Co-living spaces offer modern, community-focused living environments where residents share amenities and common areas, fostering social interaction and flexibility. Boarding houses provide more traditional, often long-term lodging with private or shared rooms and fewer communal features. Explore the key differences and benefits of each to determine the ideal living solution for your needs.
Why it is important
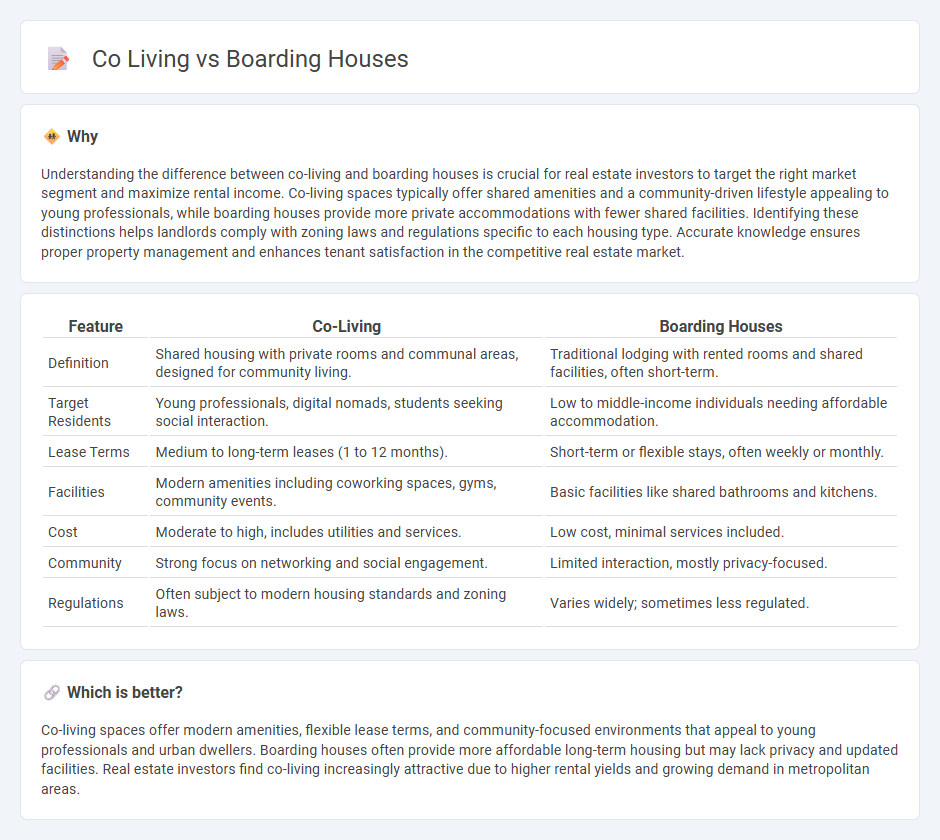
Understanding the difference between co-living and boarding houses is crucial for real estate investors to target the right market segment and maximize rental income. Co-living spaces typically offer shared amenities and a community-driven lifestyle appealing to young professionals, while boarding houses provide more private accommodations with fewer shared facilities. Identifying these distinctions helps landlords comply with zoning laws and regulations specific to each housing type. Accurate knowledge ensures proper property management and enhances tenant satisfaction in the competitive real estate market.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Co-Living | Boarding Houses |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared housing with private rooms and communal areas, designed for community living. | Traditional lodging with rented rooms and shared facilities, often short-term. |
| Target Residents | Young professionals, digital nomads, students seeking social interaction. | Low to middle-income individuals needing affordable accommodation. |
| Lease Terms | Medium to long-term leases (1 to 12 months). | Short-term or flexible stays, often weekly or monthly. |
| Facilities | Modern amenities including coworking spaces, gyms, community events. | Basic facilities like shared bathrooms and kitchens. |
| Cost | Moderate to high, includes utilities and services. | Low cost, minimal services included. |
| Community | Strong focus on networking and social engagement. | Limited interaction, mostly privacy-focused. |
| Regulations | Often subject to modern housing standards and zoning laws. | Varies widely; sometimes less regulated. |
Which is better?
Co-living spaces offer modern amenities, flexible lease terms, and community-focused environments that appeal to young professionals and urban dwellers. Boarding houses often provide more affordable long-term housing but may lack privacy and updated facilities. Real estate investors find co-living increasingly attractive due to higher rental yields and growing demand in metropolitan areas.
Connection
Co-living and boarding houses both provide affordable, shared housing solutions, catering primarily to urban professionals, students, and transient populations seeking community-oriented living spaces. These models maximize space utilization and offer communal amenities that reduce individual costs while fostering social interaction. The rise of co-living and boarding houses reflects a growing demand for flexible, cost-effective housing in high-density real estate markets.
Key Terms
Lease Agreement
Lease agreements in boarding houses often involve shorter terms with more flexible cancellation policies, catering to transient tenants seeking affordability and convenience. Co-living spaces typically offer longer lease agreements emphasizing community rules, shared responsibilities, and inclusive utilities that foster a collaborative living environment. Explore the detailed differences in lease terms to determine which housing model best suits your lifestyle and legal preferences.
Shared Amenities
Boarding houses typically offer basic shared amenities such as communal kitchens and laundry facilities, catering mainly to long-term residents seeking affordability. Co-living spaces emphasize modern shared amenities, including coworking areas, fitness centers, and social lounges designed to foster community interaction. Explore more about how shared amenities impact lifestyle choices in boarding houses and co-living environments.
Occupancy Regulations
Boarding houses are typically subject to stricter occupancy regulations set by local housing authorities, often limiting the number of unrelated tenants per unit to ensure safety and habitability standards. Co-living spaces, on the other hand, usually operate under more flexible zoning laws and lease agreements designed for communal living, allowing higher occupant density with shared amenities. Explore detailed occupancy regulations to determine which housing model best fits your urban living needs.
Source and External Links
Boarding house - Boarding houses are typically family homes where lodgers rent rooms, often including meals and shared services, with arrangements ranging from nightly stays to extended periods and different meal plans (room only, half-board, or full-board).
A History of Boarding Houses: Ideal Forms of Affordable ... - Boarding houses historically served as affordable, communal housing options in cities, allowing social mixing and mobility, and were either private homes with added lodgers or dedicated buildings for boarders, playing a significant role until zoning changes reduced their prevalence.
What Are Boarding Houses? And How Do They Work? - Boarding houses provide rooms and meals (sometimes with extra services like laundry), can be run from a spare room in a private home, and include modern variations such as bed & breakfasts, student housing, and short-term rentals, with local regulations often shaping their operation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com