Opportunity Zone investing offers significant tax incentives by allowing investors to defer and potentially reduce capital gains taxes when investing in designated low-income communities. Ground leases provide a stable income stream by leasing land while allowing tenants to build and maintain improvements, preserving the landowner's long-term equity. Explore how each strategy can maximize your real estate portfolio benefits and tax advantages.
Why it is important
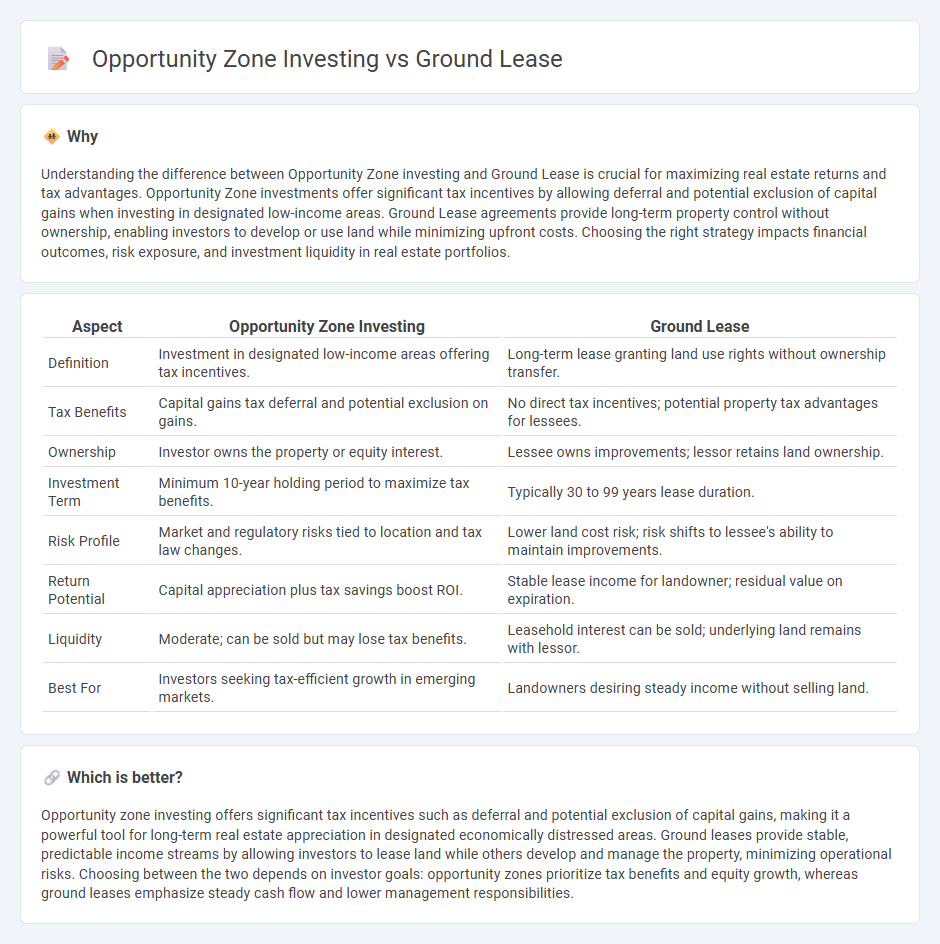
Understanding the difference between Opportunity Zone investing and Ground Lease is crucial for maximizing real estate returns and tax advantages. Opportunity Zone investments offer significant tax incentives by allowing deferral and potential exclusion of capital gains when investing in designated low-income areas. Ground Lease agreements provide long-term property control without ownership, enabling investors to develop or use land while minimizing upfront costs. Choosing the right strategy impacts financial outcomes, risk exposure, and investment liquidity in real estate portfolios.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Opportunity Zone Investing | Ground Lease |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in designated low-income areas offering tax incentives. | Long-term lease granting land use rights without ownership transfer. |
| Tax Benefits | Capital gains tax deferral and potential exclusion on gains. | No direct tax incentives; potential property tax advantages for lessees. |
| Ownership | Investor owns the property or equity interest. | Lessee owns improvements; lessor retains land ownership. |
| Investment Term | Minimum 10-year holding period to maximize tax benefits. | Typically 30 to 99 years lease duration. |
| Risk Profile | Market and regulatory risks tied to location and tax law changes. | Lower land cost risk; risk shifts to lessee's ability to maintain improvements. |
| Return Potential | Capital appreciation plus tax savings boost ROI. | Stable lease income for landowner; residual value on expiration. |
| Liquidity | Moderate; can be sold but may lose tax benefits. | Leasehold interest can be sold; underlying land remains with lessor. |
| Best For | Investors seeking tax-efficient growth in emerging markets. | Landowners desiring steady income without selling land. |
Which is better?
Opportunity zone investing offers significant tax incentives such as deferral and potential exclusion of capital gains, making it a powerful tool for long-term real estate appreciation in designated economically distressed areas. Ground leases provide stable, predictable income streams by allowing investors to lease land while others develop and manage the property, minimizing operational risks. Choosing between the two depends on investor goals: opportunity zones prioritize tax benefits and equity growth, whereas ground leases emphasize steady cash flow and lower management responsibilities.
Connection
Opportunity Zone investing allows investors to defer and reduce capital gains taxes by investing in designated low-income areas, enhancing real estate development potential. Ground Lease agreements, where tenants lease land for long periods while owning improvements, complement Opportunity Zone projects by providing stable, long-term financing structures. Combining these strategies attracts capital for revitalizing underserved communities while maximizing tax benefits and securing sustainable property control.
Key Terms
Leasehold Interest
Ground leases grant leasehold interests, allowing tenants to control property use without owning the land, generating steady income streams often linked to long-term, inflation-protected leases. Opportunity zone investing provides tax incentives for capital gains reinvested in designated low-income areas, fostering economic growth and offering potential for significant appreciation. Explore the strategic benefits of leasehold interests in ground leases compared to the tax advantages of opportunity zone investments to make informed real estate decisions.
Tax Deferral
Ground lease investments provide steady income streams and potential property appreciation while offering tax deferral through depreciation and interest expense deductions. Opportunity zone investing enables deferral and potential elimination of capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds in designated zones, with added incentives for long-term holdings. Explore the advantages of each strategy to optimize your tax deferral benefits effectively.
Capital Gains
Ground lease investments generate steady income without property ownership, minimizing exposure to capital gains tax upon sale. Opportunity zone investing offers significant capital gains tax deferral and potential exclusion benefits by reinvesting gains into designated economically distressed areas. Explore detailed comparisons of ground lease structures and opportunity zone tax advantages to optimize your investment strategy.
Source and External Links
Ground Lease vs Land Lease: Key Differences - This webpage explores the differences between ground leases and land leases, highlighting ground leases as long-term agreements where the landowner retains ownership while the tenant develops the property.
Key Considerations in a Ground Lease - This article discusses the key considerations and advantages for both landlords and tenants in negotiating a ground lease, including stable income and avoidance of upfront costs.
How do Ground Leases Work in Dallas - This webpage explains how ground leases function in Dallas, covering aspects such as lease terms, rent payments, use restrictions, and types of ground leases.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com