Agrihoods integrate sustainable farming and residential living, creating communities centered around agricultural spaces that promote local food production and environmental stewardship. Workforce housing focuses on affordable residential options for essential workers, addressing housing shortages near employment centers to boost economic stability. Explore the unique benefits and challenges of agrihoods versus workforce housing to determine the best fit for your real estate investments.
Why it is important
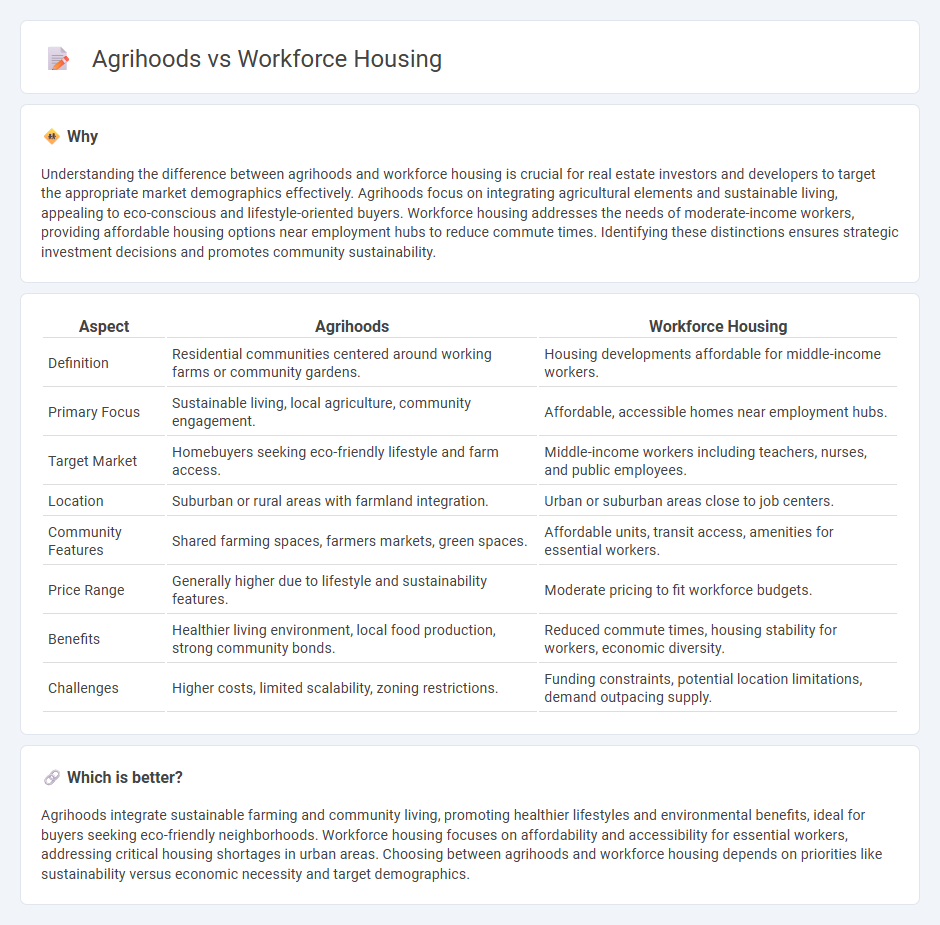
Understanding the difference between agrihoods and workforce housing is crucial for real estate investors and developers to target the appropriate market demographics effectively. Agrihoods focus on integrating agricultural elements and sustainable living, appealing to eco-conscious and lifestyle-oriented buyers. Workforce housing addresses the needs of moderate-income workers, providing affordable housing options near employment hubs to reduce commute times. Identifying these distinctions ensures strategic investment decisions and promotes community sustainability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Agrihoods | Workforce Housing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Residential communities centered around working farms or community gardens. | Housing developments affordable for middle-income workers. |
| Primary Focus | Sustainable living, local agriculture, community engagement. | Affordable, accessible homes near employment hubs. |
| Target Market | Homebuyers seeking eco-friendly lifestyle and farm access. | Middle-income workers including teachers, nurses, and public employees. |
| Location | Suburban or rural areas with farmland integration. | Urban or suburban areas close to job centers. |
| Community Features | Shared farming spaces, farmers markets, green spaces. | Affordable units, transit access, amenities for essential workers. |
| Price Range | Generally higher due to lifestyle and sustainability features. | Moderate pricing to fit workforce budgets. |
| Benefits | Healthier living environment, local food production, strong community bonds. | Reduced commute times, housing stability for workers, economic diversity. |
| Challenges | Higher costs, limited scalability, zoning restrictions. | Funding constraints, potential location limitations, demand outpacing supply. |
Which is better?
Agrihoods integrate sustainable farming and community living, promoting healthier lifestyles and environmental benefits, ideal for buyers seeking eco-friendly neighborhoods. Workforce housing focuses on affordability and accessibility for essential workers, addressing critical housing shortages in urban areas. Choosing between agrihoods and workforce housing depends on priorities like sustainability versus economic necessity and target demographics.
Connection
Agrihoods integrate agricultural spaces within residential communities, promoting local food production and sustainable living, which aligns with workforce housing goals by providing affordable homes near employment hubs. Both agrihoods and workforce housing prioritize community access to essential resources, reducing commute times and fostering economic stability for residents. This synergy supports urban planning strategies that enhance quality of life and environmental responsibility while addressing housing affordability.
Key Terms
**Workforce Housing:**
Workforce housing provides affordable living options for middle-income workers, addressing the growing demand for residences near employment centers and urban amenities. This type of housing supports economic stability by reducing commute times and increasing access to essential services, benefiting both employees and local businesses. Explore the benefits and strategies of workforce housing development to understand its role in fostering sustainable communities.
Affordability
Workforce housing addresses affordability by providing cost-effective living options close to employment centers, reducing commuting expenses for essential workers. Agrihoods combine residential development with sustainable agriculture, offering fresh local produce and fostering community while potentially influencing housing costs through land use for farming. Explore how these models impact affordability to determine suitable solutions for diverse housing needs.
Proximity to Employment
Workforce housing is strategically located near major employment centers, reducing commute times and enhancing job accessibility for moderate-income workers. Agrihoods, often situated in suburban or rural areas, emphasize a lifestyle integrated with farming and green spaces but may require longer commutes to urban job hubs. Explore further to understand how proximity to employment shapes the benefits of workforce housing and agrihood living.
Source and External Links
Workforce Housing - Wikipedia - Workforce housing refers to affordable housing for households with earned income insufficient to secure quality housing near their workplace, often targeting essential workers.
Workforce Housing - Apartments in Indianapolis, IN - This page describes workforce housing at 220 Meridian, focusing on quality, affordable housing for middle-income essential workers at or below specific Area Median Income levels.
Workforce Housing - Wesmont Apartments - Wesmont offers workforce housing for middle-income workers, with select apartments reserved for renters at or below 60% or 80% of the Area Median Income.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com