Upzoning increases building density in existing urban areas, allowing for more housing units and mixed-use developments, which maximizes land use efficiency and supports sustainable growth. Greenfield development involves constructing new properties on previously undeveloped land, often on the outskirts of cities, leading to urban sprawl and increased infrastructure costs. Explore the advantages and challenges of upzoning versus greenfield development to understand their impact on real estate and urban planning.
Why it is important
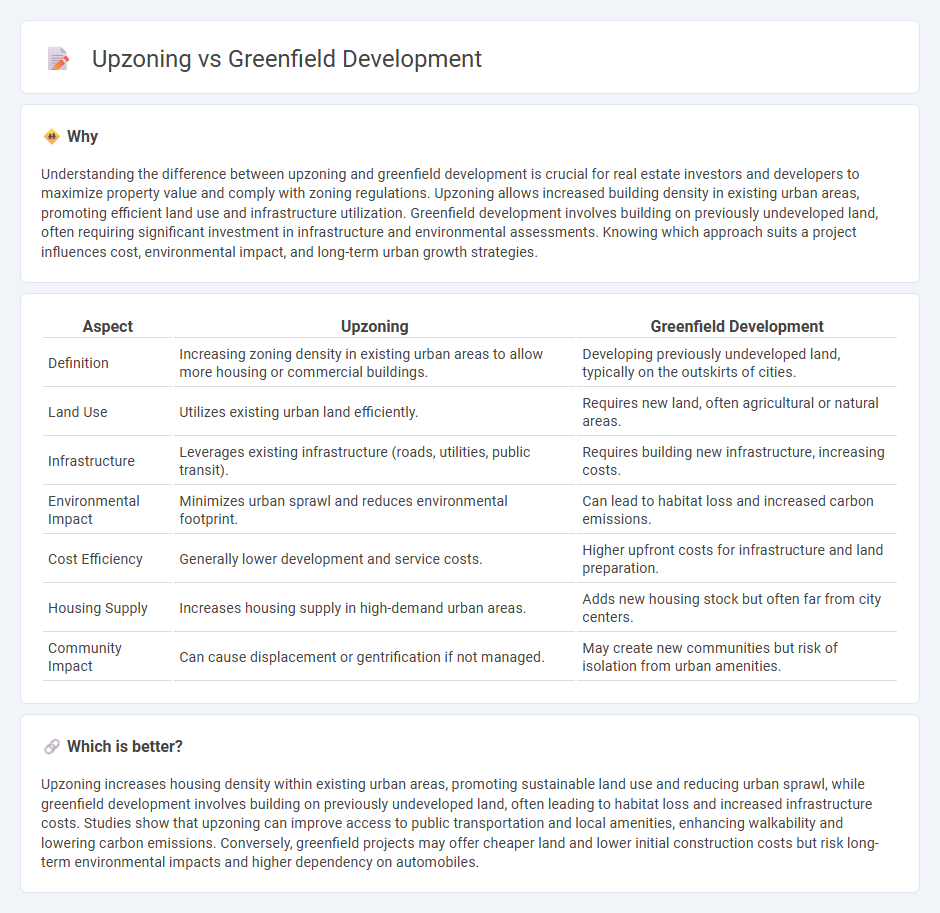
Understanding the difference between upzoning and greenfield development is crucial for real estate investors and developers to maximize property value and comply with zoning regulations. Upzoning allows increased building density in existing urban areas, promoting efficient land use and infrastructure utilization. Greenfield development involves building on previously undeveloped land, often requiring significant investment in infrastructure and environmental assessments. Knowing which approach suits a project influences cost, environmental impact, and long-term urban growth strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Upzoning | Greenfield Development |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increasing zoning density in existing urban areas to allow more housing or commercial buildings. | Developing previously undeveloped land, typically on the outskirts of cities. |
| Land Use | Utilizes existing urban land efficiently. | Requires new land, often agricultural or natural areas. |
| Infrastructure | Leverages existing infrastructure (roads, utilities, public transit). | Requires building new infrastructure, increasing costs. |
| Environmental Impact | Minimizes urban sprawl and reduces environmental footprint. | Can lead to habitat loss and increased carbon emissions. |
| Cost Efficiency | Generally lower development and service costs. | Higher upfront costs for infrastructure and land preparation. |
| Housing Supply | Increases housing supply in high-demand urban areas. | Adds new housing stock but often far from city centers. |
| Community Impact | Can cause displacement or gentrification if not managed. | May create new communities but risk of isolation from urban amenities. |
Which is better?
Upzoning increases housing density within existing urban areas, promoting sustainable land use and reducing urban sprawl, while greenfield development involves building on previously undeveloped land, often leading to habitat loss and increased infrastructure costs. Studies show that upzoning can improve access to public transportation and local amenities, enhancing walkability and lowering carbon emissions. Conversely, greenfield projects may offer cheaper land and lower initial construction costs but risk long-term environmental impacts and higher dependency on automobiles.
Connection
Upzoning increases allowable building density, making greenfield development more attractive by enabling higher returns on previously low-density land. Greenfield development involves constructing new buildings on undeveloped land, often benefiting from upzoning that permits larger-scale projects. This synergy accelerates urban expansion, addressing housing shortages through increased supply on fresh land parcels facilitated by adjusted zoning regulations.
Key Terms
Land Use
Greenfield development involves constructing new projects on previously undeveloped land, often on the urban fringe, leading to expanded land use and potential habitat disruption. Upzoning modifies existing zoning regulations to allow higher density or diverse land uses in developed areas, optimizing land efficiency and infrastructure utilization. Explore the implications of these land use strategies to determine the best approach for sustainable urban growth.
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations play a crucial role in greenfield development by designating undeveloped land for new construction, often promoting suburban expansion and new infrastructure. Upzoning modifies existing zoning laws to allow for higher-density buildings and mixed-use developments, encouraging urban infill and better land use efficiency. Explore the impact of these zoning strategies on sustainable urban growth and housing markets to understand their long-term benefits.
Infrastructure
Greenfield development involves building new infrastructure on previously undeveloped land, enabling customized design and modern utilities tailored to growth demands. Upzoning focuses on increasing density within existing urban areas, leveraging existing infrastructure but often requiring upgrades to support higher population loads, such as expanded public transit and utilities. Explore the key differences in infrastructure impact and planning strategies between greenfield development and upzoning to optimize urban growth.
Source and External Links
A Guide to Greenfield Development - This guide explains what greenfield development is, its differences from brownfield development, and its benefits in terms of flexibility and cost.
What Is Greenfield Development? - Greenfield development refers to the development of previously undeveloped land, including natural areas or agricultural land, often attracting controversy and regulatory oversight.
Greenfield Development: Building from Scratch for a Sustainable Future - This article discusses greenfield development as a means to create sustainable infrastructure and communities by starting from scratch on unused land.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com