Lease-to-own models offer tenants the opportunity to apply a portion of their monthly rent toward the eventual purchase of the property, creating a pathway to homeownership without immediate mortgage financing. Rent-to-own agreements combine rental and purchase options, often including a fixed purchase price and contract terms that benefit both landlords and tenants through flexibility and investment in the property's future value. Explore detailed comparisons and benefits of lease-to-own versus rent-to-own strategies to determine the best fit for your real estate goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between lease to own models and rent-to-own agreements is crucial for making informed real estate investment decisions and securing favorable financial terms. Lease to own typically involves predetermined purchase conditions and price, whereas rent-to-own allows renters to apply rental payments toward a future purchase. Recognizing these distinctions helps buyers assess legal obligations, potential risks, and long-term benefits. This knowledge ensures strategic planning in property acquisition and equity building.
Comparison Table
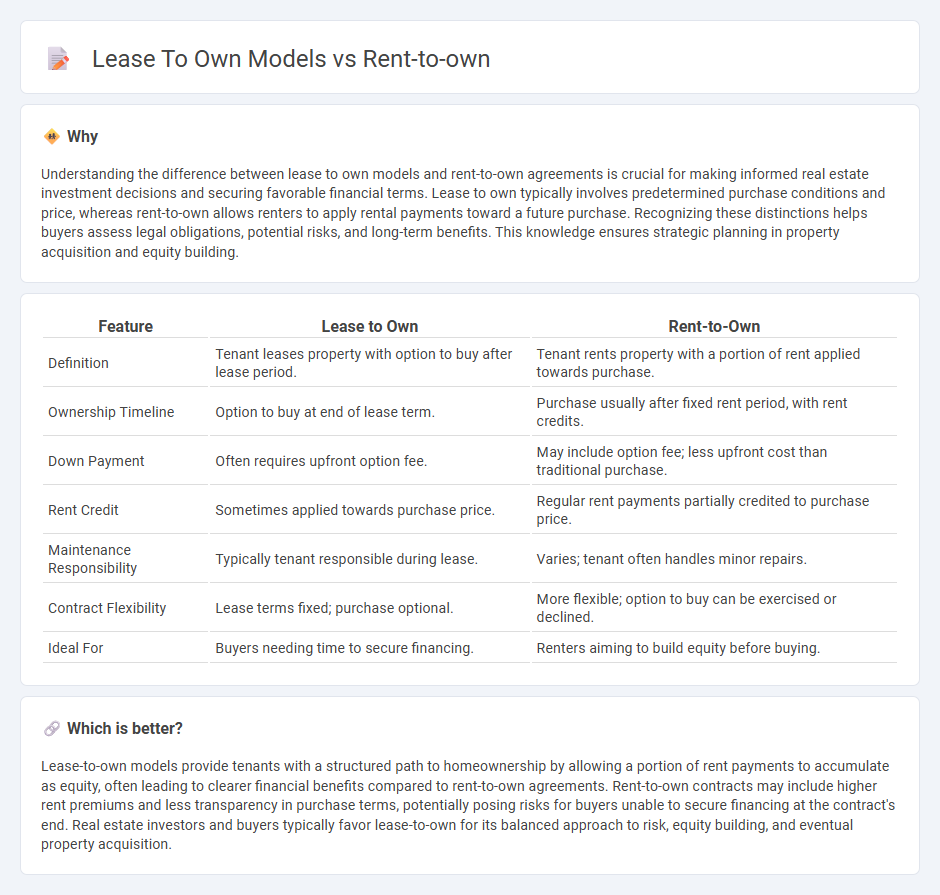
| Feature | Lease to Own | Rent-to-Own |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tenant leases property with option to buy after lease period. | Tenant rents property with a portion of rent applied towards purchase. |
| Ownership Timeline | Option to buy at end of lease term. | Purchase usually after fixed rent period, with rent credits. |
| Down Payment | Often requires upfront option fee. | May include option fee; less upfront cost than traditional purchase. |
| Rent Credit | Sometimes applied towards purchase price. | Regular rent payments partially credited to purchase price. |
| Maintenance Responsibility | Typically tenant responsible during lease. | Varies; tenant often handles minor repairs. |
| Contract Flexibility | Lease terms fixed; purchase optional. | More flexible; option to buy can be exercised or declined. |
| Ideal For | Buyers needing time to secure financing. | Renters aiming to build equity before buying. |
Which is better?
Lease-to-own models provide tenants with a structured path to homeownership by allowing a portion of rent payments to accumulate as equity, often leading to clearer financial benefits compared to rent-to-own agreements. Rent-to-own contracts may include higher rent premiums and less transparency in purchase terms, potentially posing risks for buyers unable to secure financing at the contract's end. Real estate investors and buyers typically favor lease-to-own for its balanced approach to risk, equity building, and eventual property acquisition.
Connection
Lease-to-own models and rent-to-own agreements both provide pathways for tenants to purchase property by applying rental payments toward future ownership, bridging the gap between renting and buying. These arrangements often include contractual terms specifying the portion of rent credited toward the purchase price, making homeownership accessible to individuals with limited upfront capital or credit challenges. Real estate markets leverage these models to expand buyer pools and facilitate property sales in competitive or uncertain economic environments.
Key Terms
Option to Purchase
Rent-to-own and lease-to-own models both provide tenants with the option to purchase the property during or at the end of the rental agreement, allowing a portion of the rent to be credited toward the eventual purchase price. The option to purchase agreement outlines specific terms such as the duration of the rental period, purchase price, and conditions for exercising the option, which can vary significantly between the two models depending on jurisdiction and contract structure. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which model best aligns with your financial goals and homeownership timeline.
Lease Agreement
Lease-to-own models provide consumers with a lease agreement that includes an option to purchase the leased asset after a predefined period, often applying a portion of the lease payments toward the final purchase price. These agreements specify terms such as duration, payment schedule, and conditions for exercising the ownership option, distinguishing them from traditional rent-to-own contracts that may have more flexible or shorter terms. Explore the key differences and benefits of lease-to-own agreements to determine the best fit for your ownership goals.
Rent Credits
Rent-to-own and lease-to-own models both allow tenants to apply a portion of their monthly payments, known as rent credits, toward the eventual purchase of the property. Rent credits accumulate over time, lowering the final purchase price or serving as a down payment, which can make homeownership more accessible for renters with limited upfront capital. Explore how rent credits work in different agreements to determine which model best supports your path to owning a home.
Source and External Links
How Does Rent-To-Own Work? - This webpage explains how rent-to-own agreements work, involving a rental agreement with an option or requirement to buy the property later.
Rent-to-own - This Wikipedia article describes rent-to-own as a transaction where property is leased with the option to purchase, commonly used for both consumer goods and real estate.
What You Need to Know About Rent-to-Own in Illinois - This blog post discusses the benefits and risks of rent-to-own agreements in Illinois, including lease-option and lease-purchase contracts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com