Smart lease agreements utilize advanced technology to automate rent payments, maintenance requests, and contract management, enhancing efficiency and transparency in property rental. Net leases transfer some or all operating expenses--such as property taxes, insurance, and maintenance--to the tenant, creating a clear cost structure favored in commercial real estate. Explore the distinct advantages of smart lease agreements versus net leases to optimize your property investment strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between smart lease agreements and net leases is crucial for real estate investors to optimize risk management and cash flow predictability. Smart leases integrate technology for automated rent collection and maintenance tracking, enhancing operational efficiency. Net leases require tenants to pay property expenses like taxes, insurance, and maintenance, shifting financial responsibility from landlords. Distinguishing these lease types helps investors make informed decisions on property management and investment returns.
Comparison Table
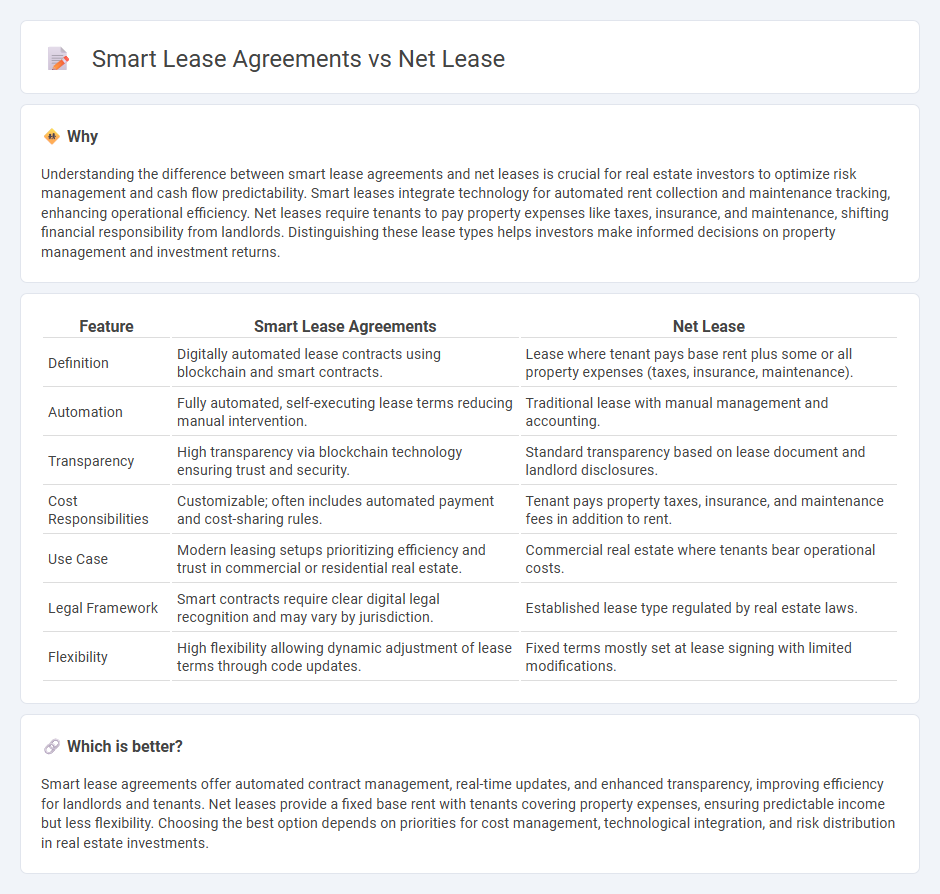
| Feature | Smart Lease Agreements | Net Lease |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digitally automated lease contracts using blockchain and smart contracts. | Lease where tenant pays base rent plus some or all property expenses (taxes, insurance, maintenance). |
| Automation | Fully automated, self-executing lease terms reducing manual intervention. | Traditional lease with manual management and accounting. |
| Transparency | High transparency via blockchain technology ensuring trust and security. | Standard transparency based on lease document and landlord disclosures. |
| Cost Responsibilities | Customizable; often includes automated payment and cost-sharing rules. | Tenant pays property taxes, insurance, and maintenance fees in addition to rent. |
| Use Case | Modern leasing setups prioritizing efficiency and trust in commercial or residential real estate. | Commercial real estate where tenants bear operational costs. |
| Legal Framework | Smart contracts require clear digital legal recognition and may vary by jurisdiction. | Established lease type regulated by real estate laws. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility allowing dynamic adjustment of lease terms through code updates. | Fixed terms mostly set at lease signing with limited modifications. |
Which is better?
Smart lease agreements offer automated contract management, real-time updates, and enhanced transparency, improving efficiency for landlords and tenants. Net leases provide a fixed base rent with tenants covering property expenses, ensuring predictable income but less flexibility. Choosing the best option depends on priorities for cost management, technological integration, and risk distribution in real estate investments.
Connection
Smart lease agreements utilize blockchain technology to automate and secure contract execution, ensuring transparency and efficiency in real estate transactions. Net leases, where tenants pay base rent plus additional expenses like taxes and maintenance, benefit from smart leases by streamlining rent calculations and expense tracking through automated data inputs. This integration reduces disputes and enhances trust between landlords and tenants in commercial real estate management.
Key Terms
Operating Expenses
Net lease agreements require tenants to pay a portion or all operating expenses, including property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs, shifting financial responsibility from landlords to tenants. Smart lease agreements leverage technology and data analytics to provide more transparent and precise allocation of operating expenses, optimizing cost efficiency and reducing disputes. Explore how smart leases can transform your approach to managing operating expenses in commercial real estate.
Automation Technology
Net lease agreements typically require tenants to handle property expenses such as maintenance, insurance, and taxes, limiting automation integration to tenant-specific systems. Smart lease agreements incorporate automation technology extensively, allowing remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and dynamic energy management to optimize operational efficiency for both landlords and tenants. Explore how smart lease automation can transform property management and tenant experience.
Tenant Responsibilities
Net lease agreements typically place most property expenses, including maintenance, taxes, and insurance, on the tenant, increasing their financial obligations beyond base rent. Smart lease agreements often leverage technology to monitor usage and optimize costs while providing tenants with clearer, data-driven insights into their responsibilities for utilities and maintenance. Explore detailed comparisons of tenant responsibilities in both lease types to make informed leasing decisions.
Source and External Links
net lease | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - A net lease is a commercial lease where the tenant pays base rent plus some or all operating expenses like taxes, insurance, and maintenance; types include single net (tenant pays rent plus property taxes), double net (tenant pays rent plus taxes and insurance), and triple net (tenant pays rent plus all expenses including maintenance).
Net Lease - Glossary of CRE Terms - A net lease means the tenant pays base rent plus a pro rata share of operating expenses, with common types being single net, double net, triple net, and absolute triple net, where the tenant assumes increasing responsibility for costs, benefiting landlords by reducing their management responsibilities and stabilizing income.
Net lease - Wikipedia - In commercial real estate, a net lease requires the tenant to pay rent plus some or all property expenses typically paid by the owner, commonly property taxes, insurance, and maintenance, with the triple net lease (NNN) being the standard where tenants cover all three nets, differing from gross leases where the landlord pays expenses out of rent.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com