Brownfield redevelopment involves revitalizing previously industrial or contaminated sites, transforming underutilized land into safe, productive real estate, often requiring environmental cleanup that boosts community health and property values. Infill development focuses on building within existing urban areas on vacant or underused parcels, promoting sustainable growth by maximizing infrastructure and reducing urban sprawl. Explore how these distinct strategies impact real estate markets and urban planning to determine the best fit for your investment or development goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between brownfield redevelopment and infill development is crucial for real estate investors to assess environmental risks and potential remediation costs versus maximizing urban land use efficiency and community revitalization. Brownfield redevelopment involves transforming previously contaminated or industrial land, often requiring environmental cleanup, while infill development focuses on building within existing urban areas on vacant or underused parcels without significant contamination concerns. Knowing these distinctions impacts project feasibility, regulatory compliance, and long-term value creation in urban real estate markets. This knowledge guides strategic planning and investment decisions, optimizing returns while supporting sustainable urban growth.
Comparison Table
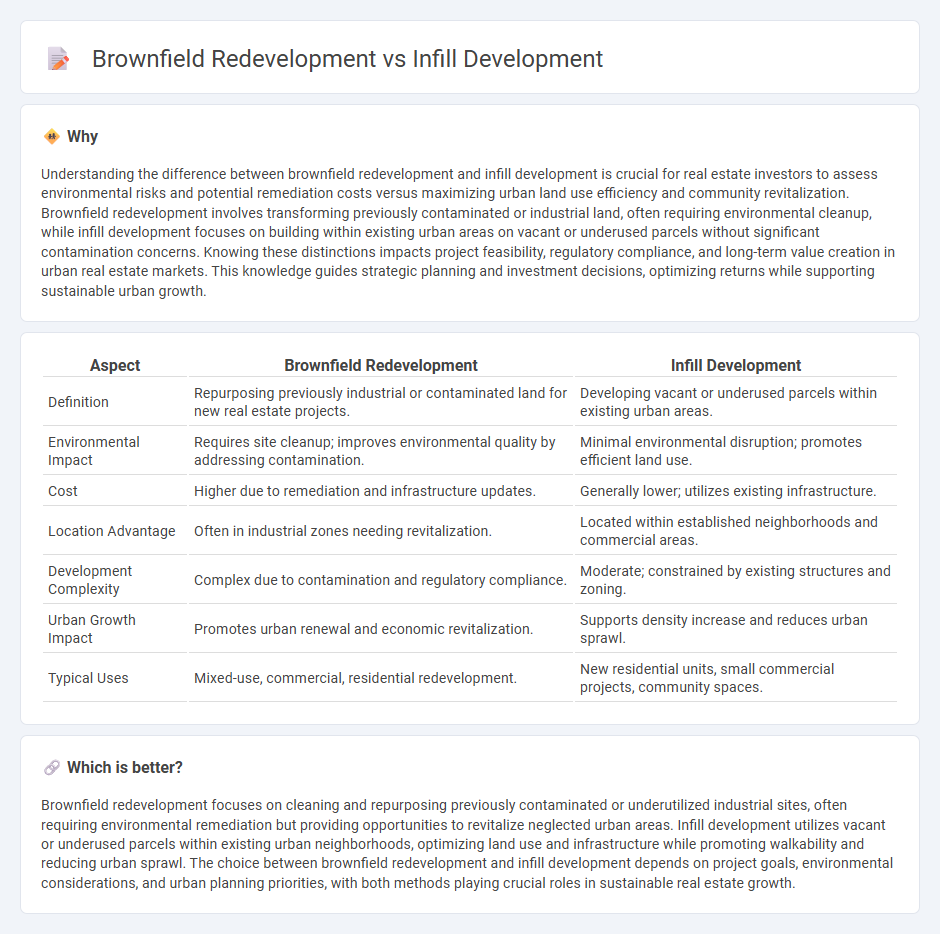
| Aspect | Brownfield Redevelopment | Infill Development |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repurposing previously industrial or contaminated land for new real estate projects. | Developing vacant or underused parcels within existing urban areas. |
| Environmental Impact | Requires site cleanup; improves environmental quality by addressing contamination. | Minimal environmental disruption; promotes efficient land use. |
| Cost | Higher due to remediation and infrastructure updates. | Generally lower; utilizes existing infrastructure. |
| Location Advantage | Often in industrial zones needing revitalization. | Located within established neighborhoods and commercial areas. |
| Development Complexity | Complex due to contamination and regulatory compliance. | Moderate; constrained by existing structures and zoning. |
| Urban Growth Impact | Promotes urban renewal and economic revitalization. | Supports density increase and reduces urban sprawl. |
| Typical Uses | Mixed-use, commercial, residential redevelopment. | New residential units, small commercial projects, community spaces. |
Which is better?
Brownfield redevelopment focuses on cleaning and repurposing previously contaminated or underutilized industrial sites, often requiring environmental remediation but providing opportunities to revitalize neglected urban areas. Infill development utilizes vacant or underused parcels within existing urban neighborhoods, optimizing land use and infrastructure while promoting walkability and reducing urban sprawl. The choice between brownfield redevelopment and infill development depends on project goals, environmental considerations, and urban planning priorities, with both methods playing crucial roles in sustainable real estate growth.
Connection
Brownfield redevelopment and infill development are connected through their mutual focus on maximizing underutilized urban land, reducing urban sprawl, and promoting sustainable growth. Brownfield sites, often contaminated or abandoned industrial properties, present opportunities for infill development by transforming these neglected spaces into valuable residential, commercial, or mixed-use real estate. Both strategies enhance property values, improve infrastructure efficiency, and support environmental remediation within existing city boundaries.
Key Terms
Land Utilization
Infill development maximizes underused urban parcels within established areas, enhancing land utilization by reducing urban sprawl and promoting efficient infrastructure use. Brownfield redevelopment involves revitalizing previously contaminated or industrial sites, transforming them into productive spaces that restore land value and mitigate environmental hazards. Explore detailed strategies and benefits of both approaches to optimize land use in urban planning.
Environmental Remediation
Environmental remediation plays a critical role in both infill development and brownfield redevelopment, with the latter often requiring extensive cleanup of contaminated sites due to previous industrial use. Infill development typically addresses underutilized urban land, focusing on minimizing environmental impacts while enhancing green spaces and reducing urban sprawl. Explore further to understand how remediation strategies differ and impact sustainable urban growth.
Urban Density
Infill development enhances urban density by utilizing vacant or underused land within existing urban areas, promoting efficient land use and reducing urban sprawl. Brownfield redevelopment revitalizes contaminated or previously industrial sites, increasing density while addressing environmental concerns and improving community health. Explore the benefits and challenges of these strategies to understand their impact on sustainable urban growth.
Source and External Links
What is Infill Development? | Definition, Key Components & Examples - Infill development involves utilizing vacant or underutilized urban land to increase density and improve community functionality.
What Is Infill Development? | Planopedia - Infill development is a strategy to construct buildings on unused land within urban areas, promoting density and sustainable urban growth.
Smart Growth and Infill Brownfields Redevelopment | US EPA - Infill development can be used to increase density by redeveloping underused sites, such as brownfields, near existing infrastructure.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com