Upzoning increases allowable building density, promoting urban growth and higher property values, while downzoning restricts development to preserve neighborhood character and reduce congestion. These zoning changes impact housing supply, affordability, and local infrastructure demands, shaping community development trends. Explore the benefits and challenges of upzoning versus downzoning to understand their effects on real estate markets.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between upzoning and downzoning is crucial in real estate because it directly impacts property values, development potential, and community growth patterns. Upzoning increases allowable building density, enabling developers to construct larger projects and potentially raising land value significantly. Downzoning restricts development, preserving neighborhood character but possibly reducing property worth and limiting investment opportunities. Knowing these zoning changes helps investors, homeowners, and planners make informed decisions about property use and future market trends.
Comparison Table
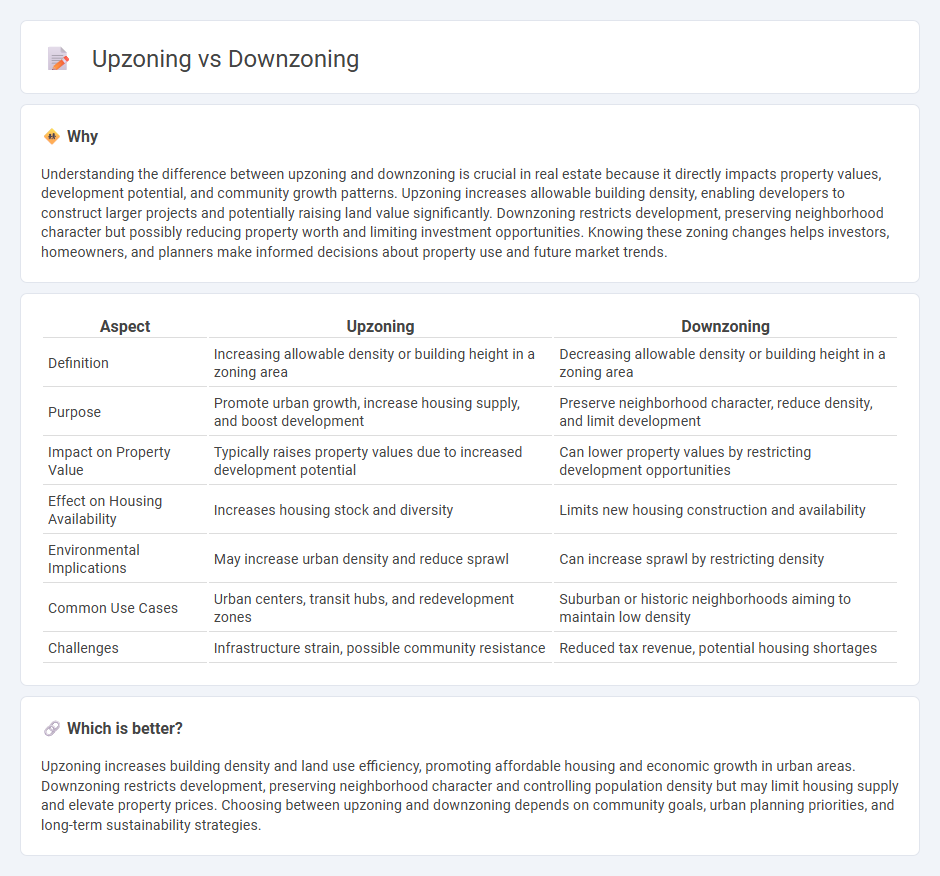
| Aspect | Upzoning | Downzoning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increasing allowable density or building height in a zoning area | Decreasing allowable density or building height in a zoning area |
| Purpose | Promote urban growth, increase housing supply, and boost development | Preserve neighborhood character, reduce density, and limit development |
| Impact on Property Value | Typically raises property values due to increased development potential | Can lower property values by restricting development opportunities |
| Effect on Housing Availability | Increases housing stock and diversity | Limits new housing construction and availability |
| Environmental Implications | May increase urban density and reduce sprawl | Can increase sprawl by restricting density |
| Common Use Cases | Urban centers, transit hubs, and redevelopment zones | Suburban or historic neighborhoods aiming to maintain low density |
| Challenges | Infrastructure strain, possible community resistance | Reduced tax revenue, potential housing shortages |
Which is better?
Upzoning increases building density and land use efficiency, promoting affordable housing and economic growth in urban areas. Downzoning restricts development, preserving neighborhood character and controlling population density but may limit housing supply and elevate property prices. Choosing between upzoning and downzoning depends on community goals, urban planning priorities, and long-term sustainability strategies.
Connection
Upzoning and downzoning are land use regulations that directly impact real estate development density and property values by adjusting allowable building heights and uses. Upzoning permits higher density and taller structures, often increasing supply and attracting investment, while downzoning restricts development intensity to preserve neighborhood character or control growth. These zoning changes influence market dynamics, urban planning, and housing availability by shaping the scale and type of real estate projects permitted in specific areas.
Key Terms
Density
Downzoning reduces allowable building density, limiting the number of units or floor area ratio (FAR) to preserve neighborhood character and control urban sprawl. Upzoning increases density, permitting higher building heights, more units, and greater FAR to promote urban growth and housing supply. Explore detailed impacts of zoning density on community development and real estate markets.
Land Use
Downzoning restricts land use by lowering allowable building density, reducing commercial or residential development potential to preserve community character or limit environmental impact. Upzoning increases land use intensity, permitting higher-density buildings and mixed-use developments to promote urban growth, affordable housing, and economic activity. Explore more about the impacts of zoning changes on urban planning and property values.
Property Value
Downzoning typically reduces property value by limiting the allowable density or land use, thereby restricting development potential and future income opportunities. Upzoning often increases property value by enabling higher density buildings, mixed-use developments, or commercial uses that boost demand and profitability. Explore further to understand how zoning changes impact real estate investments and local market dynamics.
Source and External Links
Downzoning: Definition, Purpose, and Implications - Downzoning is the process where authorities reduce the allowable density or intensity of land use, typically to preserve open spaces, control urban sprawl, reduce infrastructure strain, or maintain community character by shifting zoning to lower-impact uses like single-family homes.
Limits on "Down-Zoning" - Coates' Canons NC Local ... - Downzoning broadly means rezoning property to a less dense or less intense use, and laws may require owner consent before reducing development density to protect property rights.
Understanding Downzoning. - Downzoning often occurs against landowner objections, reducing land use intensity and property value, yet it remains legal within constitutional limits as a tool of local government planning.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com