Tiny home villages focus on compact, affordable living spaces designed to maximize efficiency and minimize environmental impact through shared amenities and sustainable building materials. Eco-villages extend this concept by integrating broader sustainability practices such as communal agriculture, renewable energy systems, and waste reduction initiatives aimed at fostering self-sufficient, environmentally conscious communities. Explore the key differences and benefits of these innovative housing solutions to find out which one aligns with your lifestyle and values.
Why it is important
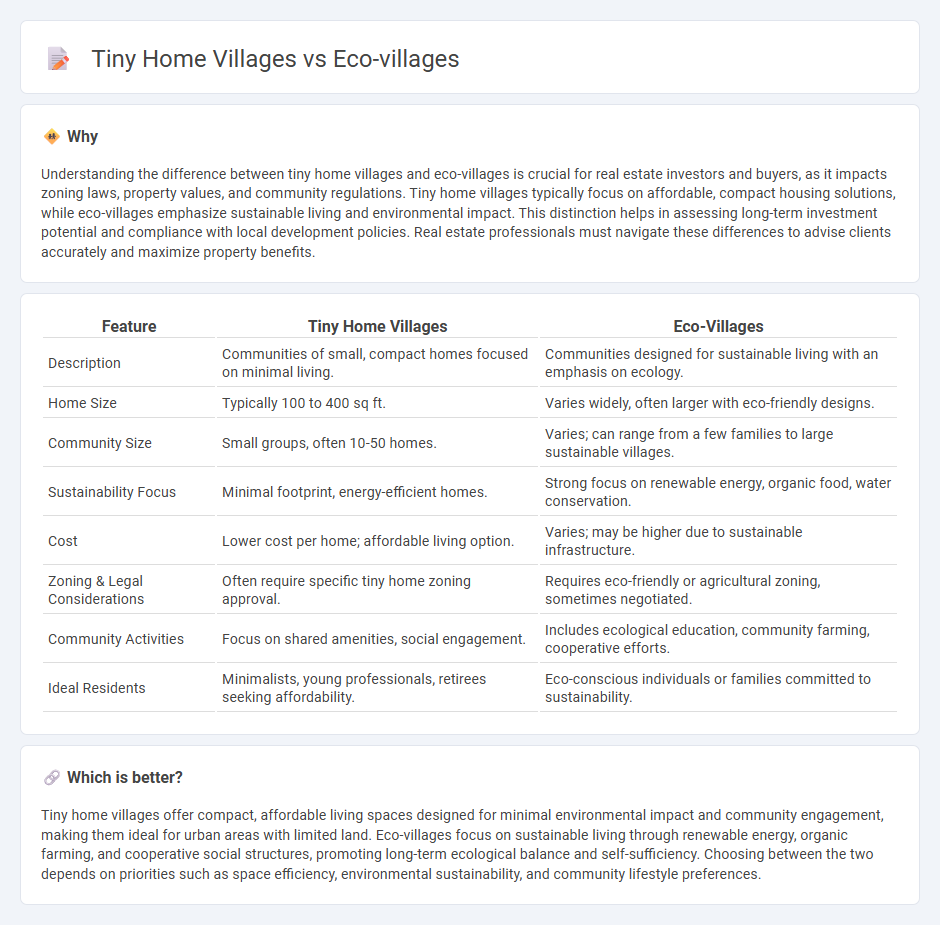
Understanding the difference between tiny home villages and eco-villages is crucial for real estate investors and buyers, as it impacts zoning laws, property values, and community regulations. Tiny home villages typically focus on affordable, compact housing solutions, while eco-villages emphasize sustainable living and environmental impact. This distinction helps in assessing long-term investment potential and compliance with local development policies. Real estate professionals must navigate these differences to advise clients accurately and maximize property benefits.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tiny Home Villages | Eco-Villages |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Communities of small, compact homes focused on minimal living. | Communities designed for sustainable living with an emphasis on ecology. |
| Home Size | Typically 100 to 400 sq ft. | Varies widely, often larger with eco-friendly designs. |
| Community Size | Small groups, often 10-50 homes. | Varies; can range from a few families to large sustainable villages. |
| Sustainability Focus | Minimal footprint, energy-efficient homes. | Strong focus on renewable energy, organic food, water conservation. |
| Cost | Lower cost per home; affordable living option. | Varies; may be higher due to sustainable infrastructure. |
| Zoning & Legal Considerations | Often require specific tiny home zoning approval. | Requires eco-friendly or agricultural zoning, sometimes negotiated. |
| Community Activities | Focus on shared amenities, social engagement. | Includes ecological education, community farming, cooperative efforts. |
| Ideal Residents | Minimalists, young professionals, retirees seeking affordability. | Eco-conscious individuals or families committed to sustainability. |
Which is better?
Tiny home villages offer compact, affordable living spaces designed for minimal environmental impact and community engagement, making them ideal for urban areas with limited land. Eco-villages focus on sustainable living through renewable energy, organic farming, and cooperative social structures, promoting long-term ecological balance and self-sufficiency. Choosing between the two depends on priorities such as space efficiency, environmental sustainability, and community lifestyle preferences.
Connection
Tiny home villages and eco-villages share a commitment to sustainable living and efficient land use, promoting community-oriented designs that reduce environmental impact. Both concepts emphasize minimalistic housing structures, renewable energy sources, and shared resources to foster economic and ecological sustainability. These models appeal to environmentally conscious individuals seeking affordable housing solutions within close-knit, resource-efficient communities.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Eco-villages prioritize sustainable living through community-driven practices such as renewable energy use, organic farming, and resource sharing, reducing overall ecological footprints. Tiny home villages emphasize minimalistic design and reduced living space to lower energy consumption and waste generation, fostering sustainable lifestyles on a smaller scale. Explore the key principles and benefits of each model to understand their impact on sustainable development.
Zoning Regulations
Eco-villages often face complex zoning regulations due to their emphasis on sustainable living, shared resources, and communal land use, which may conflict with traditional residential zoning codes. Tiny home villages, while also impacted by zoning laws, typically navigate these challenges by adhering to specific size restrictions and utilizing accessory dwelling unit (ADU) or mobile home classifications. Explore the nuances of zoning regulations and how they affect the development and sustainability of both eco-villages and tiny home villages to understand their growth potential.
Community Governance
Eco-villages emphasize collective decision-making through consensus or sociocracy, fostering shared values around sustainability and social equity. Tiny home villages often combine private ownership with community rules, balancing individual autonomy with collaborative governance models. Explore how these approaches shape resilient, inclusive living by learning more about their community governance frameworks.
Source and External Links
Ecovillages From Around the World for Sustainable Living - Earth.Org - An ecovillage is an intentional, traditional, or urban community focused on achieving social, cultural, ecological, and economic sustainability through participatory processes and locally owned solutions.
5 of the World's Coolest EcoVillages - The World Economic Forum - Ecovillages are intentional communities designed to minimize environmental impact and often feature innovative sustainable practices like renewable energy, green building, and local food production.
Ecovillage - Wikipedia - Ecovillages prioritize environmental stewardship, resource conservation, and strong social connections, striving for self-sufficiency and resilience through shared responsibilities and sustainable design.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com