass production | Higher initial investment; long-term savings on utilities |
| Design Flexibility | Limited by modular dimensions | Highly flexible; can form complex shapes |
| Environmental Impact | Less waste due to controlled factory environment | Material intensive but energy-efficient over lifespan |
| Sound Insulation | Moderate | Superior soundproofing due to concrete core |
Which is better?
Modular home construction offers faster build times and cost efficiency by assembling pre-fabricated sections in a controlled factory environment, reducing on-site labor and weather delays. Insulated Concrete Form (ICF) construction provides superior energy efficiency, soundproofing, and structural strength through reinforced concrete walls insulated with foam panels, ideal for long-term durability and climate resilience. Choosing between modular and ICF construction depends on project priorities such as speed, budget, and desired energy performance in real estate development.
Connection
Modular home construction and insulated concrete form (ICF) construction are connected through their emphasis on energy efficiency and reduced build times in the real estate sector. ICFs provide superior insulation and structural integrity, which complements the precision and factory-controlled environment of modular homes, resulting in durable, high-performance residential buildings. Both methods contribute to sustainable development by minimizing waste and enhancing thermal efficiency, appealing to modern buyers and investors focused on long-term value.
Key Terms
Thermal Efficiency
Insulated concrete form (ICF) construction provides superior thermal efficiency through continuous insulation and airtight design, reducing heat loss and energy consumption in buildings. Modular home construction incorporates prefabricated sections, often with standard insulation materials, offering moderate thermal performance but benefiting from factory-controlled quality and faster assembly. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how these construction methods impact energy savings and comfort in your next project.
Construction Method
Insulated Concrete Form (ICF) construction utilizes interlocking foam blocks filled with reinforced concrete, offering superior energy efficiency and structural strength through a continuous insulation barrier and solid concrete core. Modular home construction involves prefabricated sections built in controlled factory environments, enabling faster onsite assembly and reduced construction waste while maintaining flexibility in design. Explore more about the advantages and applications of each construction method to determine the best fit for your building project.
Structural Integrity
Insulated Concrete Form (ICF) construction offers superior structural integrity due to its reinforced concrete core, which provides enhanced resistance to extreme weather, fire, and seismic forces compared to modular homes built with standard framing materials. Modular home construction relies on factory-built sections that are transported and assembled on-site, which may introduce vulnerabilities at joint connections and limit overall durability under stress. Explore the detailed comparison of structural performance and longevity between ICF and modular home construction methods to make an informed decision.
Source and External Links
Insulating concrete form - Wikipedia - Insulated concrete forms (ICF) are modular building systems made of interlocking foam blocks filled with reinforced concrete, which remain in place as permanent insulation and structural formwork for walls, floors, or roofs, increasingly used due to energy efficiency and disaster resistance benefits since the 1970s.
Insulated Concrete Forms - Quad-Lock ICF for Amazing Buildings - ICFs create strong, insulated concrete buildings quickly with one-step assembly, providing excellent insulation, structural strength, and a healthy living environment without needing additional framing or insulation.
What are Insulated Concrete Forms - YouTube - ICFs consist of two styrofoam panels tied together and filled with concrete, delivering superior insulation (R24) compared to conventional walls and eliminating the need for interior stud walls, which improves basement space, moisture resistance, and energy efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com