Adaptive reuse transforms existing properties by repurposing structures to meet new functional requirements, enhancing sustainability and preserving architectural heritage. Expansion involves enlarging current buildings or properties to increase space and capacity, often addressing immediate growth demands. Explore the benefits and considerations of both strategies to determine the best approach for your real estate development projects.
Why it is important
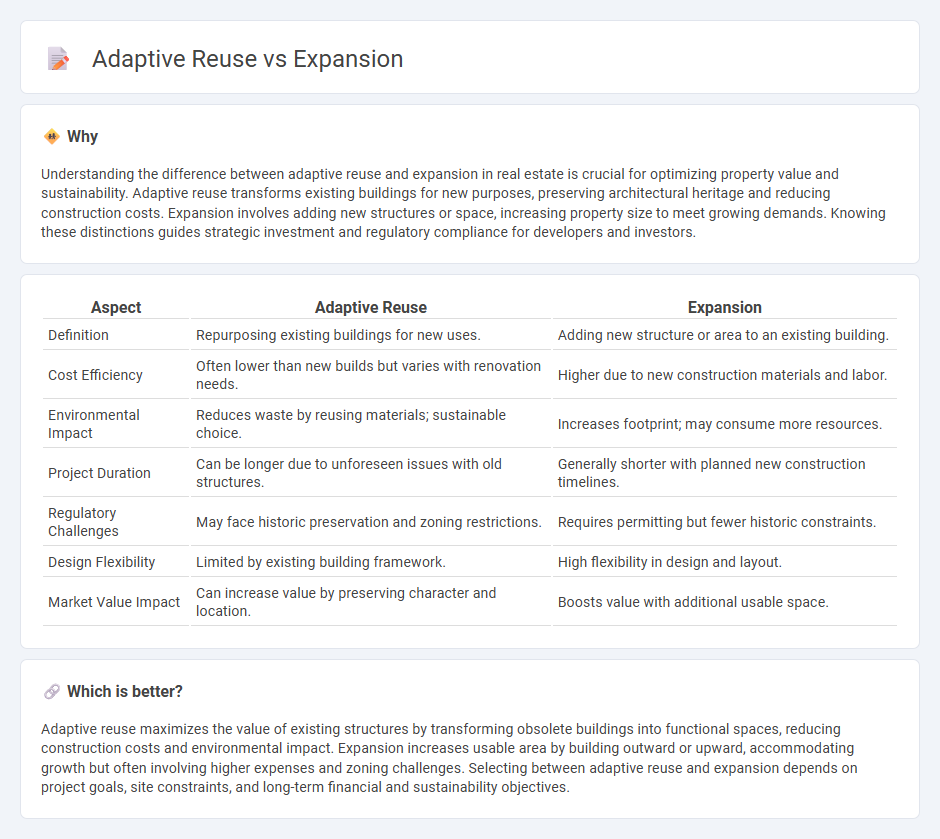
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse and expansion in real estate is crucial for optimizing property value and sustainability. Adaptive reuse transforms existing buildings for new purposes, preserving architectural heritage and reducing construction costs. Expansion involves adding new structures or space, increasing property size to meet growing demands. Knowing these distinctions guides strategic investment and regulatory compliance for developers and investors.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Adaptive Reuse | Expansion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repurposing existing buildings for new uses. | Adding new structure or area to an existing building. |
| Cost Efficiency | Often lower than new builds but varies with renovation needs. | Higher due to new construction materials and labor. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste by reusing materials; sustainable choice. | Increases footprint; may consume more resources. |
| Project Duration | Can be longer due to unforeseen issues with old structures. | Generally shorter with planned new construction timelines. |
| Regulatory Challenges | May face historic preservation and zoning restrictions. | Requires permitting but fewer historic constraints. |
| Design Flexibility | Limited by existing building framework. | High flexibility in design and layout. |
| Market Value Impact | Can increase value by preserving character and location. | Boosts value with additional usable space. |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse maximizes the value of existing structures by transforming obsolete buildings into functional spaces, reducing construction costs and environmental impact. Expansion increases usable area by building outward or upward, accommodating growth but often involving higher expenses and zoning challenges. Selecting between adaptive reuse and expansion depends on project goals, site constraints, and long-term financial and sustainability objectives.
Connection
Adaptive reuse transforms underutilized or historic buildings into modern, functional real estate assets, increasing property value while preserving urban character. Expansion complements this by adding new square footage or facilities, enhancing usability and market appeal without the need for land acquisition. Together, adaptive reuse and expansion drive sustainable development, maximize real estate investment, and meet evolving community demands.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations play a critical role in determining whether expansion or adaptive reuse projects are feasible, with each approach subject to different compliance requirements. Expansion often triggers setbacks, height limits, and floor area ratio (FAR) restrictions, while adaptive reuse must typically align with zoning classifications for current or new use cases, including occupancy and parking standards. Explore detailed zoning codes and case studies to understand how these regulatory frameworks impact development strategies and optimize project outcomes.
Site Utilization
Expansion projects maximize site utilization by increasing building footprint or height to accommodate growth, often requiring additional structural modifications and zoning considerations. Adaptive reuse prioritizes sustainable site utilization by repurposing existing structures, preserving architectural elements, and minimizing environmental impact while meeting new functional needs. Explore how strategic site utilization can optimize project outcomes in both expansion and adaptive reuse scenarios.
Building Code Compliance
Expansion projects must meet current building codes, often requiring extensive upgrades to structural elements, fire safety systems, and accessibility features to comply with modern standards. Adaptive reuse involves modifying existing structures to new functions while ensuring they conform to updated codes, which can include addressing seismic retrofitting, hazardous materials removal, and energy efficiency improvements. Explore further to understand how building code compliance challenges differ between expansion and adaptive reuse strategies.
Source and External Links
Expansion | Cambridge Dictionary - The term "expansion" refers to the increase in size, number, or importance of something, often related to industries or territories.
Expansion (geometry) - Wikipedia - In geometry, expansion is an operation where facets of a polytope are separated and moved apart, forming new facets at separated elements.
Expansion | Collins Dictionary - Expansion refers to the process of becoming greater in size, number, or amount, often used in contexts such as economic or industrial growth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com