Retrofitting for net zero involves comprehensive modifications to a building's structure and systems to eliminate greenhouse gas emissions, often incorporating renewable energy sources like solar panels and advanced insulation technologies. Energy-efficient upgrades focus on reducing energy consumption by enhancing existing systems such as HVAC, lighting, and windows without necessarily achieving zero emissions. Explore how these strategies transform property value and sustainability in the real estate market.
Why it is important
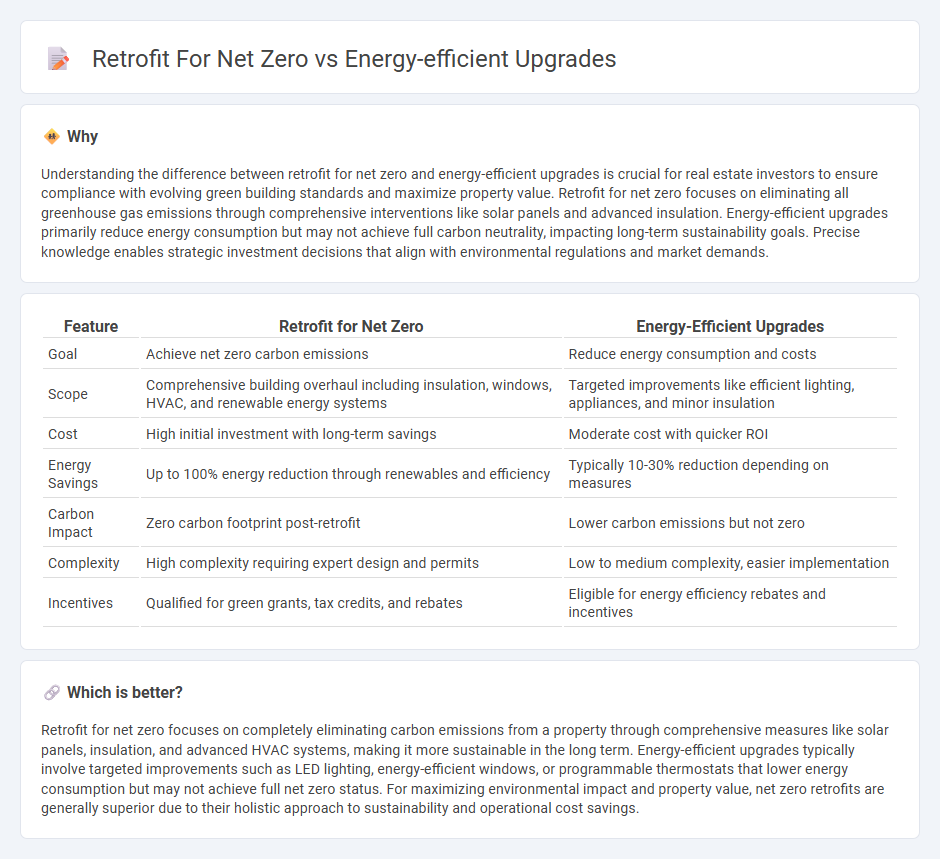
Understanding the difference between retrofit for net zero and energy-efficient upgrades is crucial for real estate investors to ensure compliance with evolving green building standards and maximize property value. Retrofit for net zero focuses on eliminating all greenhouse gas emissions through comprehensive interventions like solar panels and advanced insulation. Energy-efficient upgrades primarily reduce energy consumption but may not achieve full carbon neutrality, impacting long-term sustainability goals. Precise knowledge enables strategic investment decisions that align with environmental regulations and market demands.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Retrofit for Net Zero | Energy-Efficient Upgrades |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Achieve net zero carbon emissions | Reduce energy consumption and costs |
| Scope | Comprehensive building overhaul including insulation, windows, HVAC, and renewable energy systems | Targeted improvements like efficient lighting, appliances, and minor insulation |
| Cost | High initial investment with long-term savings | Moderate cost with quicker ROI |
| Energy Savings | Up to 100% energy reduction through renewables and efficiency | Typically 10-30% reduction depending on measures |
| Carbon Impact | Zero carbon footprint post-retrofit | Lower carbon emissions but not zero |
| Complexity | High complexity requiring expert design and permits | Low to medium complexity, easier implementation |
| Incentives | Qualified for green grants, tax credits, and rebates | Eligible for energy efficiency rebates and incentives |
Which is better?
Retrofit for net zero focuses on completely eliminating carbon emissions from a property through comprehensive measures like solar panels, insulation, and advanced HVAC systems, making it more sustainable in the long term. Energy-efficient upgrades typically involve targeted improvements such as LED lighting, energy-efficient windows, or programmable thermostats that lower energy consumption but may not achieve full net zero status. For maximizing environmental impact and property value, net zero retrofits are generally superior due to their holistic approach to sustainability and operational cost savings.
Connection
Retrofit for net zero involves upgrading existing buildings with energy-efficient technologies such as insulation, high-performance windows, and advanced HVAC systems to drastically reduce energy consumption. These upgrades lower carbon emissions and utility costs, aligning with sustainability goals in real estate development. Energy-efficient retrofits enhance property value and marketability by meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations and consumer demand for green living spaces.
Key Terms
Building Envelope
Energy-efficient upgrades for the building envelope involve enhancing insulation, installing high-performance windows, and sealing air leaks to reduce thermal bridging and improve overall energy retention. Retrofit projects may include replacing outdated materials with sustainable alternatives and integrating advanced vapor barriers to meet net zero energy standards. Explore detailed strategies to optimize your building envelope for maximum energy efficiency and sustainability.
HVAC Systems
Energy-efficient upgrades for HVAC systems involve integrating advanced technologies such as variable speed drives and high-efficiency heat pumps to reduce energy consumption and enhance indoor climate control. Retrofit solutions focus on modifying existing HVAC infrastructure, including adding smart thermostats and improving duct insulation, to meet net zero targets while minimizing disruption and cost. Explore detailed strategies and case studies to determine the optimal path for your net zero HVAC transformation.
Renewable Energy Integration
Energy-efficient upgrades reduce overall energy consumption by improving insulation, lighting, and HVAC systems, creating a strong foundation for achieving net-zero targets. Retrofit initiatives focus on integrating renewable energy technologies such as solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems to replace or offset conventional energy sources. Explore in-depth strategies to balance energy efficiency with renewable energy integration for effective net-zero outcomes.
Source and External Links
4 Types of Energy-Efficient Improvements You Can Finance - Four main energy-efficient home upgrades include HVAC systems, weatherization and insulation, energy-saving windows and doors, and water heaters, with financing options to help cover their costs.
Energy Efficiency Strategies and Upgrades | ACEEE - A whole-building approach to energy efficiency involves improving insulation, HVAC, water-heating systems, appliances, and equipment to maximize savings and reduce emissions.
The 8 Best Energy Efficient Home Upgrades - Sealed - Top upgrades include upgrading insulation and air sealing, switching to heat pump water heaters, installing solar panels, using energy-efficient windows, and converting from fossil fuels to electric systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com