Vertical farming buildings utilize innovative agricultural technology to maximize crop yield in urban environments, optimizing space and resource efficiency. Hospitals prioritize patient care and medical infrastructure, requiring specialized design for health services, safety, and accessibility. Explore the key differences in design and functionality between these two vital real estate developments to understand their unique contributions to urban landscapes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between vertical farming buildings and hospitals is crucial for real estate investors and developers because these structures serve vastly different purposes, requiring unique design, zoning, and operational considerations. Vertical farms emphasize sustainable agriculture with controlled environments, influencing factors like energy consumption and crop yield optimization, while hospitals prioritize patient care, safety regulations, and specialized medical infrastructure. Knowing these distinctions aids accurate property valuation, proper regulatory compliance, and strategic investment decisions in diverse urban development projects. This knowledge supports targeted real estate planning that aligns with industry-specific needs and community benefits.
Comparison Table
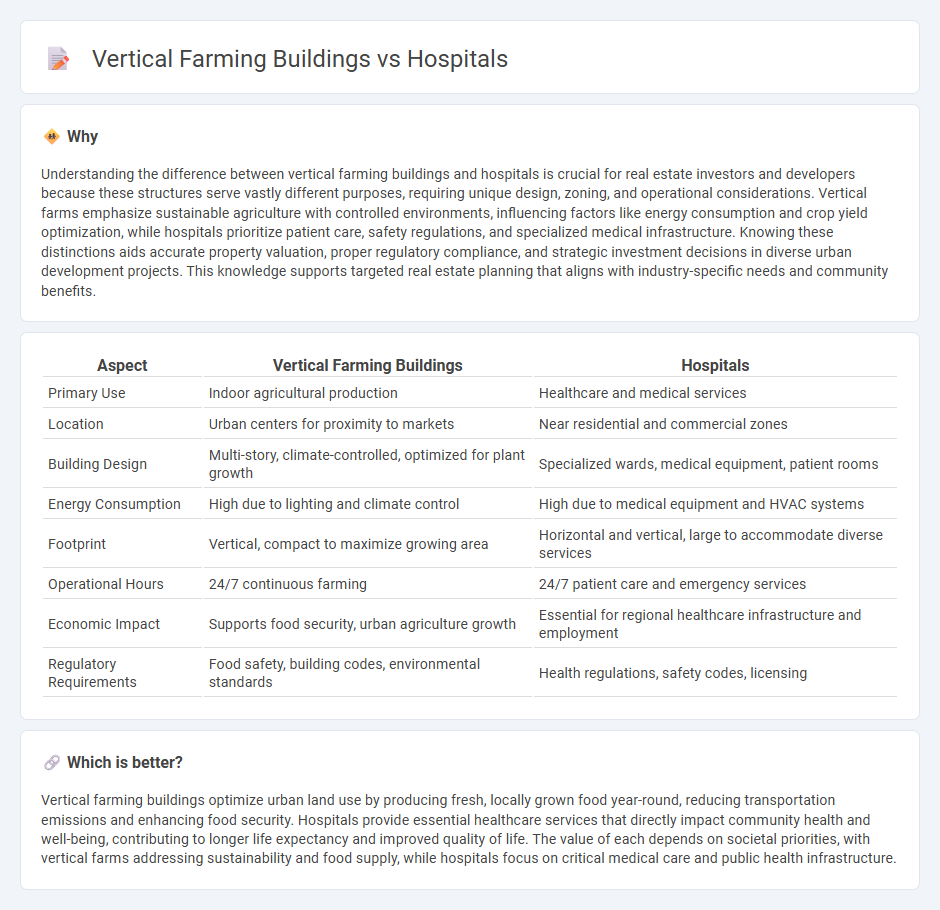
| Aspect | Vertical Farming Buildings | Hospitals |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Indoor agricultural production | Healthcare and medical services |
| Location | Urban centers for proximity to markets | Near residential and commercial zones |
| Building Design | Multi-story, climate-controlled, optimized for plant growth | Specialized wards, medical equipment, patient rooms |
| Energy Consumption | High due to lighting and climate control | High due to medical equipment and HVAC systems |
| Footprint | Vertical, compact to maximize growing area | Horizontal and vertical, large to accommodate diverse services |
| Operational Hours | 24/7 continuous farming | 24/7 patient care and emergency services |
| Economic Impact | Supports food security, urban agriculture growth | Essential for regional healthcare infrastructure and employment |
| Regulatory Requirements | Food safety, building codes, environmental standards | Health regulations, safety codes, licensing |
Which is better?
Vertical farming buildings optimize urban land use by producing fresh, locally grown food year-round, reducing transportation emissions and enhancing food security. Hospitals provide essential healthcare services that directly impact community health and well-being, contributing to longer life expectancy and improved quality of life. The value of each depends on societal priorities, with vertical farms addressing sustainability and food supply, while hospitals focus on critical medical care and public health infrastructure.
Connection
Vertical farming buildings and hospitals share a connection through their integration within urban real estate developments aimed at enhancing sustainability and health outcomes. Both structures require advanced architectural designs to optimize space, energy efficiency, and environmental control, contributing to improved air quality and resource management in densely populated areas. This synergy supports the growing trend of mixed-use real estate projects that combine healthcare facilities and agricultural innovation to promote community well-being and resilience.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations significantly impact the development of both hospitals and vertical farming buildings by dictating land use, building height, and environmental compliance within urban areas. Hospitals require zoning that supports healthcare infrastructure, emergency access, and proximity to residential zones, while vertical farming buildings often need allowances for agricultural use in commercial or industrial districts with considerations for water management and energy efficiency. Explore how specific zoning laws shape the future of sustainable urban development in healthcare and agriculture.
Building Infrastructure Requirements
Hospitals require advanced HVAC systems, stringent fire safety measures, and robust electrical infrastructure to support medical equipment and ensure patient safety. Vertical farming buildings prioritize controlled environment agriculture technology, including LED grow lights, climate control, and water recycling systems to maximize crop yield in limited spaces. Explore detailed comparisons of building infrastructure requirements to optimize design for healthcare and urban agriculture.
Environmental Impact
Hospitals typically have high energy demands due to medical equipment, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, leading to significant carbon footprints, whereas vertical farming buildings are designed to optimize energy efficiency through LED lighting and controlled environments, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Vertical farms utilize renewable energy sources and water recycling systems, minimizing environmental impact compared to traditional hospital operations that generate substantial medical waste and water usage. Explore the latest studies comparing the sustainability and environmental benefits of hospitals versus vertical farming facilities to understand future urban planning possibilities.
Source and External Links
Hospitals near Irvine, CA - Healthgrades - Provides a list of hospitals near Irvine, including Foothill Regional Medical Center and Kaiser Permanente Orange County-Irvine Medical Center.
Hoag: Best Health System in Orange County - Known for superior patient outcomes with top-ranked hospitals and urgent care locations throughout Orange County.
About Our Locations - UCI Health - Offers comprehensive outpatient care and state-of-the-art medical centers across Southern California, including locations in Irvine and other areas.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com